A reinsurance broker specializes in facilitating agreements between insurance companies and reinsurers, helping insurers manage risk by transferring portions of their liabilities. In contrast, a primary broker works directly with clients to secure insurance policies that best fit their individual or business needs. Understanding the distinct roles and expertise of reinsurance brokers versus primary brokers is crucial for effective risk management and insurance coverage optimization.
Table of Comparison
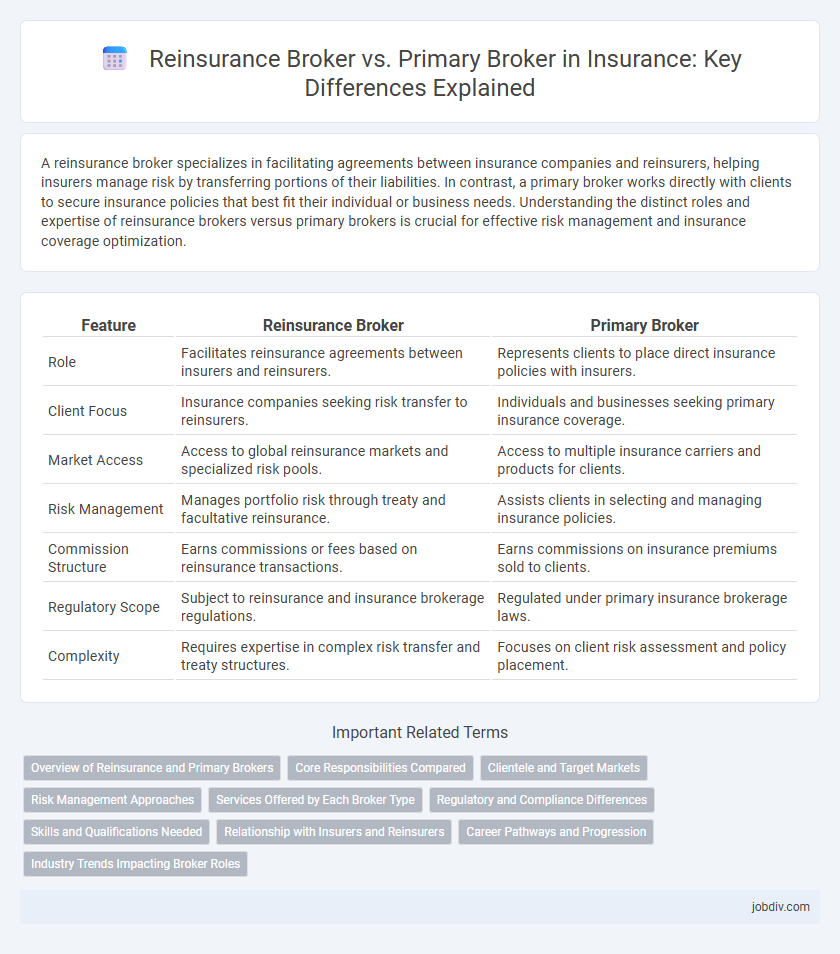
| Feature | Reinsurance Broker | Primary Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Facilitates reinsurance agreements between insurers and reinsurers. | Represents clients to place direct insurance policies with insurers. |
| Client Focus | Insurance companies seeking risk transfer to reinsurers. | Individuals and businesses seeking primary insurance coverage. |
| Market Access | Access to global reinsurance markets and specialized risk pools. | Access to multiple insurance carriers and products for clients. |
| Risk Management | Manages portfolio risk through treaty and facultative reinsurance. | Assists clients in selecting and managing insurance policies. |
| Commission Structure | Earns commissions or fees based on reinsurance transactions. | Earns commissions on insurance premiums sold to clients. |
| Regulatory Scope | Subject to reinsurance and insurance brokerage regulations. | Regulated under primary insurance brokerage laws. |
| Complexity | Requires expertise in complex risk transfer and treaty structures. | Focuses on client risk assessment and policy placement. |
Overview of Reinsurance and Primary Brokers
Reinsurance brokers specialize in facilitating agreements between insurance companies and reinsurers to manage risk exposure and optimize capital usage. Primary brokers work directly with individual clients, underwriting policies and placing coverage with insurance carriers based on personal and commercial insurance needs. Both roles require deep market knowledge, but reinsurance brokers operate at the corporate level, dealing with complex treaty and facultative reinsurance contracts.
Core Responsibilities Compared
Reinsurance brokers specialize in negotiating and arranging coverage between primary insurers and reinsurers, managing risk transfer to protect insurers from significant losses. Primary brokers focus on securing insurance policies for individual clients or businesses, tailoring coverage to specific needs and providing ongoing client support. Both play critical roles in the insurance ecosystem, with reinsurance brokers addressing risk aggregation while primary brokers concentrate on direct policy placement.
Clientele and Target Markets
Reinsurance brokers primarily serve insurance companies, focusing on large-scale risk transfer and capacity building in complex or high-risk markets. Primary brokers engage directly with individuals and businesses, targeting personal lines and commercial insurance markets to provide tailored coverage solutions. The clientele of reinsurance brokers consists mostly of insurers seeking risk mitigation, whereas primary brokers cater to end clients requiring customized insurance policies.
Risk Management Approaches
Reinsurance brokers specialize in transferring portions of risk from primary insurers to reinsurers, enhancing overall risk diversification and capital efficiency. Primary brokers focus on assessing client risk and securing appropriate insurance policies, emphasizing tailored coverage and direct risk mitigation. Efficient risk management integrates both brokers' expertise to optimize risk allocation and financial stability across the insurance value chain.
Services Offered by Each Broker Type
Reinsurance brokers specialize in structuring complex risk transfer solutions by facilitating agreements between primary insurers and reinsurers, offering services such as risk assessment, treaty negotiation, and portfolio analysis. Primary brokers primarily engage with clients to provide tailored insurance policies, risk management advice, and claims support, focusing on matching individual or corporate clients with appropriate coverage. Both broker types serve critical roles in the insurance ecosystem, with reinsurance brokers handling large-scale risk redistribution and primary brokers managing direct client relationships and policy servicing.
Regulatory and Compliance Differences
Reinsurance brokers operate under distinct regulatory frameworks compared to primary brokers, often requiring specific licenses due to the complex nature of global risk transfer transactions. Compliance mandates for reinsurance brokers emphasize transparency and adherence to international standards, including Solvency II in Europe and equivalent regulations worldwide. Primary brokers typically focus on direct client policy placement and are regulated primarily under local insurance laws, with compliance centered around consumer protection and market conduct.
Skills and Qualifications Needed
Reinsurance brokers require advanced expertise in risk assessment, contract negotiation, and global market dynamics, often holding professional certifications such as the Associate in Reinsurance (ARe) or Chartered Property Casualty Underwriter (CPCU). Primary brokers need strong client relationship management skills, proficiency in insurance product knowledge, and licensing specific to their jurisdiction, with qualifications like the Certified Insurance Counselor (CIC) enhancing their credibility. Both roles demand excellent analytical abilities and communication skills, but reinsurance brokers focus more on large-scale risk pooling and strategic placement.
Relationship with Insurers and Reinsurers
A reinsurance broker serves as an intermediary between insurers and reinsurers, facilitating risk transfer and negotiating terms to optimize coverage and pricing. Primary brokers work directly with clients to secure insurance policies from insurers, focusing on client needs and policy placement. The relationship of a reinsurance broker centers on specialized expertise in the reinsurance market, while primary brokers maintain close connections with insurers to manage client portfolios effectively.
Career Pathways and Progression
A career pathway for a reinsurance broker typically involves specialized knowledge in risk assessment, treaty structuring, and global market dynamics, often leading to roles such as reinsurance placement specialists or underwriting consultants. Primary brokers focus on direct client relationships, contract negotiation, and policy management, progressing into senior account executives or brokerage managers within retail insurance markets. Both pathways offer opportunities in leadership, but reinsurance careers demand deeper analytical expertise and international regulatory awareness.
Industry Trends Impacting Broker Roles
Reinsurance brokers specialize in negotiating and placing coverage between insurers and reinsurers, navigating complex risk portfolios, while primary brokers focus on securing insurance policies directly for clients. Industry trends such as increasing regulatory scrutiny, the rise of data analytics, and evolving risk landscapes are reshaping broker roles, demanding higher expertise in risk assessment and compliance from reinsurance brokers. Digital transformation and the growing importance of cyber risk are pushing both broker types to adopt advanced technologies to enhance client service and operational efficiency.
Reinsurance Broker vs Primary Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com