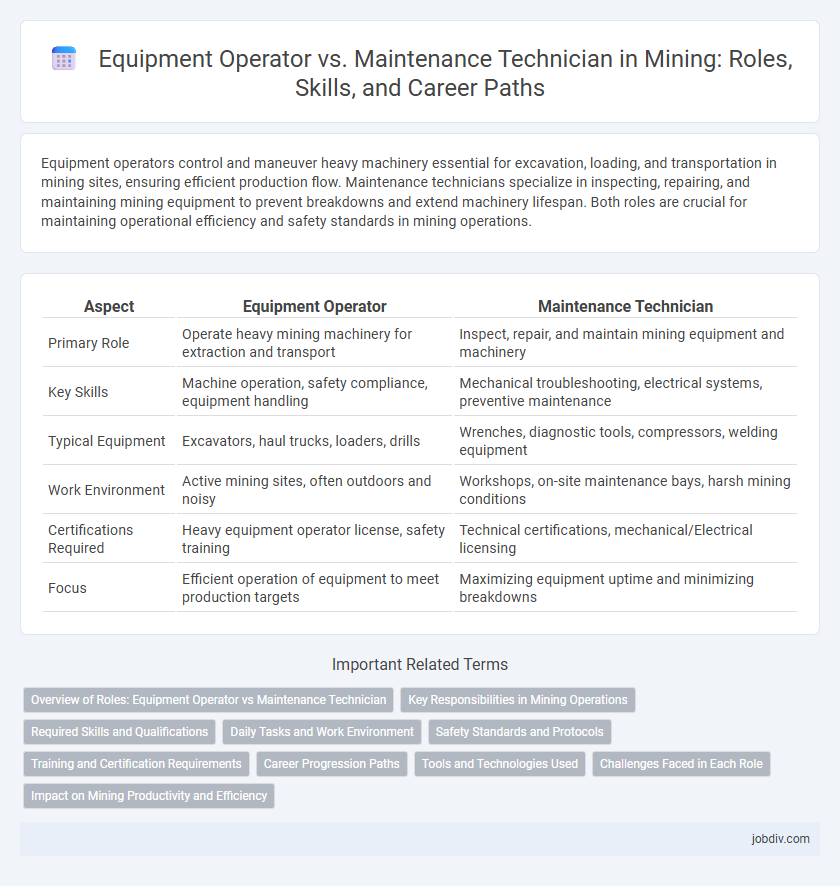
Equipment operators control and maneuver heavy machinery essential for excavation, loading, and transportation in mining sites, ensuring efficient production flow. Maintenance technicians specialize in inspecting, repairing, and maintaining mining equipment to prevent breakdowns and extend machinery lifespan. Both roles are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and safety standards in mining operations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Equipment Operator | Maintenance Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Operate heavy mining machinery for extraction and transport | Inspect, repair, and maintain mining equipment and machinery |
| Key Skills | Machine operation, safety compliance, equipment handling | Mechanical troubleshooting, electrical systems, preventive maintenance |
| Typical Equipment | Excavators, haul trucks, loaders, drills | Wrenches, diagnostic tools, compressors, welding equipment |
| Work Environment | Active mining sites, often outdoors and noisy | Workshops, on-site maintenance bays, harsh mining conditions |
| Certifications Required | Heavy equipment operator license, safety training | Technical certifications, mechanical/Electrical licensing |
| Focus | Efficient operation of equipment to meet production targets | Maximizing equipment uptime and minimizing breakdowns |
Overview of Roles: Equipment Operator vs Maintenance Technician
Equipment operators in mining are responsible for operating heavy machinery such as excavators, loaders, and haul trucks, ensuring efficient extraction and transport of materials. Maintenance technicians specialize in diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining mining equipment to minimize downtime and extend machinery lifespan. Both roles are critical for optimizing operational productivity and safety in mining environments.
Key Responsibilities in Mining Operations
Equipment Operators in mining are responsible for the safe and efficient operation of heavy machinery such as excavators, haul trucks, and loaders to extract and transport minerals. Maintenance Technicians focus on diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining mechanical, electrical, and hydraulic systems to ensure continuous equipment functionality and minimize downtime. Both roles are critical to optimizing mining productivity and safety, with Operators handling daily production tasks and Technicians managing equipment reliability.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Equipment operators in mining must possess strong mechanical aptitude, proficiency in operating heavy machinery such as excavators and loaders, and a solid understanding of safety protocols and site regulations to ensure efficient and secure operations. Maintenance technicians require advanced troubleshooting skills, expertise in diagnosing and repairing electrical and hydraulic systems, and relevant certifications such as a journeyman mechanic or industrial maintenance technician qualification to maintain equipment reliability and minimize downtime. Both roles demand physical stamina and technical knowledge, but maintenance technicians typically need deeper technical training and problem-solving abilities related to machinery upkeep.
Daily Tasks and Work Environment
Equipment Operators in mining are responsible for controlling heavy machinery such as excavators, bulldozers, and haul trucks to move earth and materials efficiently within active mining sites. Maintenance Technicians focus on inspecting, diagnosing, and repairing mechanical and electrical systems to ensure continuous operation of mining equipment and minimize downtime. Operators typically work outdoors in dynamic, weather-exposed environments, while Maintenance Technicians split time between fieldwork and workshop settings, often performing preventative maintenance in confined or elevated spaces.
Safety Standards and Protocols
Equipment operators in mining strictly adhere to safety standards such as wearing personal protective equipment (PPE) and following machinery operation protocols to prevent accidents. Maintenance technicians prioritize safety by conducting regular inspections, repairs, and ensuring lockout/tagout procedures are rigorously implemented to eliminate hazards during equipment servicing. Both roles require comprehensive training on mining safety regulations from organizations like MSHA to maintain a secure working environment.
Training and Certification Requirements
Equipment operators in mining typically require specialized training in heavy machinery operation and certifications such as MSHA (Mine Safety and Health Administration) operator qualifications to ensure safe and efficient handling of equipment. Maintenance technicians need extensive technical training in mechanical, electrical, and hydraulic systems, often holding certifications like NACE (National Association of Corrosion Engineers) or specific trade licenses to perform repairs and preventative maintenance. Both roles demand ongoing safety training and adherence to industry regulations to maintain compliance and operational efficiency in mining environments.
Career Progression Paths
Equipment operators in mining typically advance by gaining expertise in heavy machinery, leading to supervisory roles or specialized operator positions such as drill rig or haul truck operators. Maintenance technicians progress through acquiring skills in mechanical, electrical, and hydraulic systems, often moving toward senior technician roles or maintenance management. Both paths offer opportunities for certification and training that enhance career growth and salary potential within the mining industry.
Tools and Technologies Used
Equipment operators in mining primarily use heavy machinery such as excavators, bulldozers, and haul trucks equipped with GPS and telematics for precise excavation and material transport. Maintenance technicians rely on diagnostic tools, including vibration analyzers, thermal imaging cameras, and computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) to identify faults and perform repairs on mining equipment. Both roles integrate advanced technologies like automation controls and predictive analytics to enhance operational efficiency and equipment longevity.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Equipment Operators in mining face challenges such as navigating rough terrains, managing heavy machinery with precision, and ensuring continuous equipment operation under harsh environmental conditions. Maintenance Technicians encounter difficulties in diagnosing mechanical failures, performing timely repairs to minimize downtime, and adapting to complex, ever-evolving mining machinery technologies. Both roles require specialized skills to address safety hazards, operational efficiency, and equipment reliability critical to mining productivity.
Impact on Mining Productivity and Efficiency
Equipment operators directly influence mining productivity by skillfully managing heavy machinery to maximize extraction rates and minimize downtime. Maintenance technicians ensure operational efficiency through regular servicing and timely repairs, reducing equipment failures and extending machinery lifespan. Together, their roles synergize to optimize mining output and cost-effectiveness.
Equipment Operator vs Maintenance Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com