Facilities maintenance involves the upkeep of building structures, including plumbing, electrical systems, and HVAC units, ensuring a safe and functional environment. Equipment maintenance focuses specifically on machinery and tools used in operations, aiming to prevent breakdowns and extend service life. Both types of maintenance are crucial for operational efficiency but require distinct strategies and expertise tailored to their respective components.
Table of Comparison
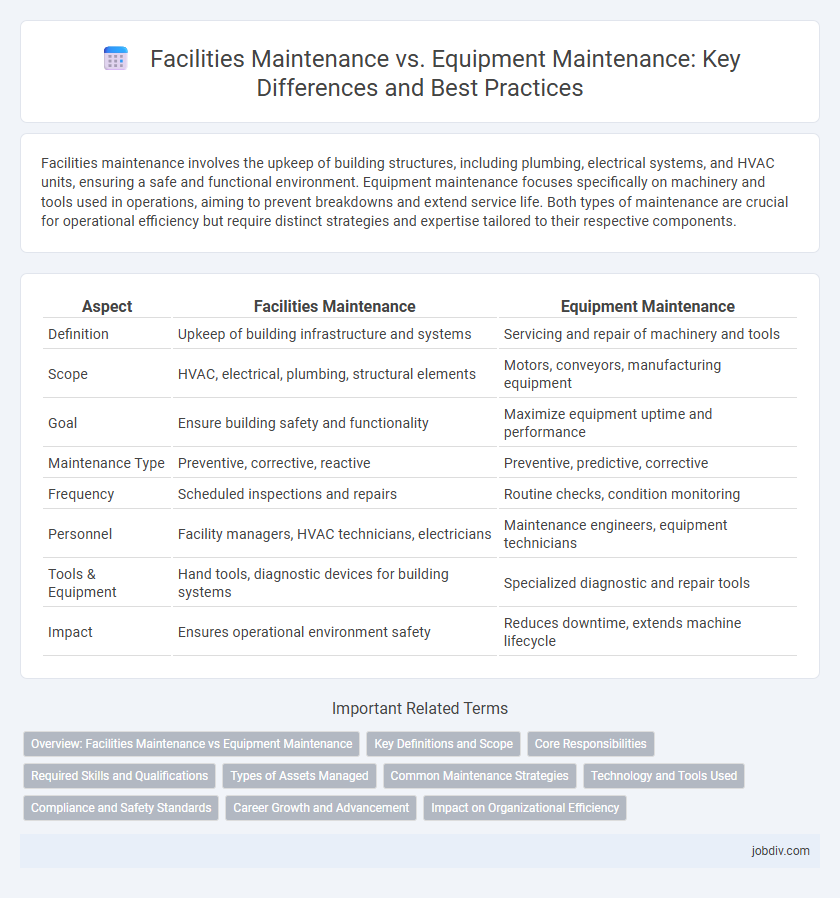
| Aspect | Facilities Maintenance | Equipment Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Upkeep of building infrastructure and systems | Servicing and repair of machinery and tools |
| Scope | HVAC, electrical, plumbing, structural elements | Motors, conveyors, manufacturing equipment |
| Goal | Ensure building safety and functionality | Maximize equipment uptime and performance |
| Maintenance Type | Preventive, corrective, reactive | Preventive, predictive, corrective |
| Frequency | Scheduled inspections and repairs | Routine checks, condition monitoring |
| Personnel | Facility managers, HVAC technicians, electricians | Maintenance engineers, equipment technicians |
| Tools & Equipment | Hand tools, diagnostic devices for building systems | Specialized diagnostic and repair tools |
| Impact | Ensures operational environment safety | Reduces downtime, extends machine lifecycle |
Overview: Facilities Maintenance vs Equipment Maintenance
Facilities maintenance encompasses the upkeep and management of building systems, structural components, and common areas to ensure safety, functionality, and compliance with regulations. Equipment maintenance involves the inspection, repair, and servicing of machinery and tools to optimize performance and prevent downtime. Both types of maintenance are critical for operational efficiency, with facilities focusing on the environment and infrastructure, while equipment maintenance targets mechanical and electrical assets.
Key Definitions and Scope
Facilities maintenance encompasses the upkeep and repair of the physical infrastructure, including buildings, HVAC systems, plumbing, and electrical layouts, ensuring a safe and functional environment. Equipment maintenance targets machinery and tools used in operations, focusing on preventing breakdowns and extending the lifespan through regular inspections, lubrication, calibration, and part replacements. Both maintenance types are critical for operational efficiency but differ in scope, with facilities maintenance addressing structural integrity and environmental conditions, while equipment maintenance concentrates on mechanical performance and reliability.
Core Responsibilities
Facilities maintenance primarily focuses on the upkeep of building structures, including HVAC systems, electrical wiring, plumbing, and overall cleanliness to ensure a safe and functional environment. Equipment maintenance centers on inspecting, repairing, and servicing machinery and technical tools to maximize performance and prevent breakdowns. Both disciplines require scheduled inspections, preventive measures, and prompt corrective actions to sustain operational efficiency.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Facilities maintenance requires skills in HVAC systems, plumbing, electrical work, and building inspections, with qualifications typically including certifications in building management or relevant technical training. Equipment maintenance demands expertise in mechanical systems, troubleshooting, and repair techniques, often necessitating technical diplomas or certifications such as CMRP (Certified Maintenance & Reliability Professional). Both roles benefit from strong problem-solving abilities, safety knowledge, and experience with maintenance management software.
Types of Assets Managed
Facilities maintenance primarily manages physical infrastructure assets such as buildings, HVAC systems, electrical installations, and plumbing networks. Equipment maintenance focuses on operational machinery and tools, including manufacturing equipment, vehicles, and production line devices. Both types require specialized strategies to ensure asset longevity, reliability, and optimal performance.
Common Maintenance Strategies
Facilities maintenance primarily involves preventive strategies such as routine inspections, cleaning, and repairs to ensure building systems operate efficiently and safely. Equipment maintenance emphasizes predictive approaches using condition monitoring and performance data to prevent unexpected failures and optimize machinery lifespan. Both maintenance types benefit from integrated computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) to schedule tasks, track work orders, and analyze maintenance performance metrics.
Technology and Tools Used
Facilities maintenance relies heavily on building management systems (BMS), computer-aided facility management (CAFM) software, and IoT sensors to monitor HVAC, lighting, and structural components efficiently. Equipment maintenance utilizes predictive maintenance tools, such as vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) to track machine performance and schedule repairs. Both domains increasingly adopt AI-driven analytics and mobile applications to optimize maintenance workflows and reduce downtime.
Compliance and Safety Standards
Facilities maintenance ensures that buildings and infrastructure comply with safety codes, fire regulations, and environmental standards, reducing hazards and legal risks. Equipment maintenance focuses on the regular inspection, calibration, and repair of machinery to meet industry compliance requirements and prevent accidents. Both play critical roles in maintaining operational safety and adhering to regulatory frameworks.
Career Growth and Advancement
Facilities maintenance focuses on managing building operations and infrastructure, offering career advancement through roles such as facilities manager or operations director. Equipment maintenance specializes in machinery upkeep and troubleshooting, leading to opportunities like maintenance engineer or reliability specialist. Both paths provide strong career growth, with increasing demand for technical skills and leadership in industrial and commercial sectors.
Impact on Organizational Efficiency
Facilities maintenance ensures the physical environment, such as buildings and utilities, operates smoothly, directly affecting employee comfort and safety. Equipment maintenance focuses on machinery and tools, preventing unexpected breakdowns and prolonging asset lifespan, which reduces downtime. Together, optimizing both maintenance types significantly enhances overall organizational efficiency and productivity.
Facilities Maintenance vs Equipment Maintenance Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com