A Scrum Master facilitates agile project management by guiding teams through sprints, removing obstacles, and ensuring efficient collaboration. A Trade Analyst focuses on analyzing market trends, evaluating trade data, and providing actionable insights to optimize trading strategies. Both roles require strong communication skills, but the Scrum Master emphasizes process facilitation while the Trade Analyst centers on data-driven decision making.
Table of Comparison
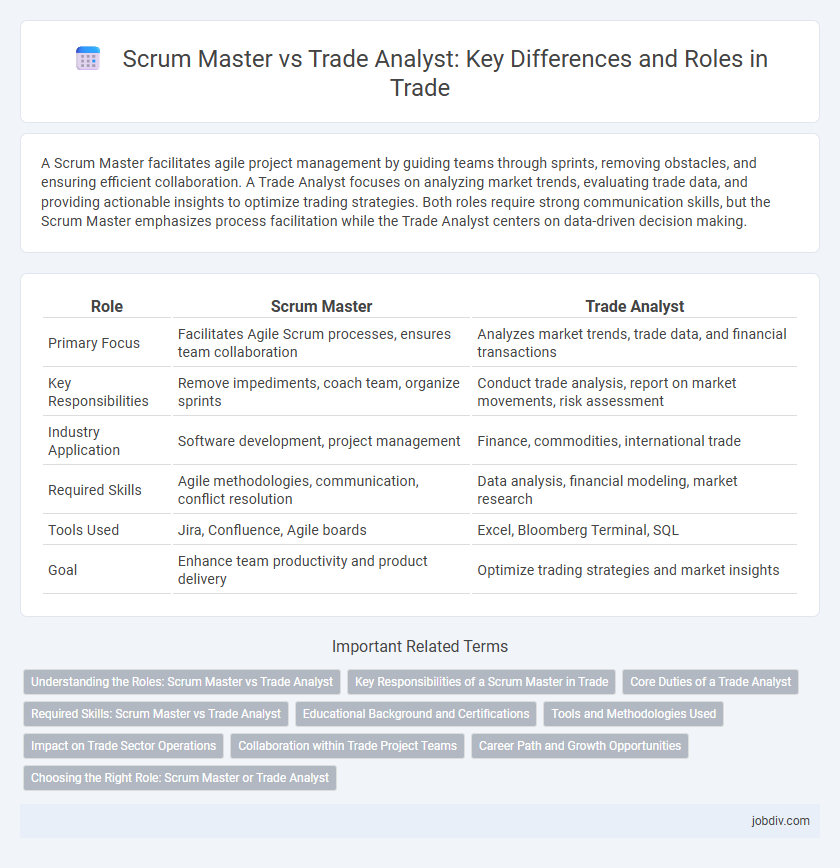
| Role | Scrum Master | Trade Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Facilitates Agile Scrum processes, ensures team collaboration | Analyzes market trends, trade data, and financial transactions |
| Key Responsibilities | Remove impediments, coach team, organize sprints | Conduct trade analysis, report on market movements, risk assessment |
| Industry Application | Software development, project management | Finance, commodities, international trade |
| Required Skills | Agile methodologies, communication, conflict resolution | Data analysis, financial modeling, market research |
| Tools Used | Jira, Confluence, Agile boards | Excel, Bloomberg Terminal, SQL |
| Goal | Enhance team productivity and product delivery | Optimize trading strategies and market insights |
Understanding the Roles: Scrum Master vs Trade Analyst
The Scrum Master facilitates Agile project management by ensuring the team follows Scrum practices and removes obstacles to enhance productivity. A Trade Analyst focuses on analyzing market trends, assessing trade performance, and providing insights to optimize trading strategies. Both roles require strong communication skills but differ in focus: the Scrum Master emphasizes team dynamics and process efficiency, while the Trade Analyst centers on data-driven trade analysis and market understanding.
Key Responsibilities of a Scrum Master in Trade
The Scrum Master in trade facilitates agile project management by ensuring teams follow Scrum practices to deliver trading software efficiently and adapt to market changes swiftly. They remove impediments, coordinate communication between traders, developers, and stakeholders, and promote continuous improvement through sprint planning and retrospectives. Their role enhances collaboration and responsiveness in trade systems development, driving faster deployment of trading strategies and compliance solutions.
Core Duties of a Trade Analyst
A Trade Analyst primarily focuses on analyzing market trends, evaluating trade data, and providing actionable insights to optimize trading strategies and supply chain efficiency. They conduct risk assessments, monitor compliance with trade regulations, and support decision-making processes by interpreting economic indicators and trade policies. Unlike Scrum Masters who facilitate agile project management, Trade Analysts drive data-driven trade operations and strategic planning to enhance profitability and market responsiveness.
Required Skills: Scrum Master vs Trade Analyst
Scrum Masters require strong skills in agile project management, facilitation, and team leadership to drive collaborative workflows and remove impediments. Trade Analysts need expertise in market analysis, data interpretation, and financial modeling to provide insights on trade trends and support decision-making. Both roles demand effective communication and problem-solving abilities tailored to their distinct operational environments.
Educational Background and Certifications
Scrum Masters typically possess certifications such as Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) or Professional Scrum Master (PSM), with educational backgrounds in computer science, business administration, or project management. Trade Analysts often hold degrees in finance, economics, or international trade, alongside certifications like Certified Trade Finance Professional (CTFP) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA). Both roles require continuous professional development, but Scrum Masters emphasize Agile and Scrum methodologies, whereas Trade Analysts prioritize financial regulations and market analysis.
Tools and Methodologies Used
Scrum Masters primarily utilize Agile frameworks such as Scrum and Kanban, leveraging tools like Jira, Trello, and Confluence to facilitate sprint planning, backlog management, and team collaboration. Trade Analysts focus on financial and market analysis tools including Bloomberg Terminal, MetaTrader, and Excel for quantitative data analysis, forecasting, and generating trade reports. Both roles require proficiency in data visualization software like Tableau or Power BI to enhance decision-making and communication.
Impact on Trade Sector Operations
Scrum Masters enhance trade sector operations by facilitating Agile project management, improving team collaboration, and accelerating product delivery cycles, which leads to faster adaptation to market changes. Trade Analysts impact operations by analyzing market trends, trade volumes, and regulatory data to provide actionable insights that optimize trading strategies and risk management. Both roles drive operational efficiency, but Scrum Masters focus on process improvement while Trade Analysts deliver data-driven decision support.
Collaboration within Trade Project Teams
Scrum Masters facilitate cross-functional collaboration by ensuring Agile practices are followed, removing impediments, and fostering communication among trade project teams to accelerate delivery. Trade Analysts provide critical market insights and data analysis that inform decision-making and align project objectives with business goals. Effective collaboration between Scrum Masters and Trade Analysts enhances transparency, responsiveness, and strategic alignment in trade initiatives.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
Scrum Masters typically advance by gaining expertise in agile project management, moving toward roles such as Agile Coach or Product Owner, with growth driven by improved team facilitation and leadership skills. Trade Analysts progress by deepening their market analysis, gaining financial modeling expertise, and often transition into trading, portfolio management, or strategic advisory positions. Both career paths offer distinct growth trajectories: Scrum Masters focus on process optimization in product development, while Trade Analysts emphasize data-driven decision-making in financial markets.
Choosing the Right Role: Scrum Master or Trade Analyst
Choosing the right role between Scrum Master and Trade Analyst depends on your expertise and career goals; Scrum Masters specialize in agile project management, facilitating Scrum practices to enhance team productivity and deliverables. Trade Analysts focus on market analysis, data interpretation, and strategic decision-making within trading environments to optimize financial performance. Understanding the core responsibilities and industry demands of each role ensures alignment with your skills and offers the best opportunity for professional growth in trade-related sectors.
Scrum Master vs Trade Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com