Customs agents specialize in navigating complex import and export regulations, ensuring shipments comply with all legal requirements and duties. Freight forwarders coordinate the entire logistics process, from arranging transportation to handling warehousing and documentation for smooth international trade. Choosing between a customs agent and a freight forwarder depends on whether the priority is regulatory compliance or comprehensive shipping management.
Table of Comparison
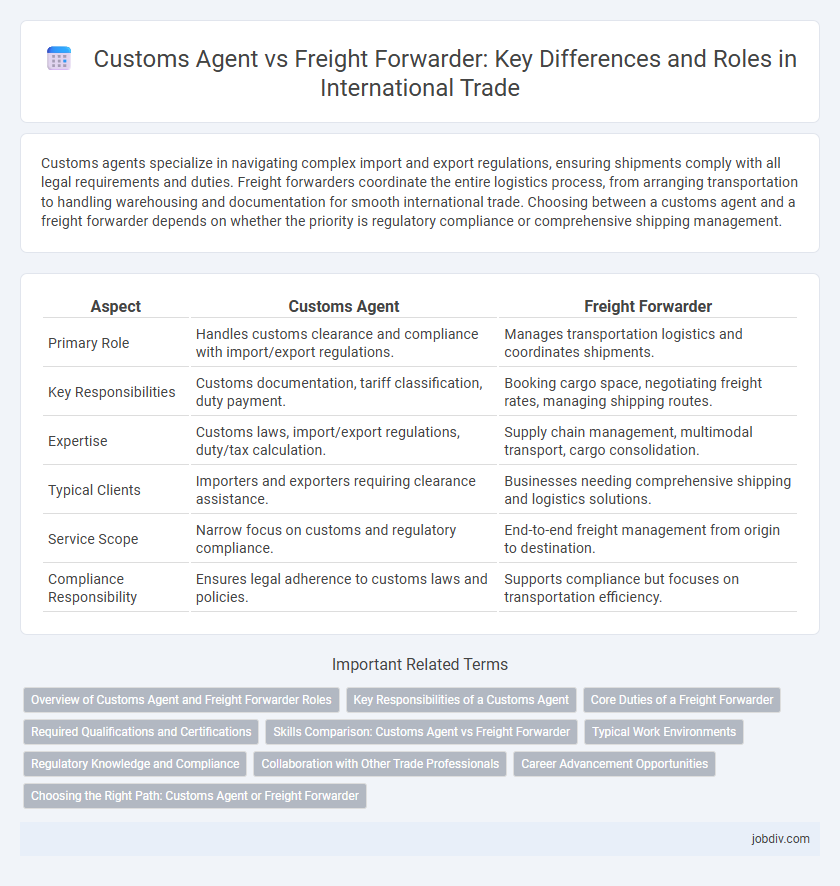
| Aspect | Customs Agent | Freight Forwarder |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Handles customs clearance and compliance with import/export regulations. | Manages transportation logistics and coordinates shipments. |
| Key Responsibilities | Customs documentation, tariff classification, duty payment. | Booking cargo space, negotiating freight rates, managing shipping routes. |
| Expertise | Customs laws, import/export regulations, duty/tax calculation. | Supply chain management, multimodal transport, cargo consolidation. |
| Typical Clients | Importers and exporters requiring clearance assistance. | Businesses needing comprehensive shipping and logistics solutions. |
| Service Scope | Narrow focus on customs and regulatory compliance. | End-to-end freight management from origin to destination. |
| Compliance Responsibility | Ensures legal adherence to customs laws and policies. | Supports compliance but focuses on transportation efficiency. |
Overview of Customs Agent and Freight Forwarder Roles
Customs agents specialize in ensuring shipments comply with all legal requirements and regulations for importing and exporting goods, handling customs documentation and tariff classifications. Freight forwarders coordinate the logistics of shipping, arranging transportation, warehouse storage, and cargo insurance to optimize supply chain efficiency. Both roles are critical in facilitating international trade, with customs agents focusing on regulatory compliance and freight forwarders managing end-to-end shipment logistics.
Key Responsibilities of a Customs Agent
A Customs Agent specializes in ensuring compliance with import and export regulations, managing customs documentation, and facilitating the clearance of goods through customs authorities. Key responsibilities include classification and valuation of goods, payment of duties and taxes, and advising clients on regulatory requirements to avoid delays and penalties. Their expertise reduces the risk of customs violations and supports efficient cross-border trade operations.
Core Duties of a Freight Forwarder
A freight forwarder coordinates the shipment of goods by arranging transportation, managing documentation, and ensuring compliance with international trade regulations. Their core duties include negotiating freight charges, booking cargo space, and consolidating shipments to optimize logistics efficiency. Freight forwarders act as intermediaries between exporters, importers, and carriers, providing end-to-end supply chain solutions.
Required Qualifications and Certifications
Customs agents must obtain specific licenses such as the Customs Broker License, ensuring compliance with import-export regulations and mastery of tariff classifications, while freight forwarders often hold certifications like the International Air Transport Association (IATA) accreditation, which validates expertise in air cargo logistics. Both roles may require knowledge of Incoterms, shipping documentation, and supply chain management, but customs agents focus more on regulatory compliance and customs clearance processes. Professional certifications such as the Certified Customs Specialist (CCS) and Certified Freight Forwarder (CFF) enhance credibility and demonstrate specialized knowledge in their respective fields.
Skills Comparison: Customs Agent vs Freight Forwarder
Customs agents possess in-depth knowledge of import-export regulations, tariff classification, and customs clearance processes, ensuring compliance with government authorities. Freight forwarders specialize in logistics management, including transportation coordination, cargo insurance, and route optimization. Both require strong communication skills and attention to detail, but customs agents focus more on legal documentation while freight forwarders excel in supply chain coordination.
Typical Work Environments
Customs agents typically operate within government customs offices, ports, and border checkpoints, ensuring compliance with import-export regulations and managing tariff classifications. Freight forwarders usually work in logistics companies, freight terminals, or warehouse hubs, coordinating the transportation, storage, and shipment of goods across international borders. Both roles require close collaboration with shipping lines, airlines, and regulatory authorities to facilitate efficient trade operations.
Regulatory Knowledge and Compliance
Customs agents specialize in ensuring shipments meet all regulatory requirements by managing customs documentation, tariff classification, and import/export compliance, which minimizes delays and penalties. Freight forwarders coordinate the entire logistics process, including transportation and warehousing, and may rely on customs agents for detailed regulatory expertise. Companies benefit from engaging customs agents for precise adherence to customs laws, while freight forwarders streamline supply chain operations through comprehensive freight management.
Collaboration with Other Trade Professionals
Customs agents and freight forwarders collaborate closely with trade professionals including importers, exporters, and regulatory authorities to ensure seamless movement of goods across borders. Customs agents specialize in clearance processes and compliance with customs regulations, providing essential documentation and tariff classification expertise. Freight forwarders coordinate transportation logistics, optimize shipping routes, and manage carrier relationships, enhancing overall supply chain efficiency through integrated communication with customs brokers and trade stakeholders.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Career advancement opportunities for customs agents often involve specialization in regulatory compliance and customs brokerage, leading to roles such as customs compliance manager or trade compliance analyst. Freight forwarders can progress to senior positions like logistics manager or supply chain director by gaining expertise in freight management, transportation coordination, and global shipping regulations. Mastery of international trade laws and digital logistics platforms significantly enhances career growth potential in both customs agency and freight forwarding fields.
Choosing the Right Path: Customs Agent or Freight Forwarder
Selecting between a customs agent and a freight forwarder hinges on the specific requirements of international trade compliance and logistics management. Customs agents specialize in navigating complex import-export regulations to ensure smooth customs clearance, while freight forwarders coordinate the entire shipping process, offering integrated services from transport to documentation. Evaluating factors such as shipment complexity, regulatory compliance needs, and logistical support helps businesses optimize supply chain efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Customs Agent vs Freight Forwarder Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com