Warehouse Managers oversee the overall operations of the storage facility, ensuring efficient space utilization, safety compliance, and timely order fulfillment. Inventory Managers focus on maintaining accurate stock levels, monitoring inventory turnover, and coordinating replenishment to prevent stockouts or overstock situations. Both roles are critical for optimizing supply chain performance but prioritize different aspects of warehouse management.
Table of Comparison
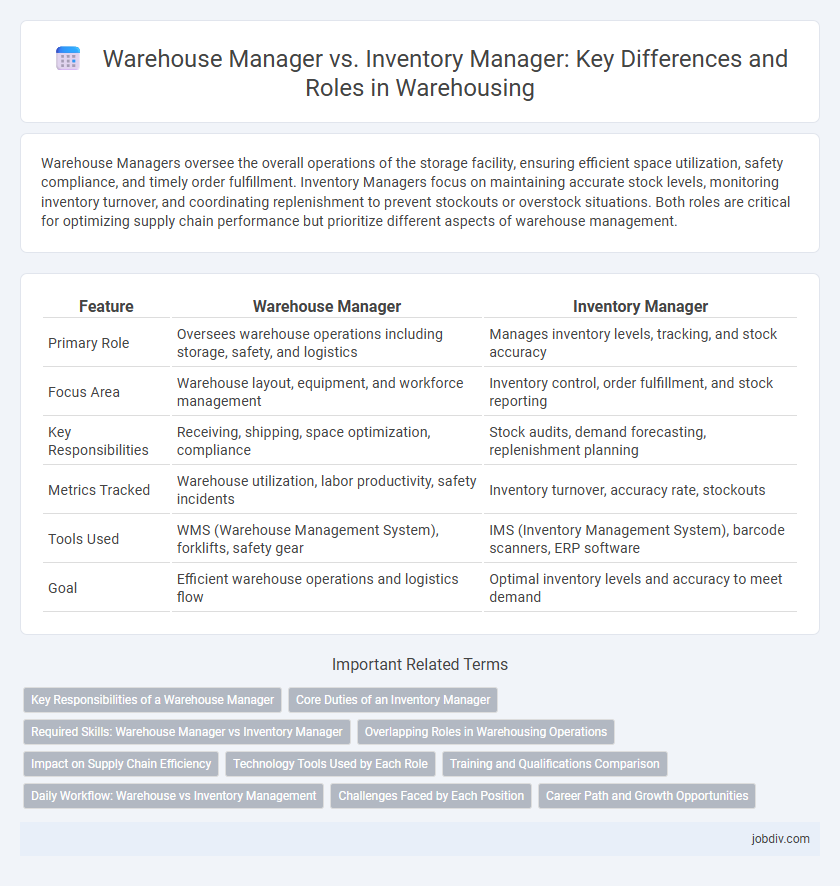
| Feature | Warehouse Manager | Inventory Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Oversees warehouse operations including storage, safety, and logistics | Manages inventory levels, tracking, and stock accuracy |
| Focus Area | Warehouse layout, equipment, and workforce management | Inventory control, order fulfillment, and stock reporting |
| Key Responsibilities | Receiving, shipping, space optimization, compliance | Stock audits, demand forecasting, replenishment planning |
| Metrics Tracked | Warehouse utilization, labor productivity, safety incidents | Inventory turnover, accuracy rate, stockouts |
| Tools Used | WMS (Warehouse Management System), forklifts, safety gear | IMS (Inventory Management System), barcode scanners, ERP software |
| Goal | Efficient warehouse operations and logistics flow | Optimal inventory levels and accuracy to meet demand |
Key Responsibilities of a Warehouse Manager
A Warehouse Manager oversees the efficient receipt, storage, and dispatch of goods, ensuring inventory accuracy and optimal warehouse layout. This role involves supervising staff, implementing safety standards, and coordinating logistics to meet operational deadlines. Continuous monitoring of stock levels and maintaining equipment functionality are crucial for streamlining warehouse processes.
Core Duties of an Inventory Manager
An Inventory Manager is responsible for overseeing stock levels, ensuring accurate inventory records, and coordinating procurement to prevent shortages or overstock situations. They utilize inventory management software to track product movement, manage reorder points, and conduct regular audits to maintain data integrity. Inventory Managers play a crucial role in optimizing supply chain efficiency by forecasting demand and collaborating closely with purchasing and warehouse teams.
Required Skills: Warehouse Manager vs Inventory Manager
Warehouse Managers require strong leadership abilities, proficiency in logistics coordination, and expertise in staff supervision to ensure smooth warehouse operations. Inventory Managers must excel in data analysis, demand forecasting, and inventory control software to maintain accurate stock levels and reduce carrying costs. Both roles demand excellent communication skills and a solid understanding of supply chain management principles.
Overlapping Roles in Warehousing Operations
Warehouse managers oversee the storage, organization, and movement of goods within the facility, ensuring efficient space utilization and timely order fulfillment. Inventory managers focus on tracking stock levels, conducting audits, and managing replenishment to prevent shortages or overstocking. Both roles intersect in tasks like inventory accuracy, coordinating stock transfers, and collaborating on demand forecasting to optimize warehousing operations.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency
Warehouse Managers oversee the storage, organization, and timely dispatch of goods, ensuring efficient space utilization and reducing delays in order fulfillment. Inventory Managers maintain accurate stock levels through systematic tracking and demand forecasting, preventing overstocking and stockouts that disrupt supply chain continuity. Their combined efforts streamline warehouse operations, optimize inventory turnover, and significantly enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
Technology Tools Used by Each Role
Warehouse Managers utilize advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to optimize space, track shipments, and coordinate labor efficiently, often integrating RFID and barcode scanning technologies for real-time inventory tracking. Inventory Managers rely heavily on Inventory Control Software and Demand Forecasting Tools to monitor stock levels, manage reorder points, and reduce holding costs through data analytics and automated alerts. Both roles leverage cloud-based platforms for enhanced visibility and seamless communication across supply chain operations.
Training and Qualifications Comparison
Warehouse Managers typically require comprehensive training in logistics, supply chain management, and leadership skills, often holding a bachelor's degree in business or logistics. Inventory Managers emphasize expertise in inventory control systems, data analysis, and demand forecasting, with certifications such as Certified in Production and Inventory Management (CPIM) enhancing their qualifications. Both roles benefit from strong problem-solving abilities, but Warehouse Managers focus more on operational oversight while Inventory Managers prioritize accuracy and efficiency in stock management.
Daily Workflow: Warehouse vs Inventory Management
Warehouse managers oversee daily warehouse operations including receiving, storage, order picking, and shipping to ensure efficient inventory flow and space utilization. Inventory managers focus on tracking stock levels, conducting regular audits, managing reorder points, and maintaining accurate inventory records to prevent stockouts and overstock. Coordination between warehouse workflow and inventory control is essential to optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Challenges Faced by Each Position
Warehouse managers confront challenges such as optimizing space utilization, ensuring efficient workflow, and maintaining safety compliance amid fluctuating shipment volumes. Inventory managers face difficulties in accurate stock level tracking, demand forecasting, and minimizing discrepancies caused by human error or system failures. Both roles require strategic problem-solving to balance operational efficiency with cost control in dynamic supply chain environments.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
Warehouse Managers typically oversee overall warehouse operations, focusing on staff supervision, workflow optimization, and safety compliance, which positions them for advancement into senior logistics or supply chain management roles. Inventory Managers specialize in stock control, data analysis, and forecasting, building expertise valuable for careers in procurement, demand planning, or supply chain analytics. Both roles offer distinct growth opportunities, with Warehouse Managers leaning towards operational leadership and Inventory Managers developing strategic skills in inventory optimization and resource allocation.
Warehouse Manager vs Inventory Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com