Predictive analytics in maintenance uses data-driven models to forecast equipment failures and anticipate maintenance needs, reducing unexpected downtime. Prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending specific actions to optimize maintenance schedules and resource allocation based on those predictions. Combining these approaches improves decision-making efficiency and extends asset life in industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
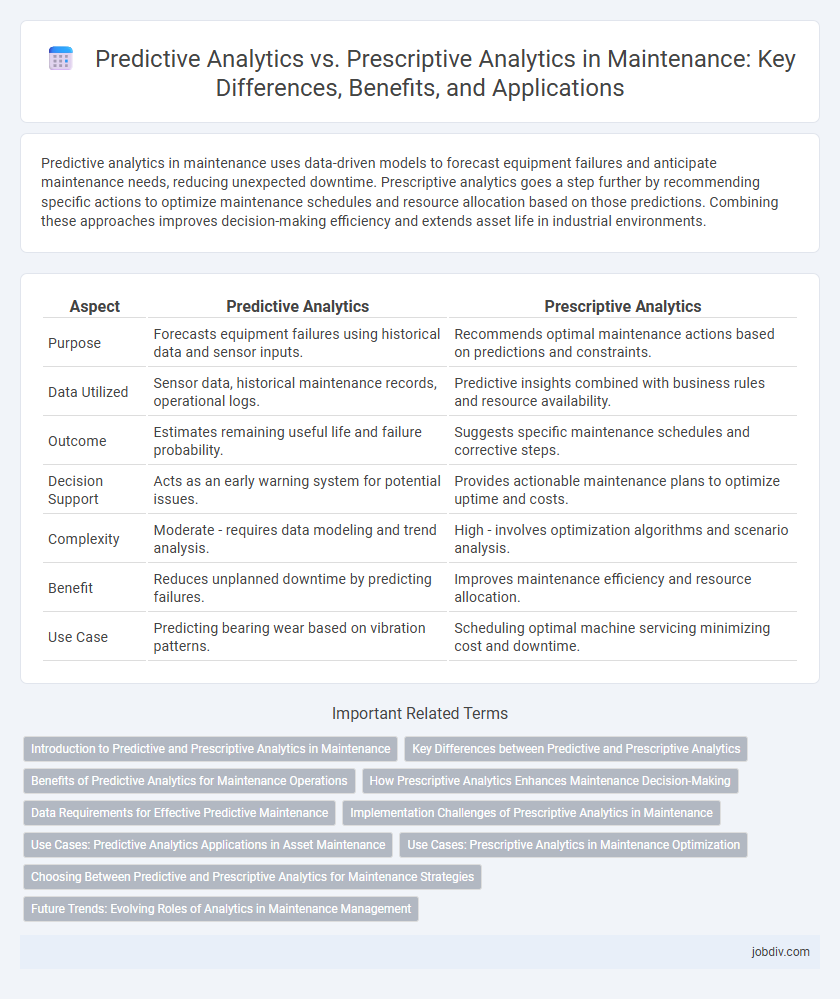
| Aspect | Predictive Analytics | Prescriptive Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Forecasts equipment failures using historical data and sensor inputs. | Recommends optimal maintenance actions based on predictions and constraints. |
| Data Utilized | Sensor data, historical maintenance records, operational logs. | Predictive insights combined with business rules and resource availability. |
| Outcome | Estimates remaining useful life and failure probability. | Suggests specific maintenance schedules and corrective steps. |
| Decision Support | Acts as an early warning system for potential issues. | Provides actionable maintenance plans to optimize uptime and costs. |
| Complexity | Moderate - requires data modeling and trend analysis. | High - involves optimization algorithms and scenario analysis. |
| Benefit | Reduces unplanned downtime by predicting failures. | Improves maintenance efficiency and resource allocation. |
| Use Case | Predicting bearing wear based on vibration patterns. | Scheduling optimal machine servicing minimizing cost and downtime. |
Introduction to Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics in Maintenance
Predictive analytics in maintenance uses historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures and maintenance needs, enabling timely interventions that minimize downtime. Prescriptive analytics builds upon these predictions by suggesting optimal maintenance actions based on cost, risk, and resource constraints, improving decision-making processes. Integrating both approaches enhances asset reliability and operational efficiency through data-driven maintenance strategies.
Key Differences between Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
Predictive analytics in maintenance focuses on forecasting equipment failures and downtime by analyzing historical data and identifying patterns to enable timely interventions. Prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending specific maintenance actions and resource allocations based on real-time data and predictive insights to optimize operational efficiency. The key difference lies in predictive analytics providing forecasts, while prescriptive analytics delivers actionable strategies to prevent failures and improve maintenance outcomes.
Benefits of Predictive Analytics for Maintenance Operations
Predictive analytics in maintenance operations enables early identification of equipment failures by analyzing historical data and real-time sensor inputs, reducing unplanned downtime and maintenance costs. This data-driven approach improves asset reliability and extends machinery lifespan through timely interventions. Organizations leveraging predictive analytics enhance operational efficiency by optimizing maintenance schedules and resource allocation based on forecasted equipment health.
How Prescriptive Analytics Enhances Maintenance Decision-Making
Prescriptive analytics enhances maintenance decision-making by recommending specific actions based on predictive insights and real-time data, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing downtime. It integrates machine learning algorithms and optimization models to suggest the most effective maintenance schedules, spare parts inventory management, and failure prevention strategies. This approach supports proactive decision-making, leading to increased equipment reliability and reduced operational costs.
Data Requirements for Effective Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance relies heavily on historical equipment data, sensor readings, and real-time operational metrics to forecast potential failures and optimize maintenance schedules. Effective predictive analytics requires large volumes of high-quality, time-stamped data for accurate model training and anomaly detection. In contrast, prescriptive analytics combines these data inputs with simulation algorithms and optimization techniques to recommend specific maintenance actions, demanding more complex datasets integrating both operational data and decision-making parameters.
Implementation Challenges of Prescriptive Analytics in Maintenance
Implementing prescriptive analytics in maintenance faces challenges such as integrating complex algorithms with existing legacy systems and ensuring data quality across diverse equipment. The need for real-time data processing and accurate predictive models intensifies computational demands, often straining IT infrastructure. Moreover, interpreting prescriptive recommendations requires specialized expertise, increasing training costs and complicating decision-making processes.
Use Cases: Predictive Analytics Applications in Asset Maintenance
Predictive analytics in asset maintenance leverages historical and real-time data to forecast equipment failures and schedule timely interventions, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Use cases include vibration analysis for early detection of mechanical issues, temperature monitoring to prevent overheating, and oil quality assessment to anticipate lubrication failures. This proactive approach enables maintenance teams to optimize asset performance and extend equipment lifespan through data-driven decision-making.
Use Cases: Prescriptive Analytics in Maintenance Optimization
Prescriptive analytics in maintenance optimization leverages real-time data and machine learning algorithms to recommend specific maintenance actions, reducing downtime and extending asset lifespan. Use cases include optimizing maintenance schedules, dynamically allocating resources, and automating decision-making processes to prevent equipment failures. This approach enhances operational efficiency by transforming predictive insights into actionable strategies that minimize costs and improve system reliability.
Choosing Between Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics for Maintenance Strategies
Predictive analytics in maintenance leverages historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules, reducing unexpected downtime. Prescriptive analytics builds on predictions by recommending specific maintenance actions based on cost, risk, and operational priorities, enabling proactive decision-making. Choosing between predictive and prescriptive analytics depends on an organization's maturity, data quality, and strategic goals, with prescriptive analytics offering greater value for complex assets requiring optimized maintenance interventions.
Future Trends: Evolving Roles of Analytics in Maintenance Management
Predictive analytics in maintenance leverages historical and real-time data to forecast equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules, reducing downtime and costs. Prescriptive analytics advances this approach by recommending specific actions based on predictive insights, enabling dynamic decision-making and resource allocation. Future trends indicate increased integration of AI-driven prescriptive analytics with IoT sensors and digital twins, transforming maintenance management into a proactive, automated process enhancing operational efficiency.
Predictive Analytics vs Prescriptive Analytics (in maintenance context) Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com