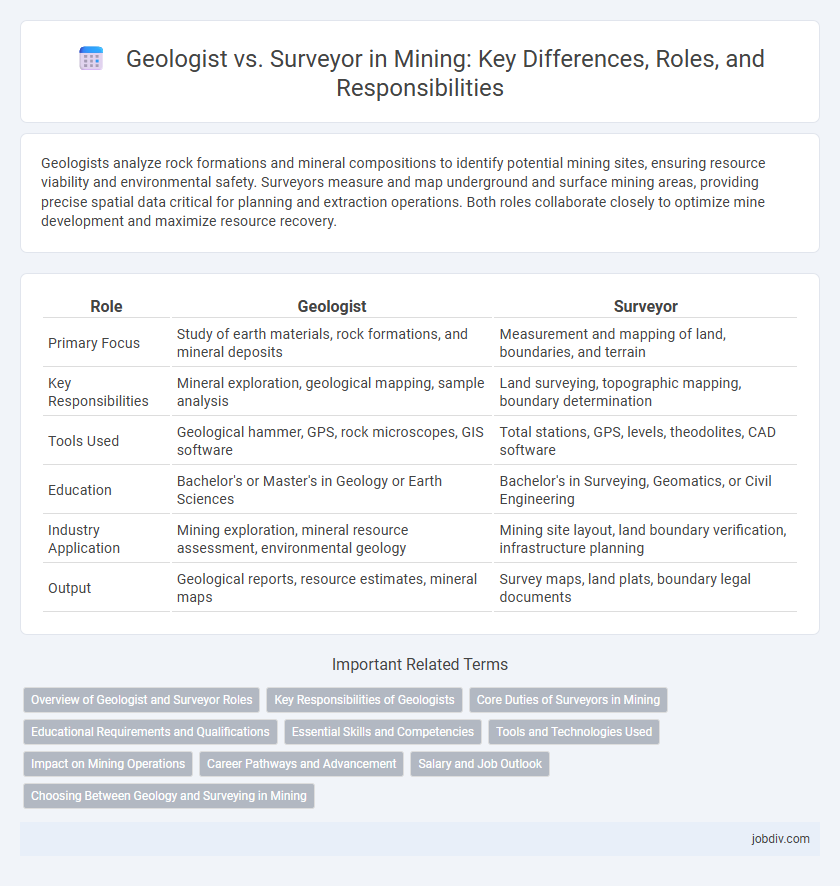
Geologists analyze rock formations and mineral compositions to identify potential mining sites, ensuring resource viability and environmental safety. Surveyors measure and map underground and surface mining areas, providing precise spatial data critical for planning and extraction operations. Both roles collaborate closely to optimize mine development and maximize resource recovery.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Geologist | Surveyor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Study of earth materials, rock formations, and mineral deposits | Measurement and mapping of land, boundaries, and terrain |
| Key Responsibilities | Mineral exploration, geological mapping, sample analysis | Land surveying, topographic mapping, boundary determination |
| Tools Used | Geological hammer, GPS, rock microscopes, GIS software | Total stations, GPS, levels, theodolites, CAD software |
| Education | Bachelor's or Master's in Geology or Earth Sciences | Bachelor's in Surveying, Geomatics, or Civil Engineering |
| Industry Application | Mining exploration, mineral resource assessment, environmental geology | Mining site layout, land boundary verification, infrastructure planning |
| Output | Geological reports, resource estimates, mineral maps | Survey maps, land plats, boundary legal documents |
Overview of Geologist and Surveyor Roles
Geologists analyze rock formations, mineral deposits, and soil characteristics to assess mining potential and ensure environmental compliance. Surveyors measure and map land features, creating precise spatial data for mine planning, boundary delineation, and construction layouts. Both roles are essential for efficient resource extraction and safe mine operations.
Key Responsibilities of Geologists
Geologists analyze rock formations, mineral compositions, and geological structures to assess mining site potential and resource estimation. They conduct field surveys, collect samples, and interpret geological data to guide exploration and extraction processes. Their expertise ensures safe, efficient mining operations by identifying hazards and advising on environmental impacts.
Core Duties of Surveyors in Mining
Surveyors in mining play a critical role in accurately mapping and measuring mining sites to ensure precise excavation and resource extraction. They establish legal boundaries, create detailed topographic maps, and monitor structural stability to support safe and efficient mining operations. Their core duties also include data collection using advanced GPS and GIS technologies for planning and compliance with regulatory standards.
Educational Requirements and Qualifications
Geologists typically require a bachelor's degree in geology, earth sciences, or a related field, often followed by advanced degrees or certifications for specialized mining roles. Surveyors must hold degrees or diplomas in surveying, geomatics, or civil engineering, with professional licensure such as a Professional Land Surveyor (PLS) required for practice. Both professions demand strong analytical skills, but geologists emphasize mineralogy and rock formations, while surveyors focus on land measurement and mapping technology.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Geologists in mining must excel in rock and mineral identification, geological mapping, and data interpretation to assess mineral deposits accurately. Surveyors require expertise in land measurement, use of GPS and total stations, and precise topographic mapping to define mining boundaries and support infrastructure planning. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in specialized software like GIS and CAD for effective resource extraction and site management.
Tools and Technologies Used
Geologists employ tools such as rock hammers, hand lenses, GPS devices, and specialized software like GIS and geological modeling programs to analyze earth materials and structures. Surveyors utilize instruments including total stations, theodolites, GNSS receivers, and laser scanners to measure land and map terrain accurately. Both professionals integrate drones and remote sensing technologies to enhance data collection and precision in mining operations.
Impact on Mining Operations
Geologists analyze mineral composition, rock formations, and soil structures, providing critical data for identifying viable mining sites and estimating resource quantities. Surveyors precisely measure and map land topography, ensuring accurate delineation of mining boundaries and infrastructure placement. Their combined expertise minimizes operational risks, optimizes extraction processes, and enhances overall efficiency in mining projects.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Geologists in mining focus on analyzing earth materials and identifying mineral resources, often advancing into roles such as senior geologist or exploration manager. Surveyors specialize in measuring and mapping mining sites, with career growth leading to chief surveyor or project manager positions. Both pathways require strong technical skills and field experience, offering opportunities for leadership roles in mining operations.
Salary and Job Outlook
Geologists in mining earn an average salary of $70,000 to $110,000 annually, reflecting their expertise in analyzing mineral deposits and earth processes, while surveyors typically earn between $55,000 and $85,000 due to their role in land measurement and mapping. Job outlook for geologists is projected to grow by 8% through 2030, driven by demand for natural resources and environmental assessment. Surveyors face a steadier growth rate of about 4%, influenced by infrastructure development and land use planning within the mining sector.
Choosing Between Geology and Surveying in Mining
Choosing between geology and surveying in mining depends on specific project needs; geologists analyze mineral composition and formation processes to guide exploration and extraction strategies, while surveyors measure and map mine sites to ensure precise boundaries and structural integrity. Geologists typically focus on subsurface data interpretation and resource estimation, whereas surveyors specialize in spatial data accuracy, land measurement, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Effective mining operations integrate both disciplines to optimize resource extraction and maintain site safety and legal standards.
Geologist vs Surveyor Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com