Mechanical repairmen specialize in diagnosing and fixing physical components such as engines, gears, and hydraulic systems, ensuring machinery operates smoothly. Electrical repairmen focus on troubleshooting and repairing electrical systems, wiring, circuits, and electronic components to restore proper functionality. Both roles require distinct skill sets but are essential for comprehensive equipment maintenance and repair.
Table of Comparison
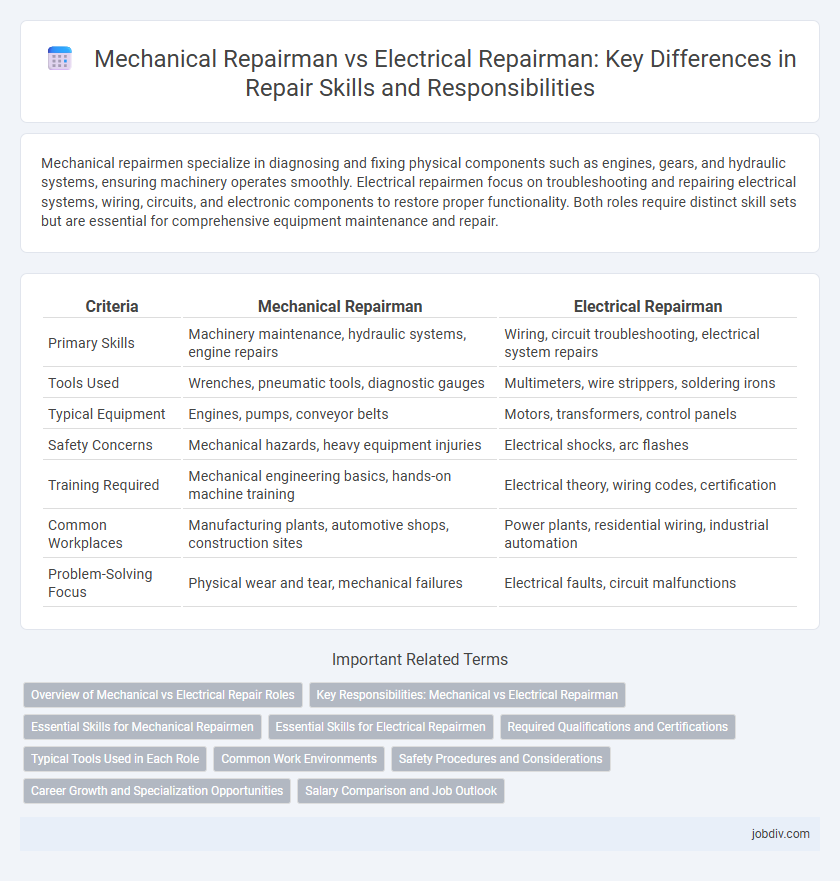
| Criteria | Mechanical Repairman | Electrical Repairman |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Skills | Machinery maintenance, hydraulic systems, engine repairs | Wiring, circuit troubleshooting, electrical system repairs |
| Tools Used | Wrenches, pneumatic tools, diagnostic gauges | Multimeters, wire strippers, soldering irons |
| Typical Equipment | Engines, pumps, conveyor belts | Motors, transformers, control panels |
| Safety Concerns | Mechanical hazards, heavy equipment injuries | Electrical shocks, arc flashes |
| Training Required | Mechanical engineering basics, hands-on machine training | Electrical theory, wiring codes, certification |
| Common Workplaces | Manufacturing plants, automotive shops, construction sites | Power plants, residential wiring, industrial automation |
| Problem-Solving Focus | Physical wear and tear, mechanical failures | Electrical faults, circuit malfunctions |
Overview of Mechanical vs Electrical Repair Roles
Mechanical repairmen specialize in diagnosing, maintaining, and fixing physical components such as engines, machinery, and HVAC systems, relying heavily on mechanical tools and engineering principles. Electrical repairmen focus on troubleshooting and repairing electrical circuits, wiring, and electronic systems, often working with control panels and diagnostic equipment to ensure proper functionality. Both roles require technical expertise but differ in emphasis on mechanical systems versus electrical systems within industrial and residential repair scenarios.
Key Responsibilities: Mechanical vs Electrical Repairman
Mechanical repairmen specialize in diagnosing, maintaining, and fixing machinery such as engines, hydraulics, and HVAC systems, focusing on physical components and mechanical systems. Electrical repairmen handle electrical wiring, circuits, and equipment, including troubleshooting power supply issues and repairing motors, control systems, and wiring faults. Both roles require detailed knowledge of their respective fields to ensure operational efficiency and safety standards are met.
Essential Skills for Mechanical Repairmen
Mechanical repairmen require strong diagnostic abilities to identify and resolve issues in engines, hydraulics, and other mechanical systems. Proficiency in using tools such as wrenches, gauges, and diagnostic equipment is essential for efficient repairs and maintenance. Knowledge of mechanical principles, blueprint reading, and safety protocols ensures accurate troubleshooting and prevents equipment failure.
Essential Skills for Electrical Repairmen
Electrical repairmen require a deep understanding of electrical systems, circuitry, and safety protocols to effectively troubleshoot and repair electrical faults. Proficiency in reading wiring diagrams, using multimeters, and knowledge of local electrical codes are essential for accurate diagnostics and compliance. Strong problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and manual dexterity enable electrical repairmen to perform precise repairs while minimizing risks associated with electrical hazards.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Mechanical repairmen typically require certifications such as EPA Section 608 for refrigeration or ASE for automotive systems, alongside technical diplomas in mechanical engineering or industrial maintenance. Electrical repairmen often need certifications like the NICET, OSHA safety training, and a journeyman electrician license, supported by qualifications in electrical engineering or applied electrical technology. Both roles demand hands-on experience and ongoing education to stay updated with evolving industry standards and safety regulations.
Typical Tools Used in Each Role
Mechanical repairmen commonly utilize wrenches, socket sets, screwdrivers, hammers, and torque wrenches to service engines, machinery, and mechanical systems. Electrical repairmen rely on multimeters, wire strippers, insulated pliers, circuit testers, and voltage detectors for diagnosing and fixing electrical circuits and components. Both roles require precision tools tailored to their specific field to ensure safe and efficient repairs.
Common Work Environments
Mechanical repairmen often work in environments such as manufacturing plants, automotive workshops, and industrial facilities where heavy machinery and mechanical systems require maintenance and repair. Electrical repairmen typically operate in settings like commercial buildings, residential properties, and electrical substations, focusing on wiring, lighting systems, and electrical equipment repairs. Both professions frequently encounter conditions that require adherence to safety protocols and the ability to troubleshoot complex systems under physical and time constraints.
Safety Procedures and Considerations
Mechanical repairmen prioritize safety procedures such as lockout/tagout protocols, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and safety goggles, and thorough machinery inspection to prevent physical injuries during repairs. Electrical repairmen focus intensely on electrical hazard prevention by verifying de-energized circuits, utilizing insulated tools, and adhering to strict grounding practices to avoid electric shock and arc flash incidents. Both roles require rigorous adherence to industry standards like OSHA regulations and continuous safety training to minimize risks in their specialized environments.
Career Growth and Specialization Opportunities
Mechanical repairmen often experience career growth through specialization in areas such as HVAC systems, automotive repair, or industrial machinery, enhancing their skill set and earning potential. Electrical repairmen can advance by focusing on complex systems like programmable logic controllers (PLCs), renewable energy installations, or high-voltage equipment maintenance, which are in increasing demand. Both career paths offer diverse specialization opportunities, but electrical repairmen may benefit from faster growth due to the rising reliance on advanced electrical and electronic systems.
Salary Comparison and Job Outlook
Mechanical repairmen typically earn an average salary ranging from $40,000 to $60,000 annually, while electrical repairmen often command higher wages, averaging between $50,000 and $70,000 due to specialized skills in electrical systems. The job outlook for electrical repairmen is projected to grow faster than that for mechanical repairmen, driven by increasing demand in renewable energy, automation, and advanced electrical infrastructures. Mechanical repair roles remain steady with consistent demand in manufacturing and automotive sectors, but electrical repair offers more opportunities in emerging technologies and smart grid systems.
Mechanical Repairman vs Electrical Repairman Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com