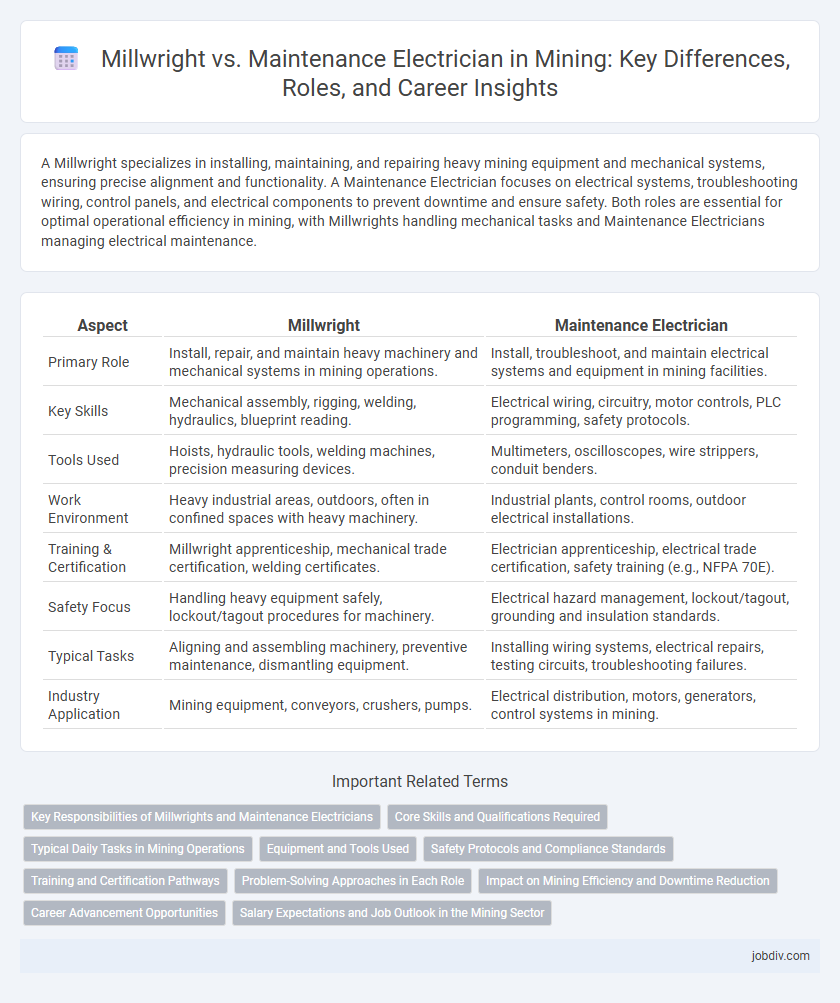
A Millwright specializes in installing, maintaining, and repairing heavy mining equipment and mechanical systems, ensuring precise alignment and functionality. A Maintenance Electrician focuses on electrical systems, troubleshooting wiring, control panels, and electrical components to prevent downtime and ensure safety. Both roles are essential for optimal operational efficiency in mining, with Millwrights handling mechanical tasks and Maintenance Electricians managing electrical maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Millwright | Maintenance Electrician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Install, repair, and maintain heavy machinery and mechanical systems in mining operations. | Install, troubleshoot, and maintain electrical systems and equipment in mining facilities. |
| Key Skills | Mechanical assembly, rigging, welding, hydraulics, blueprint reading. | Electrical wiring, circuitry, motor controls, PLC programming, safety protocols. |
| Tools Used | Hoists, hydraulic tools, welding machines, precision measuring devices. | Multimeters, oscilloscopes, wire strippers, conduit benders. |
| Work Environment | Heavy industrial areas, outdoors, often in confined spaces with heavy machinery. | Industrial plants, control rooms, outdoor electrical installations. |
| Training & Certification | Millwright apprenticeship, mechanical trade certification, welding certificates. | Electrician apprenticeship, electrical trade certification, safety training (e.g., NFPA 70E). |
| Safety Focus | Handling heavy equipment safely, lockout/tagout procedures for machinery. | Electrical hazard management, lockout/tagout, grounding and insulation standards. |
| Typical Tasks | Aligning and assembling machinery, preventive maintenance, dismantling equipment. | Installing wiring systems, electrical repairs, testing circuits, troubleshooting failures. |
| Industry Application | Mining equipment, conveyors, crushers, pumps. | Electrical distribution, motors, generators, control systems in mining. |
Key Responsibilities of Millwrights and Maintenance Electricians
Millwrights specialize in installing, maintaining, and repairing heavy machinery and mechanical equipment essential to mining operations, including conveyor systems, crushers, and pumps. Maintenance electricians focus on electrical systems, troubleshooting, and repairing wiring, motors, and control panels to ensure continuous equipment functionality. Both roles are crucial for minimizing downtime and maintaining operational safety in mining environments.
Core Skills and Qualifications Required
Millwrights require expertise in mechanical systems, including installation, alignment, and troubleshooting of heavy machinery in mining operations, along with proficiency in welding and blueprint reading. Maintenance Electricians must possess strong electrical knowledge, including wiring, circuit troubleshooting, and adherence to safety protocols specific to mining equipment. Both roles demand certifications such as apprenticeships and safety training, but millwrights focus more on mechanical aptitude while electricians emphasize electrical systems and controls.
Typical Daily Tasks in Mining Operations
Millwrights in mining operations primarily handle the installation, maintenance, and repair of heavy machinery such as conveyors, crushers, and grinding mills, ensuring mechanical systems run efficiently. Maintenance electricians focus on electrical systems servicing, including troubleshooting and repairing motors, control panels, and electrical wiring to prevent downtime. Both roles require detailed knowledge of mining equipment, but millwrights emphasize mechanical systems while maintenance electricians specialize in electrical components.
Equipment and Tools Used
Millwrights specialize in installing, aligning, and maintaining heavy mining equipment such as crushers, conveyors, and mills, utilizing tools like precision laser alignment devices, hoists, and welding equipment. Maintenance Electricians focus on electrical systems of mining machinery, using multimeters, insulation testers, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to diagnose and repair electrical faults. Both roles require expertise with hand tools, power tools, and safety gear, but millwrights emphasize mechanical components while electricians prioritize electrical diagnostics and controls.
Safety Protocols and Compliance Standards
Millwrights and Maintenance Electricians in the mining industry adhere to strict safety protocols and compliance standards to prevent workplace accidents and equipment failures. Millwrights often follow procedures related to heavy machinery installation and alignment, including lockout/tagout (LOTO) systems and confined space entry guidelines mandated by OSHA and MSHA. Maintenance Electricians prioritize electrical safety compliance such as arc flash hazard assessments, proper grounding, and adherence to NFPA 70E standards to minimize shock risks and ensure operational safety within mining facilities.
Training and Certification Pathways
Millwrights in mining require extensive training in mechanical systems, often completing apprenticeships that combine on-the-job experience with technical school courses, culminating in certification such as journeyman status. Maintenance Electricians focus on electrical systems, undergoing specialized electrical training programs and obtaining licenses, including electricians' certifications recognized by mining regulatory bodies. Both roles demand continuous skill upgrades and safety training to meet stringent mining industry standards.
Problem-Solving Approaches in Each Role
Millwrights utilize mechanical expertise to diagnose and resolve machinery alignment and structural issues, often employing precision instruments to ensure optimal equipment performance. Maintenance Electricians focus on electrical troubleshooting, using advanced diagnostic tools to identify circuit faults, wiring problems, and control system failures critical for uninterrupted mining operations. Both roles require analytical skills, but Millwrights emphasize mechanical problem-solving while Maintenance Electricians specialize in electrical system restoration.
Impact on Mining Efficiency and Downtime Reduction
Millwrights in mining specialize in installing and maintaining heavy machinery, directly enhancing equipment reliability and operational uptime. Maintenance electricians focus on electrical system diagnostics and repairs, ensuring continuous power supply and minimizing system failures. Together, their expertise significantly reduces unscheduled downtime, boosting overall mining efficiency and production output.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Millwrights in mining have broader career advancement opportunities through specialization in machinery installation, alignment, and overhaul, often progressing to supervisory or engineering roles. Maintenance electricians focus on electrical systems troubleshooting and repair, with career growth typically leading to electrical engineering or industrial automation positions. Both roles offer pathways to leadership, but millwrights benefit from a wider scope of mechanical expertise critical to mining operations.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook in the Mining Sector
Millwrights in the mining sector typically earn an average salary ranging from $60,000 to $90,000 annually, reflecting their expertise in installing, repairing, and maintaining heavy machinery critical to mining operations. Maintenance Electricians command similar salary ranges of $65,000 to $95,000 per year, with demand driven by the need to ensure electrical systems and equipment function safely and efficiently underground and on-site. Job outlook for both positions remains strong due to ongoing mining projects and the increasing reliance on advanced technology, with regional variations depending on mining activity and commodity prices.
Millwright vs Maintenance Electrician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com