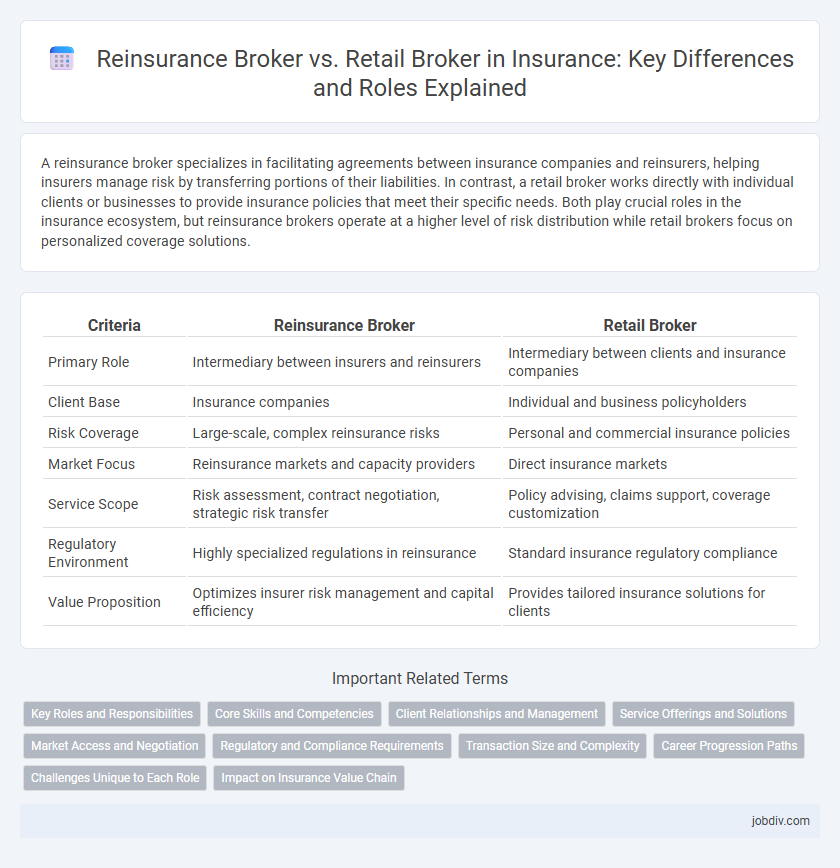
A reinsurance broker specializes in facilitating agreements between insurance companies and reinsurers, helping insurers manage risk by transferring portions of their liabilities. In contrast, a retail broker works directly with individual clients or businesses to provide insurance policies that meet their specific needs. Both play crucial roles in the insurance ecosystem, but reinsurance brokers operate at a higher level of risk distribution while retail brokers focus on personalized coverage solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Reinsurance Broker | Retail Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Intermediary between insurers and reinsurers | Intermediary between clients and insurance companies |
| Client Base | Insurance companies | Individual and business policyholders |
| Risk Coverage | Large-scale, complex reinsurance risks | Personal and commercial insurance policies |
| Market Focus | Reinsurance markets and capacity providers | Direct insurance markets |
| Service Scope | Risk assessment, contract negotiation, strategic risk transfer | Policy advising, claims support, coverage customization |
| Regulatory Environment | Highly specialized regulations in reinsurance | Standard insurance regulatory compliance |
| Value Proposition | Optimizes insurer risk management and capital efficiency | Provides tailored insurance solutions for clients |
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Reinsurance brokers specialize in negotiating and placing insurance policies between primary insurers and reinsurers, managing risk transfer on a large scale and providing expertise in complex risk assessment. Retail brokers directly interact with individual clients or businesses, tailoring insurance solutions to meet specific coverage needs and advising on policy selection and claims support. Both play critical roles in the insurance ecosystem by facilitating risk management, but reinsurance brokers operate primarily at the institutional level while retail brokers focus on client-facing services.
Core Skills and Competencies
Reinsurance brokers require advanced analytical skills and in-depth knowledge of global risk markets to structure complex treaty and facultative reinsurance agreements effectively. Retail brokers excel in client relationship management, product knowledge, and personalized risk assessment to tailor insurance solutions for individuals and businesses. Both roles demand strong negotiation abilities and regulatory expertise but differ in market focus and technical specialization.
Client Relationships and Management
Reinsurance brokers specialize in managing complex, large-scale risk transfers between insurance companies, fostering strategic partnerships that enhance insurer capacity and risk diversification. Retail brokers focus on direct client relationships, providing personalized insurance solutions and ongoing policy management tailored to individual or business needs. Effective client relationship management in reinsurance involves negotiation and market expertise, while retail brokers emphasize customer service and trust to retain and grow their client base.
Service Offerings and Solutions
Reinsurance brokers specialize in structuring complex risk transfer solutions between insurance companies and reinsurers, offering services such as risk analytics, treaty negotiation, and portfolio optimization. Retail brokers provide personalized insurance policies directly to individuals and businesses, focusing on coverage selection, claims assistance, and policy management tailored to client needs. While reinsurance brokers operate at the wholesale level managing large-scale risk and capital strategies, retail brokers serve as the primary point of contact for end-users seeking customized insurance products.
Market Access and Negotiation
A reinsurance broker specializes in providing access to global reinsurance markets, leveraging extensive networks to negotiate terms with reinsurers on behalf of insurance companies. Retail brokers primarily serve insurance clients by accessing standard insurance markets, focusing on tailoring coverage and pricing to individual or business needs. The distinction lies in market access scope and negotiation complexity, with reinsurance brokers facilitating large-scale risk transfer and retail brokers managing direct insurance placement.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Reinsurance brokers operate under stricter regulatory frameworks due to the complexity and scale of reinsurance contracts, often requiring advanced licensing and adherence to international compliance standards such as Solvency II and the IAIS guidelines. Retail brokers, primarily dealing with direct insurance products for individuals and small businesses, face regulations tailored to consumer protection, including local licensing requirements and compliance with laws like the Insurance Distribution Directive (IDD) in the EU. Both types of brokers must implement robust anti-money laundering (AML) protocols and maintain transparency in client transactions, but reinsurance brokers typically manage higher regulatory scrutiny due to their involvement in large-scale risk transfer arrangements.
Transaction Size and Complexity
Reinsurance brokers handle larger transaction sizes and more complex insurance structures compared to retail brokers, who primarily manage smaller, straightforward policies for individual or commercial clients. The intricate nature of reinsurance contracts requires specialized knowledge and expertise to negotiate multilayered coverage and risk transfer solutions. Retail brokers focus on personalized service and routine claim management, whereas reinsurance brokers facilitate high-value, complex deals often involving multiple insurers and global markets.
Career Progression Paths
Reinsurance brokers specialize in facilitating risk transfer between insurance companies, offering a career path that emphasizes complex risk assessment, negotiation skills, and international market exposure. Retail brokers focus on client-facing roles, providing personalized insurance solutions and developing expertise in customer service, sales, and product knowledge. Career progression for reinsurance brokers often leads to senior advisory or underwriting roles, while retail brokers may advance into agency management or specialized consulting positions.
Challenges Unique to Each Role
Reinsurance brokers face the challenge of navigating complex risk transfer agreements and securing capacity from global reinsurers, often dealing with high-value, low-frequency risks. Retail brokers manage numerous client policies and must balance personalized coverage advice with regulatory compliance across diverse sectors. Both roles require deep market knowledge, but reinsurance brokers emphasize strategic risk placement while retail brokers prioritize client relationship management and policy customization.
Impact on Insurance Value Chain
Reinsurance brokers play a critical role in the insurance value chain by facilitating risk transfer between primary insurers and reinsurers, enabling insurers to manage large or complex risks and maintain solvency. Retail brokers act as intermediaries between policyholders and insurance companies, providing market access, risk assessment, and tailored coverage solutions that enhance customer satisfaction and drive policy uptake. The collaboration between reinsurance and retail brokers optimizes risk distribution, capital efficiency, and overall market stability within the insurance ecosystem.
Reinsurance Broker vs Retail Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com