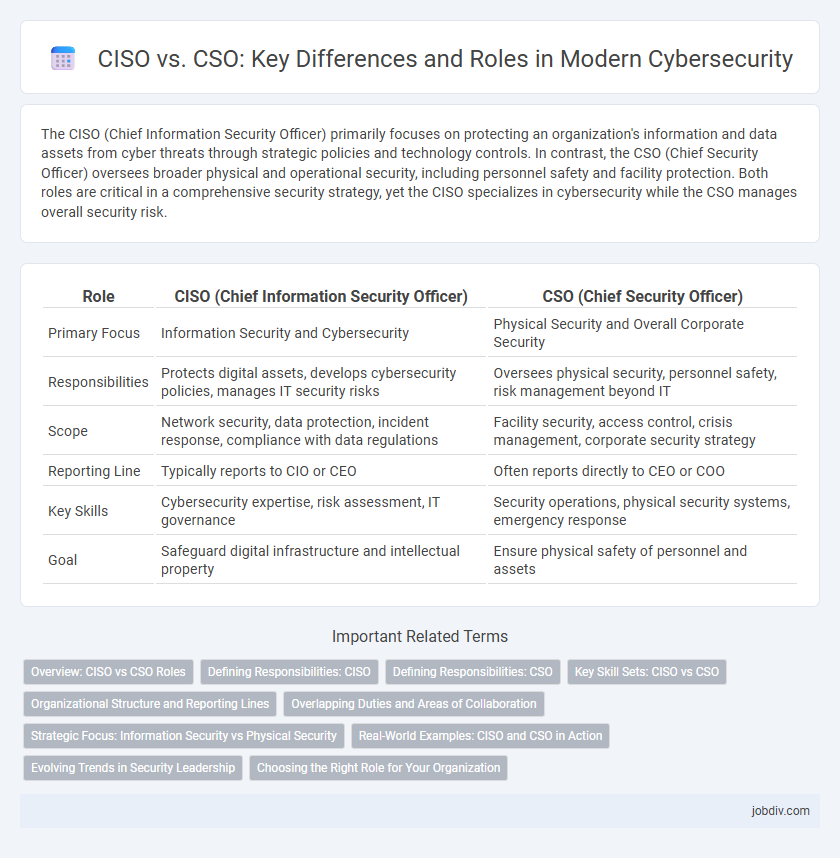
The CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) primarily focuses on protecting an organization's information and data assets from cyber threats through strategic policies and technology controls. In contrast, the CSO (Chief Security Officer) oversees broader physical and operational security, including personnel safety and facility protection. Both roles are critical in a comprehensive security strategy, yet the CISO specializes in cybersecurity while the CSO manages overall security risk.
Table of Comparison
| Role | CISO (Chief Information Security Officer) | CSO (Chief Security Officer) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Information Security and Cybersecurity | Physical Security and Overall Corporate Security |
| Responsibilities | Protects digital assets, develops cybersecurity policies, manages IT security risks | Oversees physical security, personnel safety, risk management beyond IT |
| Scope | Network security, data protection, incident response, compliance with data regulations | Facility security, access control, crisis management, corporate security strategy |
| Reporting Line | Typically reports to CIO or CEO | Often reports directly to CEO or COO |
| Key Skills | Cybersecurity expertise, risk assessment, IT governance | Security operations, physical security systems, emergency response |
| Goal | Safeguard digital infrastructure and intellectual property | Ensure physical safety of personnel and assets |
Overview: CISO vs CSO Roles
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) primarily focuses on protecting an organization's information systems, cybersecurity strategies, risk management, and compliance with data protection regulations. The Chief Security Officer (CSO) has a broader scope, overseeing both physical security measures and cybersecurity, ensuring overall organizational safety and crisis management. While the CISO is typically part of the IT leadership, the CSO often reports directly to the CEO, reflecting their extensive responsibility for corporate security policies and asset protection.
Defining Responsibilities: CISO
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is primarily responsible for establishing and maintaining an enterprise's information security program, including risk management, compliance, and data protection. The CISO oversees cybersecurity strategies, threat intelligence, and incident response to protect digital assets from internal and external threats. This role prioritizes safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring regulatory adherence across all IT systems and processes.
Defining Responsibilities: CSO
The Chief Security Officer (CSO) oversees an organization's comprehensive security program, encompassing physical security, information security, and risk management. CSOs develop and implement policies to safeguard company assets, personnel, and data against internal and external threats. They coordinate cross-functional teams to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and maintain business continuity through proactive security strategies.
Key Skill Sets: CISO vs CSO
CISOs specialize in cybersecurity, risk management, and compliance, emphasizing technical expertise in network security, threat intelligence, and incident response. CSOs focus on broader organizational security, including physical security, crisis management, and executive protection with skills in strategic planning and interdepartmental coordination. Both roles require strong leadership, communication, and risk assessment abilities tailored to their distinct security domains.
Organizational Structure and Reporting Lines
The Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) typically reports to the Chief Information Officer (CIO) or directly to the CEO, focusing on cybersecurity strategy and risk management within the IT domain. The Chief Security Officer (CSO) oversees broader organizational security, including physical, personnel, and information security, often reporting directly to the CEO or COO. Organizational structures vary, but CISOs generally manage cybersecurity teams, while CSOs coordinate cross-departmental security efforts to align with overall business objectives.
Overlapping Duties and Areas of Collaboration
The CISO and CSO share overlapping duties in risk management, incident response, and regulatory compliance, emphasizing the protection of organizational assets. Both roles collaborate closely on developing security policies, ensuring cybersecurity measures align with physical security protocols, and coordinating cross-departmental efforts to mitigate threats. Effective communication between CISO and CSO enhances the integration of digital and physical security strategies, fostering a comprehensive defense framework.
Strategic Focus: Information Security vs Physical Security
Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) primarily concentrate on safeguarding digital assets, managing cybersecurity strategies, risk assessment, and compliance related to information systems. Chief Security Officers (CSOs) focus on physical security measures, including facility protection, personnel safety, and response to physical threats. Both roles require strategic oversight to mitigate risks but differ in their core emphasis: CISOs on information security frameworks and CSOs on physical security operations.
Real-World Examples: CISO and CSO in Action
CISOs at companies like Microsoft concentrate on information security strategies, managing cyber risk and compliance, while CSOs at firms such as Johnson & Johnson oversee broader security operations including physical safety and crisis management. In real-world scenarios, a CISO spearheads initiatives like malware defense and data encryption, whereas a CSO coordinates emergency responses and security personnel deployment. These distinct yet complementary roles exemplify how organizations safeguard both digital assets and physical environments.
Evolving Trends in Security Leadership
CISOs are increasingly focusing on cybersecurity risk management and threat intelligence to protect digital assets, while CSOs broaden their scope to include physical security and corporate governance, reflecting the convergence of cyber and physical threat landscapes. The rise of integrated security platforms and zero trust architectures underscores the growing collaboration between CISOs and CSOs to create holistic security strategies. Emphasis on regulatory compliance, incident response agility, and cross-functional communication defines the evolving roles in security leadership.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Organization
Choosing between a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) and a Chief Security Officer (CSO) depends on your organization's specific security needs and strategic goals. A CISO primarily focuses on information and cybersecurity, managing risks related to data protection, compliance, and cyber threat intelligence. In contrast, a CSO oversees broader physical and corporate security, including personnel safety, facility security, and crisis management.
CISO vs CSO Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com