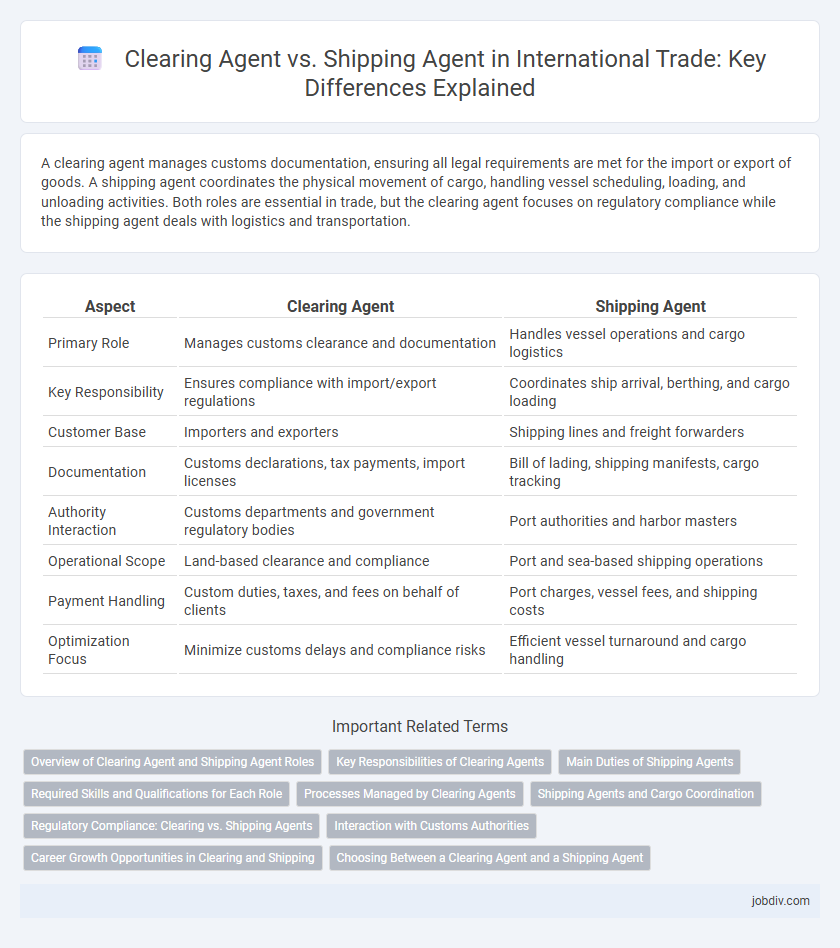
A clearing agent manages customs documentation, ensuring all legal requirements are met for the import or export of goods. A shipping agent coordinates the physical movement of cargo, handling vessel scheduling, loading, and unloading activities. Both roles are essential in trade, but the clearing agent focuses on regulatory compliance while the shipping agent deals with logistics and transportation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Clearing Agent | Shipping Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manages customs clearance and documentation | Handles vessel operations and cargo logistics |
| Key Responsibility | Ensures compliance with import/export regulations | Coordinates ship arrival, berthing, and cargo loading |
| Customer Base | Importers and exporters | Shipping lines and freight forwarders |
| Documentation | Customs declarations, tax payments, import licenses | Bill of lading, shipping manifests, cargo tracking |
| Authority Interaction | Customs departments and government regulatory bodies | Port authorities and harbor masters |
| Operational Scope | Land-based clearance and compliance | Port and sea-based shipping operations |
| Payment Handling | Custom duties, taxes, and fees on behalf of clients | Port charges, vessel fees, and shipping costs |
| Optimization Focus | Minimize customs delays and compliance risks | Efficient vessel turnaround and cargo handling |
Overview of Clearing Agent and Shipping Agent Roles
Clearing agents handle customs documentation, ensuring compliance with import and export regulations to facilitate smooth cargo clearance. Shipping agents manage vessel operations, coordinating port services, berthing, and cargo loading or unloading on behalf of shipowners. Both roles are essential for efficient trade logistics, with clearing agents focusing on regulatory clearance and shipping agents overseeing maritime operations.
Key Responsibilities of Clearing Agents
Clearing agents specialize in managing customs documentation, ensuring compliance with import-export regulations, and facilitating the smooth clearance of goods through customs authorities. Their key responsibilities include verifying shipment details, paying duties and taxes on behalf of clients, and coordinating with customs officials to prevent delays. Unlike shipping agents who handle transportation and logistics, clearing agents focus on regulatory clearance to avoid legal complications and expedite cargo release.
Main Duties of Shipping Agents
Shipping agents coordinate vessel arrivals and departures, manage documentation such as bills of lading, and ensure compliance with port and customs regulations. They arrange for pilotage, towage, and berth allocation, facilitating efficient port operations. Shipping agents also act as intermediaries between shipowners and port authorities, overseeing cargo handling and crew services.
Required Skills and Qualifications for Each Role
Clearing agents require deep expertise in customs regulations, documentation, and import-export compliance, often holding certifications such as a Customs Broker License. Shipping agents need strong knowledge of maritime laws, vessel operations, and logistics management, usually backed by maritime training or degrees in shipping and transport. Both roles demand exceptional communication skills and proficiency in handling complex trade documentation to ensure smooth international shipments.
Processes Managed by Clearing Agents
Clearing agents manage critical processes such as customs documentation, tariff calculations, and compliance verification to ensure smooth import and export transactions. They coordinate with customs authorities to facilitate the timely clearance of goods, preventing delays and penalties. These agents also handle duties, taxes, and regulatory requirements, streamlining the movement of products across international borders.
Shipping Agents and Cargo Coordination
Shipping agents play a crucial role in coordinating cargo shipments by managing vessel schedules, handling documentation, and liaising with port authorities to ensure timely loading and unloading. They optimize cargo coordination through efficient communication with freight forwarders, shipping lines, and customs officials, minimizing delays and streamlining supply chain operations. Unlike clearing agents who focus primarily on customs clearance and import/export compliance, shipping agents oversee the operational aspects of cargo movement and vessel logistics.
Regulatory Compliance: Clearing vs. Shipping Agents
Clearing agents specialize in regulatory compliance by ensuring all customs documentation, duties, and taxes are accurately processed to facilitate smooth cargo clearance. Shipping agents focus on compliance with maritime regulations, port authority requirements, and vessel documentation to coordinate efficient ship operations. Both roles are crucial in maintaining adherence to international trade laws and mitigating risks related to shipment delays or penalties.
Interaction with Customs Authorities
Clearing agents specialize in managing customs documentation, ensuring compliance with import and export regulations to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Shipping agents coordinate vessel scheduling and cargo handling but rely on clearing agents to interact directly with customs authorities. Effective collaboration between clearing agents and customs officials accelerates the clearance process, reducing delays in international trade operations.
Career Growth Opportunities in Clearing and Shipping
Career growth opportunities in clearing and shipping agents show distinct pathways; clearing agents often advance through expertise in customs regulations, import-export documentation, and logistics coordination, leading to roles such as customs compliance manager or freight operations supervisor. Shipping agents develop skills in vessel operations, port logistics, and client relationship management, paving the way for positions like port operations manager or maritime logistics coordinator. Both careers offer expansion into international trade consultancy and supply chain management, reflecting their critical roles in global commerce.
Choosing Between a Clearing Agent and a Shipping Agent
Choosing between a clearing agent and a shipping agent depends on the specific needs of your international trade operation. A clearing agent specializes in customs clearance, handling documentation, and ensuring compliance with import-export regulations, while a shipping agent coordinates the transportation, booking cargo space, and managing shipping logistics. Prioritizing your business's focus--whether on regulatory adherence or freight movement--helps determine the most effective agent to optimize supply chain efficiency and reduce delays.
Clearing Agent vs Shipping Agent Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com