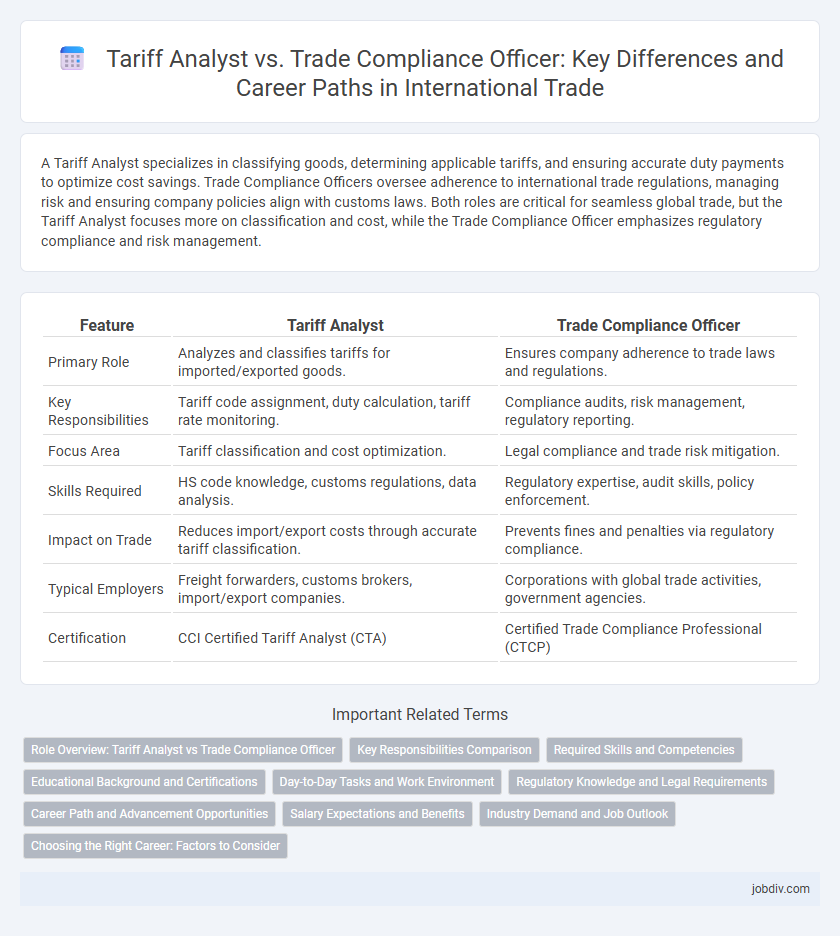
A Tariff Analyst specializes in classifying goods, determining applicable tariffs, and ensuring accurate duty payments to optimize cost savings. Trade Compliance Officers oversee adherence to international trade regulations, managing risk and ensuring company policies align with customs laws. Both roles are critical for seamless global trade, but the Tariff Analyst focuses more on classification and cost, while the Trade Compliance Officer emphasizes regulatory compliance and risk management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tariff Analyst | Trade Compliance Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Analyzes and classifies tariffs for imported/exported goods. | Ensures company adherence to trade laws and regulations. |
| Key Responsibilities | Tariff code assignment, duty calculation, tariff rate monitoring. | Compliance audits, risk management, regulatory reporting. |
| Focus Area | Tariff classification and cost optimization. | Legal compliance and trade risk mitigation. |
| Skills Required | HS code knowledge, customs regulations, data analysis. | Regulatory expertise, audit skills, policy enforcement. |
| Impact on Trade | Reduces import/export costs through accurate tariff classification. | Prevents fines and penalties via regulatory compliance. |
| Typical Employers | Freight forwarders, customs brokers, import/export companies. | Corporations with global trade activities, government agencies. |
| Certification | CCI Certified Tariff Analyst (CTA) | Certified Trade Compliance Professional (CTCP) |
Role Overview: Tariff Analyst vs Trade Compliance Officer
A Tariff Analyst specializes in classification, valuation, and application of duties on imported goods to optimize cost savings and ensure accuracy in tariff codes. A Trade Compliance Officer oversees adherence to international trade regulations, manages export controls, and implements compliance programs to mitigate legal risks and penalties. Both roles require expertise in customs regulations, but the Tariff Analyst's focus is on tariff assessment while the Trade Compliance Officer ensures overall regulatory compliance across trade operations.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Tariff Analysts specialize in determining accurate tariff classifications, analyzing import/export data to optimize duties, and ensuring compliance with customs regulations. Trade Compliance Officers oversee broader compliance strategies, manage trade policies, conduct audits, and mitigate risks related to international trade laws and sanctions. Both roles collaborate to minimize financial penalties and ensure adherence to global trade regulations.
Required Skills and Competencies
Tariff Analysts require strong analytical skills, expertise in customs classification, and in-depth knowledge of international trade regulations to accurately determine applicable duties and tariffs. Trade Compliance Officers must demonstrate thorough understanding of global trade laws, risk management abilities, and proficiency in regulatory compliance to ensure adherence to trade policies and prevent violations. Both roles demand attention to detail, effective communication, and familiarity with trade documentation and software systems.
Educational Background and Certifications
Tariff Analysts typically hold degrees in international trade, economics, or supply chain management, with certifications such as the Certified Customs Specialist (CCS) or Certified Export Specialist (CES) enhancing their expertise. Trade Compliance Officers often possess educational backgrounds in law, business administration, or international relations, complemented by certifications like the Certified Trade Compliance Professional (CTCP) or Licensed Customs Broker (LCB). Both roles benefit from industry-specific training in tariff classifications, trade regulations, and customs procedures to ensure accurate duty application and regulatory adherence.
Day-to-Day Tasks and Work Environment
Tariff Analysts primarily focus on classifying goods according to tariff schedules, researching tariff rates, and ensuring accurate cost calculations to optimize import/export expenses. Trade Compliance Officers oversee adherence to international trade laws, manage documentation for regulatory approvals, and conduct audits to prevent violations and penalties. Both roles demand collaboration with customs brokers and regulatory agencies, but Trade Compliance Officers typically work in more dynamic environments involving risk management and policy implementation.
Regulatory Knowledge and Legal Requirements
Tariff Analysts specialize in interpreting and applying tariff schedules, harmonized codes, and customs classification to ensure accurate duty assessments under international trade regulations. Trade Compliance Officers possess comprehensive expertise in regulatory knowledge encompassing import/export laws, trade sanctions, and compliance auditing to mitigate legal risks in global transactions. Both roles require a deep understanding of legal requirements but differ in scope, with Tariff Analysts focusing on tariff regulations and Trade Compliance Officers managing broader compliance obligations.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Tariff Analysts specialize in classifying goods according to customs regulations, enabling accurate tariff application and cost forecasting, which often leads to roles in global trade management or customs brokerage. Trade Compliance Officers focus on ensuring company adherence to international trade laws and regulations, positioning them for advancement into regulatory affairs or corporate compliance leadership. Both career paths offer opportunities in multinational corporations, with Trade Compliance Officers typically progressing toward strategic policy development and Tariff Analysts advancing through technical expertise and consulting roles.
Salary Expectations and Benefits
Tariff Analysts typically earn between $60,000 and $85,000 annually, reflecting their specialization in classifying goods and calculating duties, whereas Trade Compliance Officers command salaries ranging from $70,000 to $95,000 due to their broader responsibilities ensuring adherence to trade regulations. Benefits for both roles often include health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, but Trade Compliance Officers might receive additional incentives such as compliance bonuses or professional development allowances. Salary expectations vary by industry and location, with higher pay commonly found in multinational corporations and regions with complex trade regulations.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Tariff Analysts and Trade Compliance Officers are increasingly sought after in industries navigating complex global trade regulations, with demand growing due to expanding international markets and evolving tariff laws. Tariff Analysts specialize in classifying goods and applying appropriate tariffs to optimize cost efficiency, a critical role as companies face fluctuating trade policies and tariffs. Trade Compliance Officers ensure adherence to trade laws and regulations, minimizing risks of penalties and disruptions, with job outlooks favoring candidates experienced in regulatory frameworks and compliance technology.
Choosing the Right Career: Factors to Consider
When choosing between a Tariff Analyst and a Trade Compliance Officer, consider the specific expertise required in customs regulations and international trade laws. A Tariff Analyst primarily focuses on classifying goods and determining applicable duties, leveraging data analysis and tariff schedules. In contrast, a Trade Compliance Officer ensures adherence to trade policies, managing risk and regulatory compliance to prevent legal violations.
Tariff Analyst vs Trade Compliance Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com