A reinsurance broker specializes in placing risks from insurance companies with other insurers, facilitating complex risk transfer solutions that help primary insurers manage their exposure. Insurance brokers act as intermediaries between individual or commercial policyholders and insurance companies, helping clients find appropriate coverage tailored to their specific needs. Both play crucial roles in the insurance ecosystem, with reinsurance brokers focusing on risk distribution among insurers and insurance brokers concentrating on client policy placement and advice.
Table of Comparison
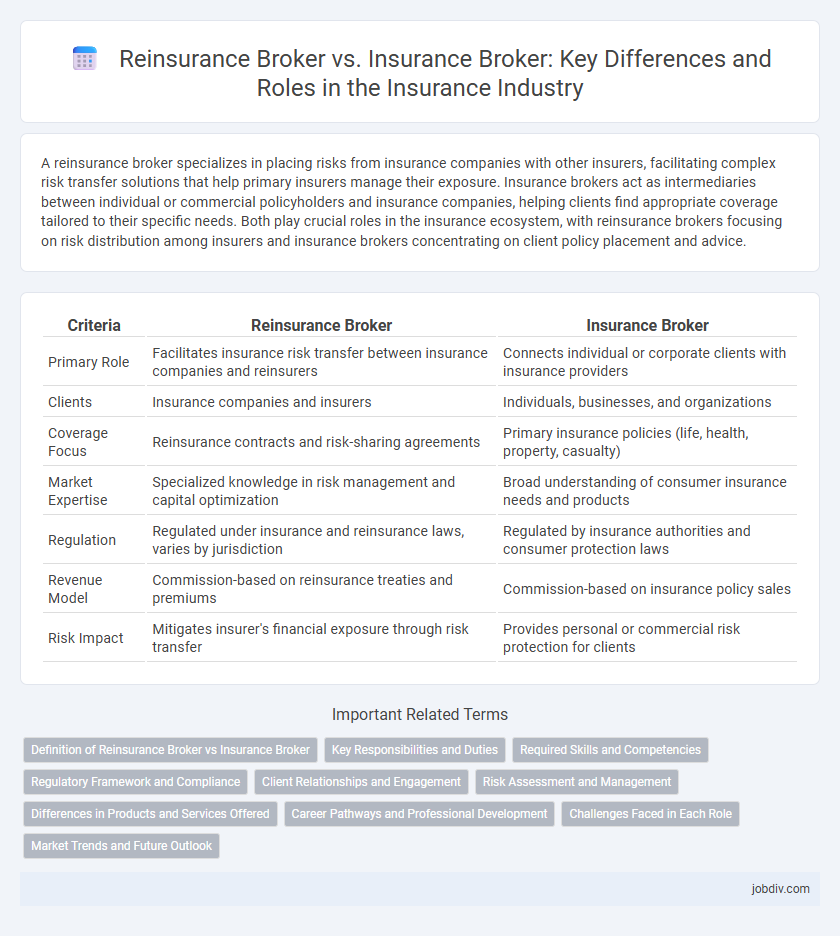
| Criteria | Reinsurance Broker | Insurance Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Facilitates insurance risk transfer between insurance companies and reinsurers | Connects individual or corporate clients with insurance providers |
| Clients | Insurance companies and insurers | Individuals, businesses, and organizations |
| Coverage Focus | Reinsurance contracts and risk-sharing agreements | Primary insurance policies (life, health, property, casualty) |
| Market Expertise | Specialized knowledge in risk management and capital optimization | Broad understanding of consumer insurance needs and products |
| Regulation | Regulated under insurance and reinsurance laws, varies by jurisdiction | Regulated by insurance authorities and consumer protection laws |
| Revenue Model | Commission-based on reinsurance treaties and premiums | Commission-based on insurance policy sales |
| Risk Impact | Mitigates insurer's financial exposure through risk transfer | Provides personal or commercial risk protection for clients |
Definition of Reinsurance Broker vs Insurance Broker
A reinsurance broker acts as an intermediary between insurance companies and reinsurance providers, facilitating the transfer of risk from insurers to reinsurers to enhance risk management and capital efficiency. In contrast, an insurance broker works directly with individuals or businesses to find, compare, and secure insurance policies from various insurers, tailoring coverage to meet client needs. Both brokers play crucial roles in the insurance market, with reinsurance brokers specializing in large-scale risk redistribution and insurance brokers focusing on client-specific insurance procurement.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Reinsurance brokers specialize in negotiating and placing reinsurance contracts that help insurance companies manage risk by transferring portions of their liabilities to other insurers. Insurance brokers focus on connecting individuals or businesses with suitable insurance policies, tailored to their specific coverage needs and financial situations. Both brokers analyze risk, advise clients, and facilitate contract agreements, but reinsurance brokers operate primarily between insurance companies, while insurance brokers serve end consumers directly.
Required Skills and Competencies
Reinsurance brokers must possess advanced analytical skills and deep knowledge of risk assessment, contract negotiation, and global insurance markets to effectively manage complex reinsurance treaties. Insurance brokers require strong interpersonal skills, client relationship management, and comprehensive understanding of diverse insurance products to tailor coverage solutions. Both roles demand expertise in regulatory compliance, market trends, and excellent communication abilities to facilitate transactions and secure optimal terms.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Reinsurance brokers operate under stringent regulatory frameworks that differ from those governing insurance brokers, primarily due to the complex nature of reinsurance contracts and risk transfer mechanisms. Compliance requirements for reinsurance brokers often include adherence to international regulations such as Solvency II, alongside local market rules, ensuring transparency and financial stability in large-scale risk management. Insurance brokers, conversely, focus on consumer protection laws and licensing standards designed to safeguard policyholders and maintain market integrity within primary insurance transactions.
Client Relationships and Engagement
Reinsurance brokers specialize in managing complex risk portfolios by connecting insurance companies with reinsurers, fostering strategic partnerships that emphasize risk transfer efficiency and long-term financial stability. Insurance brokers engage directly with individual or commercial clients, tailoring coverage solutions to meet specific needs while maintaining personal client relationships and ongoing service. Both roles require strong communication skills, but reinsurance brokers focus more on industry-wide risk management, whereas insurance brokers prioritize personalized client engagement and trust-building.
Risk Assessment and Management
Reinsurance brokers specialize in transferring and mitigating large-scale risks by placing portions of insurance portfolios with other insurers, enhancing overall risk management for primary insurers. Insurance brokers focus on assessing individual client risks and securing tailored insurance policies that provide the best coverage at competitive rates. Effective risk assessment by reinsurance brokers involves analyzing portfolio-wide exposure while insurance brokers prioritize detailed evaluations of personal or business-specific risks.
Differences in Products and Services Offered
Reinsurance brokers specialize in placing large-scale risks with reinsurance companies, offering services such as risk assessment, treaty negotiation, and portfolio management to insurance companies. Insurance brokers primarily serve individual and commercial clients by providing access to various insurance products like health, auto, property, and liability coverage, focusing on policy comparison and client support. The key difference lies in their target customers and the complexity of products: reinsurance brokers deal with transferring risk at the insurer level, while insurance brokers manage direct client insurance needs.
Career Pathways and Professional Development
A reinsurance broker specializes in placing risks between insurance companies, requiring advanced knowledge of underwriting and risk assessment, often leading to senior roles in risk management or actuarial consulting. Insurance brokers directly work with clients to find suitable insurance policies, emphasizing sales skills and product expertise, with career progression typically moving towards agency management or underwriting. Both pathways demand continuous professional development through certifications like Chartered Insurance Broker (CIB) or Associate in Reinsurance (ARe) to enhance expertise and career advancement.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Reinsurance brokers navigate complex risk assessment challenges and must secure coverage for large, often high-risk portfolios, demanding deep market knowledge and negotiation skills. Insurance brokers confront difficulties in matching diverse client needs with suitable policies while managing regulatory compliance and fluctuating market conditions. Both roles require maintaining strong relationships and adapting swiftly to industry changes to effectively serve their clients.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Reinsurance brokers specialize in placing large-scale risk portfolios with reinsurers, facilitating risk transfer in global insurance markets experiencing growth driven by increased natural disasters and regulatory changes. Insurance brokers focus on retail and commercial client needs, leveraging digital platforms to enhance customer engagement and streamline policy management amid rising demand for personalized coverage. Future market trends indicate a convergence of technology adoption, with reinsurance brokers integrating data analytics and AI to optimize risk assessment, while insurance brokers expand telematics and IoT solutions to improve underwriting precision and client retention.
Reinsurance Broker vs Insurance Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com