Trade Finance Officers specialize in managing credit, risk, and payment solutions to facilitate international trade transactions, ensuring smooth financial flows between importers and exporters. Supply Chain Finance Officers focus on optimizing working capital and cash flow across the supply chain by implementing financing solutions that benefit both suppliers and buyers, improving overall supply chain efficiency. Both roles require strong knowledge of financial instruments and trade regulations but differ in their emphasis, with Trade Finance Officers addressing transactional risks and Supply Chain Finance Officers enhancing supply chain liquidity.
Table of Comparison
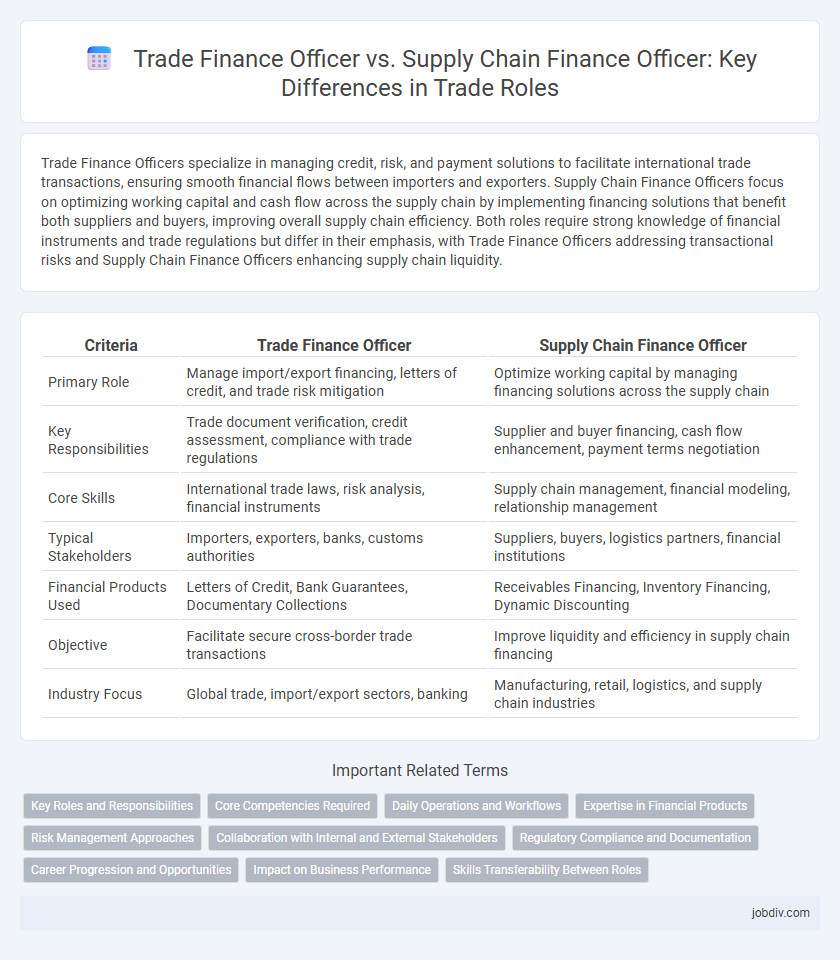
| Criteria | Trade Finance Officer | Supply Chain Finance Officer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manage import/export financing, letters of credit, and trade risk mitigation | Optimize working capital by managing financing solutions across the supply chain |
| Key Responsibilities | Trade document verification, credit assessment, compliance with trade regulations | Supplier and buyer financing, cash flow enhancement, payment terms negotiation |
| Core Skills | International trade laws, risk analysis, financial instruments | Supply chain management, financial modeling, relationship management |
| Typical Stakeholders | Importers, exporters, banks, customs authorities | Suppliers, buyers, logistics partners, financial institutions |
| Financial Products Used | Letters of Credit, Bank Guarantees, Documentary Collections | Receivables Financing, Inventory Financing, Dynamic Discounting |
| Objective | Facilitate secure cross-border trade transactions | Improve liquidity and efficiency in supply chain financing |
| Industry Focus | Global trade, import/export sectors, banking | Manufacturing, retail, logistics, and supply chain industries |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Trade Finance Officers manage and execute financial products such as letters of credit, guarantees, and documentary collections to facilitate international trade transactions. Supply Chain Finance Officers focus on optimizing cash flow by providing financing solutions that support suppliers and buyers within the supply chain, leveraging data analytics to assess risk and enhance payment terms. Both roles require collaboration with banks, clients, and internal teams to ensure compliance, mitigate risks, and streamline trade and supply chain operations.
Core Competencies Required
Trade Finance Officers require expertise in letters of credit, risk assessment, and international banking regulations to facilitate cross-border transactions securely. Supply Chain Finance Officers focus on optimizing working capital through invoice financing, payment terms negotiation, and supplier relationship management to enhance cash flow efficiency. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, compliance knowledge, and proficiency in financial instruments specific to global trade operations.
Daily Operations and Workflows
Trade Finance Officers manage letters of credit, documentary collections, and risk assessments to facilitate international trade transactions, ensuring compliance with banking regulations and timely payment processing. Supply Chain Finance Officers focus on optimizing cash flow between buyers and suppliers by coordinating invoice discounting, payment terms negotiation, and real-time data analytics to improve liquidity. Daily operations for both roles involve liaising with clients and financial institutions, but Trade Finance Officers concentrate on transaction security while Supply Chain Finance Officers prioritize supply chain efficiency and financing solutions.
Expertise in Financial Products
A Trade Finance Officer specializes in financial instruments such as letters of credit, bank guarantees, and export credit to facilitate international trade transactions securely. In contrast, a Supply Chain Finance Officer focuses on optimizing working capital and cash flow by leveraging financial products like invoice factoring, dynamic discounting, and purchase order financing within the supply chain ecosystem. Both roles require deep expertise in risk assessment, credit analysis, and regulatory compliance, but they apply distinct financial solutions tailored to trade finance and supply chain financing needs.
Risk Management Approaches
Trade Finance Officers implement risk management approaches by conducting thorough credit risk assessments, evaluating the financial health of trading counterparties, and ensuring compliance with international trade regulations to mitigate default and fraud risks. Supply Chain Finance Officers focus on managing risks related to the liquidity and operational continuity of supply chain partners by analyzing supplier creditworthiness, monitoring payment delays, and using technologies like blockchain for transparency and fraud reduction. Both roles leverage data analytics and real-time monitoring tools to enhance risk identification and mitigation in global trade environments.
Collaboration with Internal and External Stakeholders
Trade Finance Officers collaborate closely with internal teams such as credit risk, compliance, and operations to ensure seamless processing of trade transactions, while also engaging external stakeholders like banks, exporters, and importers to facilitate financing solutions. Supply Chain Finance Officers work with procurement, logistics, and supplier relationship teams internally to optimize cash flow and payment terms, coordinating externally with suppliers, financiers, and logistics providers to streamline supply chain funding. Both roles require effective communication and coordination with diverse stakeholders to manage risks, enhance liquidity, and support business growth.
Regulatory Compliance and Documentation
Trade Finance Officers ensure regulatory compliance by meticulously verifying letters of credit, guarantees, and export-import documentation to mitigate legal risks and adhere to international trade laws. Supply Chain Finance Officers focus on maintaining transparency in financing agreements and compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations while managing vendor payment terms and transactional documents. Both roles require expertise in trade regulations such as UCP 600 and Basel III to ensure documentation accuracy and regulatory adherence in cross-border financial operations.
Career Progression and Opportunities
Trade Finance Officers typically advance by gaining expertise in international trade regulations, risk assessment, and financing instruments, leading to roles such as Senior Trade Finance Manager or Head of Trade Finance. Supply Chain Finance Officers progress by specializing in optimizing working capital and financing solutions across supply chains, with career opportunities in strategic sourcing, vendor financing, and supply chain strategy roles. Both career paths offer growth in financial institutions, with expanding opportunities in global trade, fintech innovations, and integrated supply chain ecosystems.
Impact on Business Performance
A Trade Finance Officer enhances business performance by optimizing international trade transactions, ensuring smoother cash flow, and mitigating risks related to letters of credit, guarantees, and import/export financing. A Supply Chain Finance Officer improves operational efficiency by streamlining payables and receivables processes, reducing working capital requirements, and strengthening supplier relationships through tailored financing solutions. Both roles drive liquidity and reduce financial costs but focus on different stages of the trade cycle, with trade finance officers emphasizing transaction security and supply chain finance officers focusing on supply chain liquidity management.
Skills Transferability Between Roles
Trade Finance Officers and Supply Chain Finance Officers both require strong analytical skills, risk assessment capabilities, and expertise in financial instruments, enabling a significant transfer of skills between roles. Knowledge of trade regulations, letters of credit, and invoice financing is essential in both positions, facilitating smooth adaptability. Proficiency in stakeholder communication and negotiation further enhances the versatility of professionals moving between these finance specializations.
Trade Finance Officer vs Supply Chain Finance Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com