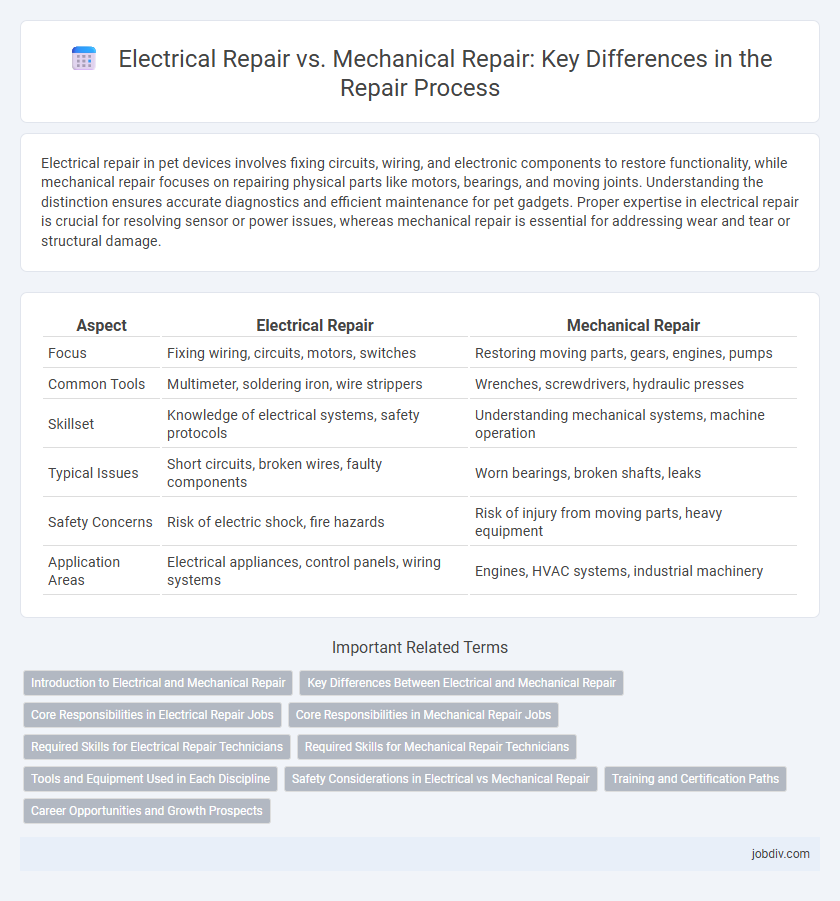
Electrical repair in pet devices involves fixing circuits, wiring, and electronic components to restore functionality, while mechanical repair focuses on repairing physical parts like motors, bearings, and moving joints. Understanding the distinction ensures accurate diagnostics and efficient maintenance for pet gadgets. Proper expertise in electrical repair is crucial for resolving sensor or power issues, whereas mechanical repair is essential for addressing wear and tear or structural damage.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Electrical Repair | Mechanical Repair |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Fixing wiring, circuits, motors, switches | Restoring moving parts, gears, engines, pumps |
| Common Tools | Multimeter, soldering iron, wire strippers | Wrenches, screwdrivers, hydraulic presses |
| Skillset | Knowledge of electrical systems, safety protocols | Understanding mechanical systems, machine operation |
| Typical Issues | Short circuits, broken wires, faulty components | Worn bearings, broken shafts, leaks |
| Safety Concerns | Risk of electric shock, fire hazards | Risk of injury from moving parts, heavy equipment |
| Application Areas | Electrical appliances, control panels, wiring systems | Engines, HVAC systems, industrial machinery |
Introduction to Electrical and Mechanical Repair
Electrical repair involves diagnosing and fixing issues related to electrical systems, circuits, and components such as wiring, switches, and motors, ensuring safe and efficient operation. Mechanical repair focuses on the maintenance and restoration of machines, engines, and mechanical parts, addressing wear-and-tear, alignment, and lubrication problems. Both disciplines require specialized tools and skills, but electrical repair emphasizes knowledge of electrical theory and safety standards, while mechanical repair centers on understanding mechanical systems and physical forces.
Key Differences Between Electrical and Mechanical Repair
Electrical repair involves diagnosing and fixing issues related to electrical systems, circuits, wiring, and components such as motors, switches, and control panels. Mechanical repair focuses on restoring mechanical parts like gears, bearings, engines, and hydraulic systems to proper function, often requiring physical adjustments or replacements. Key differences include the tools used, with electrical repair relying on multimeters and soldering equipment, while mechanical repair demands wrenches and machining tools, alongside distinct safety protocols for handling electricity versus moving mechanical parts.
Core Responsibilities in Electrical Repair Jobs
Core responsibilities in electrical repair jobs include diagnosing electrical faults, repairing or replacing wiring systems, circuit breakers, transformers, and electrical panels. Technicians ensure compliance with safety regulations and electrical codes while performing maintenance to prevent system failures. Proficiency in using diagnostic tools and interpreting electrical schematics is essential for effective troubleshooting and repair.
Core Responsibilities in Mechanical Repair Jobs
Mechanical repair jobs primarily involve diagnosing and fixing issues related to machinery and mechanical components, including engines, gearboxes, and hydraulic systems. Core responsibilities include disassembling, inspecting, cleaning, and reassembling mechanical parts to restore functionality and ensure optimal performance. Technicians also perform routine maintenance, troubleshoot mechanical failures, and use specialized tools and equipment to carry out repairs.
Required Skills for Electrical Repair Technicians
Electrical repair technicians require expertise in circuitry, wiring diagnostics, and the use of specialized testing equipment to troubleshoot and fix electrical systems safely. Proficiency in reading electrical schematics, understanding voltage and current principles, and knowledge of safety regulations are essential for effective and compliant repairs. These skills distinguish electrical repair from mechanical repair, which typically focuses on physical components and mechanical systems rather than electrical functionality.
Required Skills for Mechanical Repair Technicians
Mechanical repair technicians require expertise in diagnosing and troubleshooting complex machinery issues, including hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Proficiency in using precision measuring instruments, interpreting technical schematics, and performing hands-on equipment maintenance is essential. Strong problem-solving skills combined with knowledge of mechanical systems ensure effective repairs and minimal downtime in industrial environments.
Tools and Equipment Used in Each Discipline
Electrical repair primarily relies on specialized tools such as multimeters, wire strippers, soldering irons, and circuit testers to diagnose and fix electrical circuits and components. Mechanical repair utilizes equipment like torque wrenches, pliers, screwdrivers, hydraulic jacks, and pneumatic tools to address issues in engines, machinery, and mechanical systems. Both disciplines require safety gear, but electrical repair emphasizes insulated tools and voltage detectors to prevent electric shocks, whereas mechanical repair focuses on heavy-duty gear and impact wrenches to handle physical forces.
Safety Considerations in Electrical vs Mechanical Repair
Safety considerations in electrical repair emphasize the risk of electric shock, requiring the use of insulated tools, proper grounding, and adherence to lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental energization. Mechanical repair safety centers on preventing injuries from moving parts, employing guards, proper lifting techniques, and ensuring machinery is fully powered down to avoid unexpected startup. Both fields demand strict compliance with safety protocols and personal protective equipment to mitigate hazards unique to electrical and mechanical environments.
Training and Certification Paths
Electrical repair requires specialized training in circuitry, voltage handling, and safety protocols, often leading to certifications such as the Electrical Certified Professional (ECP) or Journeyman Electrician license. Mechanical repair demands knowledge of machinery, hydraulics, and mechanical systems, with certifications like Certified Mechanical Technician (CMT) or Automotive Service Excellence (ASE) credentials. Both paths emphasize hands-on experience, but electrical repair training prioritizes electrical codes and safety standards while mechanical repair focuses on diagnostics and mechanical components.
Career Opportunities and Growth Prospects
Electrical repair careers offer a broad range of opportunities in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and construction, driven by the increasing demand for skilled electricians proficient in modern technology and automation. Mechanical repair professions typically focus on maintaining and fixing machinery in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment, with growth prospects tied to advances in mechanical systems and renewable energy technologies. Both fields provide strong job stability and advancement potential, but electrical repair tends to experience faster growth due to the expanding reliance on electronic and computerized systems.
Electrical Repair vs Mechanical Repair Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com