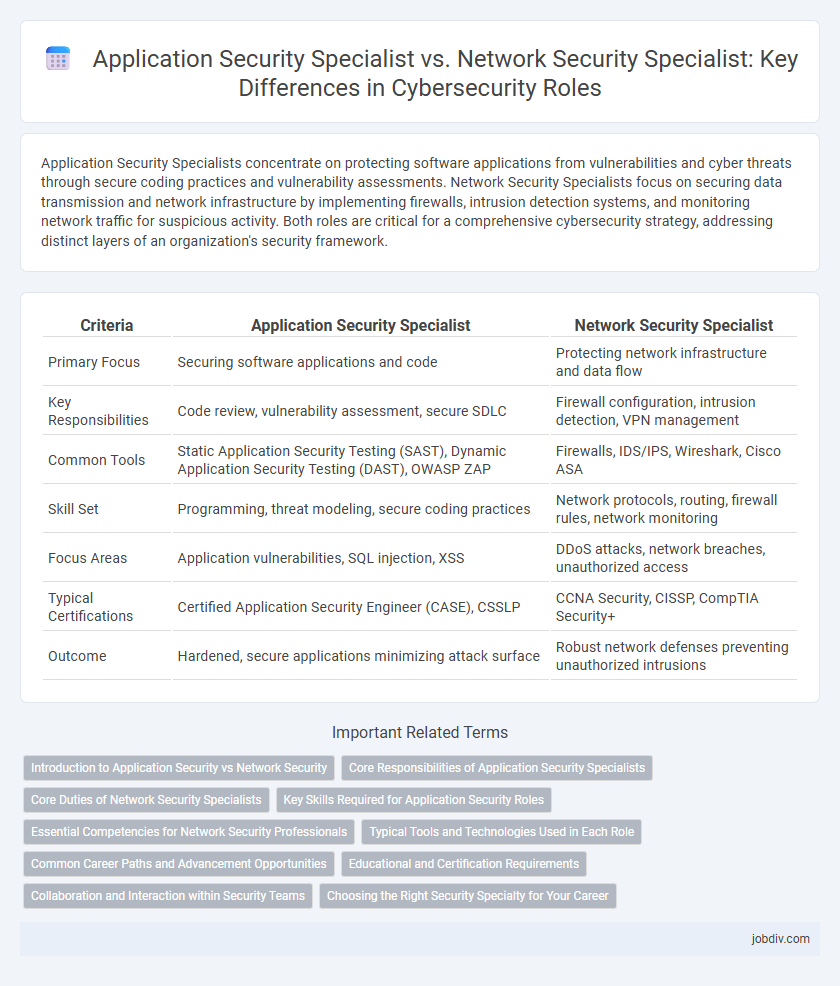
Application Security Specialists concentrate on protecting software applications from vulnerabilities and cyber threats through secure coding practices and vulnerability assessments. Network Security Specialists focus on securing data transmission and network infrastructure by implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity. Both roles are critical for a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, addressing distinct layers of an organization's security framework.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Application Security Specialist | Network Security Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Securing software applications and code | Protecting network infrastructure and data flow |
| Key Responsibilities | Code review, vulnerability assessment, secure SDLC | Firewall configuration, intrusion detection, VPN management |
| Common Tools | Static Application Security Testing (SAST), Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST), OWASP ZAP | Firewalls, IDS/IPS, Wireshark, Cisco ASA |
| Skill Set | Programming, threat modeling, secure coding practices | Network protocols, routing, firewall rules, network monitoring |
| Focus Areas | Application vulnerabilities, SQL injection, XSS | DDoS attacks, network breaches, unauthorized access |
| Typical Certifications | Certified Application Security Engineer (CASE), CSSLP | CCNA Security, CISSP, CompTIA Security+ |
| Outcome | Hardened, secure applications minimizing attack surface | Robust network defenses preventing unauthorized intrusions |
Introduction to Application Security vs Network Security
Application Security Specialists focus on protecting software applications from vulnerabilities during development and deployment, utilizing techniques such as code reviews, static and dynamic analysis, and secure coding practices. Network Security Specialists safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of data transmitted across networks by implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, VPNs, and access controls. Both roles play a critical part in an organization's overall cybersecurity strategy by addressing different threat vectors at the application and network layers.
Core Responsibilities of Application Security Specialists
Application Security Specialists focus on identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities within software applications by conducting code reviews, performing static and dynamic analysis, and implementing secure coding practices. They collaborate closely with development teams to integrate security into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and ensure compliance with security standards such as OWASP Top Ten and SANS CWE controls. Their core responsibilities also include conducting penetration testing on applications, managing application security tools, and responding to security incidents related to software vulnerabilities.
Core Duties of Network Security Specialists
Network Security Specialists are responsible for designing, implementing, and managing secure network infrastructures to protect sensitive data from cyber threats. Their core duties include monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity, configuring firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and responding to security incidents to minimize risks. They also conduct vulnerability assessments and ensure compliance with industry security standards to maintain robust network defenses.
Key Skills Required for Application Security Roles
Application Security Specialists require in-depth knowledge of secure coding practices, vulnerability assessment, and threat modeling to protect software from exploits. Expertise in software development life cycle (SDLC) integration, code review tools like static and dynamic analysis, and familiarity with languages such as Java, Python, and C++ are critical. Proficiency in understanding web application security standards like OWASP Top Ten and experience with encryption, authentication, and authorization mechanisms are essential for effective risk mitigation.
Essential Competencies for Network Security Professionals
Network Security Specialists must possess in-depth knowledge of protocols such as TCP/IP, VPNs, and firewalls to safeguard data transmission and network infrastructure. Proficiency in intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and network segmentation techniques is crucial for identifying and mitigating cyber threats. Strong skills in configuring routers, switches, and endpoint security solutions enable effective protection against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Typical Tools and Technologies Used in Each Role
Application Security Specialists typically use tools such as static application security testing (SAST), dynamic application security testing (DAST), and software composition analysis (SCA) to identify vulnerabilities within code and application environments. Network Security Specialists focus on technologies including firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), virtual private networks (VPNs), and network access control (NAC) solutions to safeguard data in transit and maintain secure network infrastructures. Both roles leverage security information and event management (SIEM) platforms for comprehensive monitoring and analysis, but their primary toolsets differ based on their specific domain focus.
Common Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Application Security Specialists often advance by gaining expertise in secure coding practices, vulnerability assessment, and DevSecOps, leading to roles such as Security Architect or Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). Network Security Specialists typically progress through mastering firewall management, intrusion detection systems, and secure network design, moving into senior positions like Network Security Manager or Security Operations Center (SOC) Director. Both paths offer opportunities to specialize further in compliance, threat intelligence, or cloud security, enhancing career growth within the cybersecurity domain.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Application Security Specialists typically require knowledge in secure coding practices, software development lifecycle, and may pursue certifications like Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional (CSSLP) or Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP). Network Security Specialists focus on protecting data in transit, network infrastructure, and often hold certifications such as Cisco Certified Network Associate Security (CCNA Security) or Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP). Both roles benefit from a foundational understanding of cybersecurity principles, with specialized training tailored to either application-layer or network-layer defense.
Collaboration and Interaction within Security Teams
Application Security Specialists and Network Security Specialists collaborate closely to ensure comprehensive organizational security by integrating secure application development practices with robust network defenses. Their interaction involves continuous communication to identify vulnerabilities, share threat intelligence, and coordinate incident response strategies, enhancing overall security posture. Effective teamwork between these specialists enables seamless protection across both application layers and network infrastructure, minimizing risks from advanced cyber threats.
Choosing the Right Security Specialty for Your Career
Application Security Specialists concentrate on securing software applications by identifying and fixing vulnerabilities in code, making them essential for organizations prioritizing software integrity and development lifecycle protection. Network Security Specialists focus on protecting the infrastructure by monitoring and defending against unauthorized access, ensuring robustness in firewalls, routers, and overall network architecture against cyber threats. Selecting the right security specialty depends on your interest in either software development and secure coding or infrastructure defense and network protocol expertise.
Application Security Specialist vs Network Security Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com