A Trade Compliance Officer ensures that all international trade activities comply with legal regulations and company policies, minimizing risks related to customs, tariffs, and sanctions. In contrast, a Trade Operations Analyst focuses on optimizing trade processes by analyzing data, improving workflows, and supporting the logistics and documentation involved in trade transactions. Both roles are essential in facilitating smooth international trade but prioritize regulatory compliance versus operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
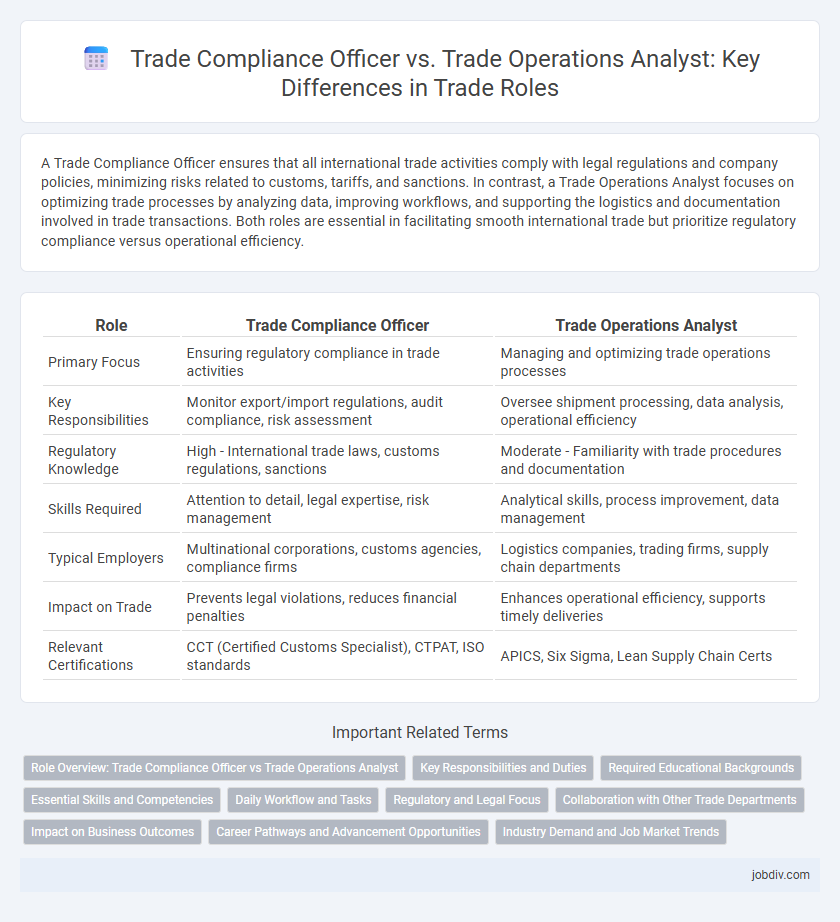
| Role | Trade Compliance Officer | Trade Operations Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Ensuring regulatory compliance in trade activities | Managing and optimizing trade operations processes |
| Key Responsibilities | Monitor export/import regulations, audit compliance, risk assessment | Oversee shipment processing, data analysis, operational efficiency |
| Regulatory Knowledge | High - International trade laws, customs regulations, sanctions | Moderate - Familiarity with trade procedures and documentation |
| Skills Required | Attention to detail, legal expertise, risk management | Analytical skills, process improvement, data management |
| Typical Employers | Multinational corporations, customs agencies, compliance firms | Logistics companies, trading firms, supply chain departments |
| Impact on Trade | Prevents legal violations, reduces financial penalties | Enhances operational efficiency, supports timely deliveries |
| Relevant Certifications | CCT (Certified Customs Specialist), CTPAT, ISO standards | APICS, Six Sigma, Lean Supply Chain Certs |
Role Overview: Trade Compliance Officer vs Trade Operations Analyst
A Trade Compliance Officer ensures adherence to international trade laws, regulations, and company policies to mitigate risks and avoid penalties, focusing on import/export compliance and documentation accuracy. A Trade Operations Analyst manages the workflow of trade transactions, optimizes supply chain processes, and analyzes data to improve operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Both roles are critical for seamless cross-border trade but differ in emphasis: compliance risk management versus operational performance analysis.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Trade Compliance Officers ensure adherence to international trade regulations by conducting risk assessments, managing import/export documentation, and implementing compliance programs to prevent violations and penalties. Trade Operations Analysts focus on optimizing trade processes through data analysis, monitoring transaction workflows, and coordinating with logistics to improve efficiency and reduce costs. While both roles support global trade functions, Compliance Officers emphasize regulatory oversight, whereas Operations Analysts prioritize process improvement and operational execution.
Required Educational Backgrounds
Trade Compliance Officers typically require a bachelor's degree in international trade, law, or business administration, with certifications such as Certified Customs Specialist (CCS) enhancing their expertise. Trade Operations Analysts often hold degrees in supply chain management, logistics, or finance, focusing on data analysis and operational efficiency within trade processes. Both roles benefit from knowledge of trade regulations, but compliance officers emphasize legal frameworks, while analysts prioritize analytical and operational skills.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Trade Compliance Officers require strong knowledge of international trade regulations, risk assessment, and compliance auditing to ensure adherence to legal standards and prevent violations. Trade Operations Analysts excel in data analysis, process optimization, and supply chain coordination, utilizing tools like ERP systems to enhance operational efficiency. Both roles demand effective communication, attention to detail, and problem-solving skills to manage complex trade activities and maintain regulatory compliance.
Daily Workflow and Tasks
A Trade Compliance Officer monitors and enforces adherence to international trade regulations, focusing on risk assessment, documentation review, and regulatory reporting to prevent legal violations. In contrast, a Trade Operations Analyst manages transaction processing, shipment tracking, and coordination between suppliers and logistics teams to ensure smooth supply chain flow. Both roles require detailed knowledge of trade laws and systems, but the Compliance Officer emphasizes regulatory compliance while the Analyst centers on operational efficiency.
Regulatory and Legal Focus
A Trade Compliance Officer ensures adherence to international trade laws, customs regulations, and corporate policies, minimizing legal risks and preventing penalties. In contrast, a Trade Operations Analyst focuses on the execution and optimization of trade processes, analyzing data to improve efficiency while supporting compliance efforts. Both roles require a strong understanding of regulatory frameworks, but the Compliance Officer prioritizes legal oversight, whereas the Operations Analyst emphasizes process improvement within regulatory boundaries.
Collaboration with Other Trade Departments
Trade Compliance Officers collaborate closely with legal, customs, and risk management teams to ensure adherence to international trade regulations and mitigate compliance risks. Trade Operations Analysts work alongside logistics, procurement, and finance departments to optimize trade processes and improve operational efficiency. Effective communication between these roles enhances regulatory compliance and streamlines cross-departmental trade functions.
Impact on Business Outcomes
Trade Compliance Officers ensure adherence to international trade laws and regulations, minimizing legal risks and preventing costly fines that impact financial stability. Trade Operations Analysts optimize trade processes by analyzing data and streamlining workflows, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs. Both roles contribute to improved business outcomes, with Compliance Officers safeguarding regulatory integrity and Analysts driving process improvements for smoother trade execution.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Trade Compliance Officers typically advance by gaining expertise in regulatory frameworks, moving into senior compliance roles or risk management positions within multinational corporations. Trade Operations Analysts often progress by developing strong analytical skills and operational knowledge, leading to roles such as trade operations manager or supply chain strategist. Both career pathways offer opportunities for specialization, with Compliance Officers focusing on legal adherence and Analysts on optimizing trade processes to enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
Trade Compliance Officers and Trade Operations Analysts are both critical in global trade, with increasing industry demand due to stricter international regulations and rising cross-border transactions. Trade Compliance Officers are sought for expertise in regulatory adherence and customs laws, driven by regulatory authorities and multinational corporations ensuring trade legality. Trade Operations Analysts see job market growth through demand for data analysis in supply chain optimization and operational efficiency, especially within logistics and import-export firms adapting to evolving trade policies.
Trade Compliance Officer vs Trade Operations Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com