Routine maintenance involves scheduled inspections and tasks designed to prevent equipment failures and extend the lifespan of assets, focusing on consistency and early issue detection. Corrective maintenance addresses unexpected breakdowns or malfunctions, requiring immediate repairs to restore functionality and minimize downtime. Balancing both approaches optimizes operational efficiency and reduces overall maintenance costs.
Table of Comparison
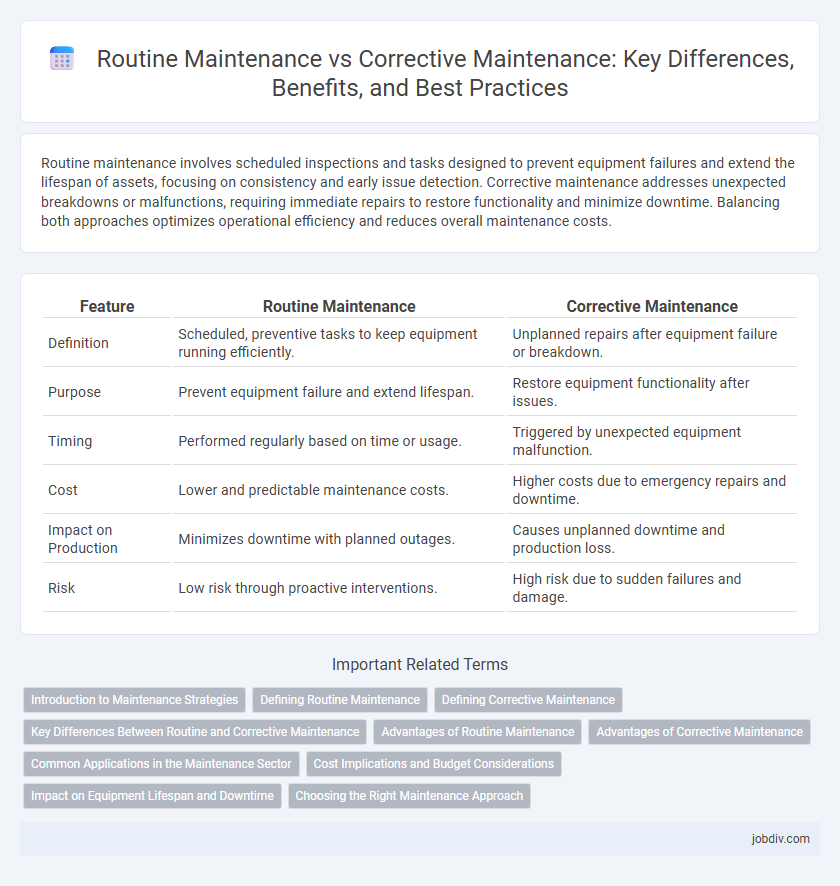
| Feature | Routine Maintenance | Corrective Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scheduled, preventive tasks to keep equipment running efficiently. | Unplanned repairs after equipment failure or breakdown. |
| Purpose | Prevent equipment failure and extend lifespan. | Restore equipment functionality after issues. |
| Timing | Performed regularly based on time or usage. | Triggered by unexpected equipment malfunction. |
| Cost | Lower and predictable maintenance costs. | Higher costs due to emergency repairs and downtime. |
| Impact on Production | Minimizes downtime with planned outages. | Causes unplanned downtime and production loss. |
| Risk | Low risk through proactive interventions. | High risk due to sudden failures and damage. |
Introduction to Maintenance Strategies
Routine maintenance involves scheduled inspections and servicing to prevent equipment failures, ensuring consistent operational efficiency. Corrective maintenance addresses unexpected breakdowns by repairing or replacing faulty components to restore functionality. Effective maintenance strategies balance these approaches to minimize downtime and extend asset lifespan.
Defining Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance consists of scheduled, preventive tasks designed to keep equipment operating efficiently and prevent unexpected breakdowns. This type of maintenance includes inspections, lubrication, adjustments, and component replacements performed at regular intervals. Implementing routine maintenance reduces downtime, extends equipment life, and lowers overall repair costs.
Defining Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance refers to the process of identifying, repairing, and restoring equipment or systems after a failure or malfunction has occurred. It aims to bring assets back to operational condition as quickly as possible to minimize downtime and prevent further damage. Unlike routine maintenance, which is scheduled and preventive, corrective maintenance is reactive and performed in response to unexpected issues.
Key Differences Between Routine and Corrective Maintenance
Routine maintenance involves scheduled, proactive tasks designed to prevent equipment failure and extend asset lifespan, such as lubrication, inspections, and part replacements. Corrective maintenance is reactive and performed after equipment malfunctions or failures occur, aiming to restore functionality as quickly as possible. The key difference lies in timing and approach: routine maintenance minimizes downtime through planned interventions, while corrective maintenance addresses unexpected breakdowns requiring urgent repair.
Advantages of Routine Maintenance
Routine maintenance enhances equipment reliability by preventing unexpected breakdowns and reducing downtime, which boosts overall operational efficiency. Regular inspections and timely interventions extend asset lifespan, lowering long-term repair costs and increasing return on investment. Consistent upkeep also ensures safety compliance and minimizes the risk of costly emergency repairs.
Advantages of Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance offers the advantage of addressing equipment failures promptly, minimizing downtime and preventing minor issues from escalating into costly repairs. It allows for targeted intervention only when problems arise, optimizing resource allocation and reducing unnecessary maintenance activities. This reactive approach can extend equipment lifespan by focusing efforts precisely where and when they are needed.
Common Applications in the Maintenance Sector
Routine maintenance involves scheduled inspections, lubrication, and part replacements to prevent equipment failure, commonly applied in manufacturing plants and HVAC systems. Corrective maintenance addresses unexpected breakdowns, often utilized in automotive repair shops and facility management to restore functionality after faults. Both approaches are integral in ensuring operational efficiency across industries such as utilities, transportation, and industrial production.
Cost Implications and Budget Considerations
Routine maintenance involves scheduled inspections and preventive actions that reduce unexpected breakdowns, resulting in lower long-term repair costs and more predictable budgeting. Corrective maintenance, performed after equipment failure, often leads to higher immediate expenses due to urgent repairs, increased downtime, and potential damage escalation. Budget considerations favor routine maintenance by enabling cost control through planned resources, whereas corrective maintenance requires flexible funds to address unexpected expenditures and operational disruptions.
Impact on Equipment Lifespan and Downtime
Routine maintenance extends equipment lifespan by preventing wear and detecting issues early, reducing unexpected failures and minimizing downtime. Corrective maintenance addresses problems after equipment breakdowns, often leading to longer downtime and accelerated component degradation. Prioritizing routine maintenance improves operational efficiency and reduces costs associated with unplanned repairs and equipment replacement.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Approach
Selecting the appropriate maintenance strategy depends on equipment criticality, operational impact, and cost-efficiency analysis. Routine maintenance prevents unexpected failures through scheduled inspections, while corrective maintenance addresses issues post-failure to minimize downtime. Balancing these approaches requires evaluating asset conditions and prioritizing tasks to optimize reliability and budget.
Routine Maintenance vs Corrective Maintenance Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com