Trade Policy Analysts evaluate and develop regulations affecting international commerce, ensuring alignment with economic goals and compliance with global agreements. Tariff Analysts specialize in assessing and interpreting tariff schedules, helping businesses optimize cost management and maintain competitiveness in global markets. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but Trade Policy Analysts offer a broader regulatory perspective while Tariff Analysts focus more narrowly on import/export duties and classification.
Table of Comparison
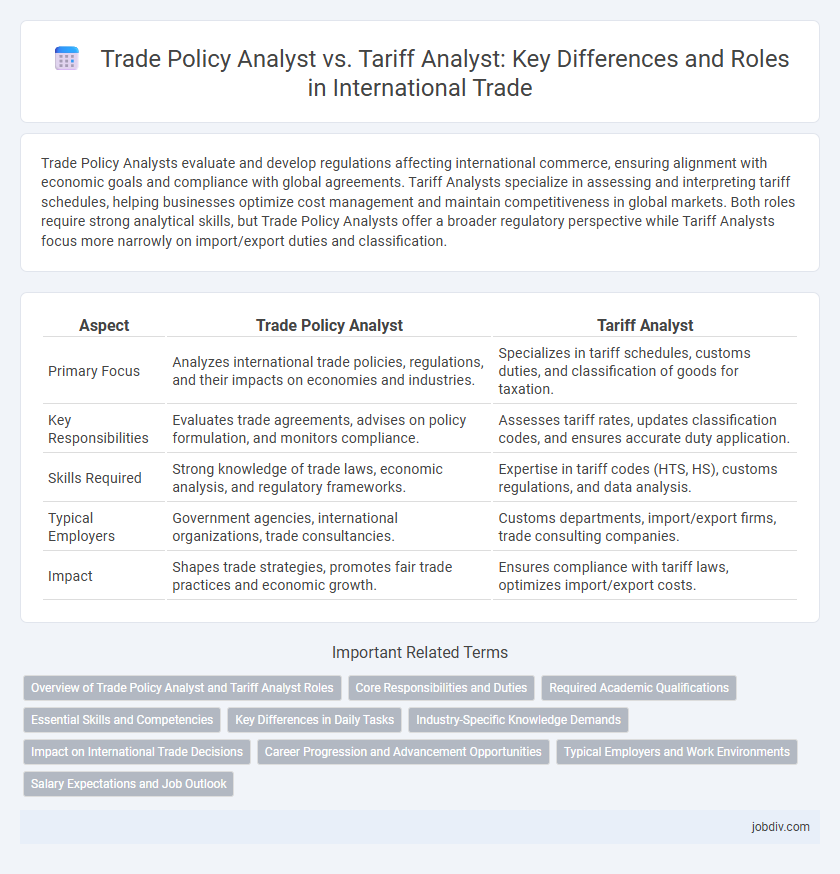
| Aspect | Trade Policy Analyst | Tariff Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Analyzes international trade policies, regulations, and their impacts on economies and industries. | Specializes in tariff schedules, customs duties, and classification of goods for taxation. |
| Key Responsibilities | Evaluates trade agreements, advises on policy formulation, and monitors compliance. | Assesses tariff rates, updates classification codes, and ensures accurate duty application. |
| Skills Required | Strong knowledge of trade laws, economic analysis, and regulatory frameworks. | Expertise in tariff codes (HTS, HS), customs regulations, and data analysis. |
| Typical Employers | Government agencies, international organizations, trade consultancies. | Customs departments, import/export firms, trade consulting companies. |
| Impact | Shapes trade strategies, promotes fair trade practices and economic growth. | Ensures compliance with tariff laws, optimizes import/export costs. |
Overview of Trade Policy Analyst and Tariff Analyst Roles
Trade Policy Analysts evaluate and develop regulations impacting international trade by analyzing economic data, government policies, and trade agreements to advise policymakers on tariff structures, market access, and compliance. Tariff Analysts specialize in classifying goods under harmonized tariff schedules, assessing duties, and ensuring correct tariff application to optimize cost efficiency and regulatory adherence for imports and exports. Both roles require expertise in trade laws, data interpretation, and strategic impact assessment to support companies and governments in navigating global trade landscapes.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
Trade Policy Analysts evaluate international trade agreements, economic data, and regulatory policies to advise on trade strategy and compliance. Tariff Analysts specialize in assessing tariff classifications, calculating duties, and advising on tariff impacts for imports and exports. Both roles require expertise in trade regulations, but Trade Policy Analysts focus more on policy development while Tariff Analysts concentrate on tariff application and cost analysis.
Required Academic Qualifications
A Trade Policy Analyst typically requires a bachelor's or master's degree in international trade, economics, or political science to analyze trade regulations and policies. A Tariff Analyst often holds a degree in economics, business, or law, specializing in tariff codes, compliance, and customs regulations. Both roles benefit from strong analytical skills and familiarity with international trade agreements and regulatory frameworks.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Trade Policy Analysts require deep understanding of international trade regulations, economic impact analysis, and policy formulation, along with strong research and communication skills to influence government and corporate strategies. Tariff Analysts specialize in tariff classification, customs regulations, and cost-benefit analysis of import-export duties, emphasizing precision in legal compliance and numeric data interpretation. Both roles demand proficiency in data analytics, attention to detail, and the ability to interpret complex trade documentation to ensure regulatory adherence and strategic decision-making.
Key Differences in Daily Tasks
Trade Policy Analysts primarily evaluate the impact of trade agreements, regulatory changes, and international trade laws to advise on policy formulation and compliance strategies. Tariff Analysts focus on classifying goods under the correct tariff codes, calculating duties, and ensuring adherence to customs regulations to optimize cost efficiency. While both roles require strong analytical skills, Trade Policy Analysts engage more with policy development and economic impact assessment, whereas Tariff Analysts emphasize operational accuracy and tariff-related data management.
Industry-Specific Knowledge Demands
Trade Policy Analysts require comprehensive understanding of international trade regulations, economic impacts, and geopolitical factors affecting multiple industries. Tariff Analysts specialize in detailed tariff schedules and customs regulations, with deep knowledge in specific sectors such as manufacturing or agriculture to assess tariff implications accurately. Industry-specific expertise enables both roles to tailor analysis and recommendations that align with sectoral trade dynamics and compliance requirements.
Impact on International Trade Decisions
Trade Policy Analysts evaluate government trade regulations and advise on compliance, shaping international agreements and market access strategies critical for businesses. Tariff Analysts specialize in examining tariff structures and customs duties to assess cost implications and optimize supply chain decisions across borders. Both roles influence international trade decisions by balancing regulatory frameworks and cost efficiencies to enhance competitive advantage in global markets.
Career Progression and Advancement Opportunities
Trade Policy Analysts typically engage in developing and evaluating trade regulations, shaping international trade agreements, and advising on policy impacts, which often leads to senior roles in government agencies or international organizations. Tariff Analysts specialize in classifying goods, determining tariff rates, and ensuring compliance with customs regulations, providing a pathway to positions in customs brokerage, trade compliance management, or tariff consultancy. Career advancement for Trade Policy Analysts often involves strategic policy leadership, while Tariff Analysts may progress toward operational management or specializing in global trade compliance sectors.
Typical Employers and Work Environments
Trade Policy Analysts typically work in government agencies, international organizations, and large multinational corporations, where they analyze and develop trade regulations and agreements. Tariff Analysts are often employed by import-export companies, customs brokerage firms, and logistics providers, focusing on classifying goods and calculating applicable tariffs. Both roles are commonly found in urban centers with strong trade activity, such as major port cities and financial hubs.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Trade Policy Analysts typically earn a median salary ranging from $70,000 to $100,000 per year, reflecting their expertise in developing and evaluating trade regulations. Tariff Analysts usually have a salary range between $60,000 and $85,000 annually, focusing primarily on assessing import duties and customs tariffs. The job outlook for both roles is positive, driven by increasing global trade complexity and the demand for specialists in trade compliance and regulatory policy.
Trade Policy Analyst vs Tariff Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com