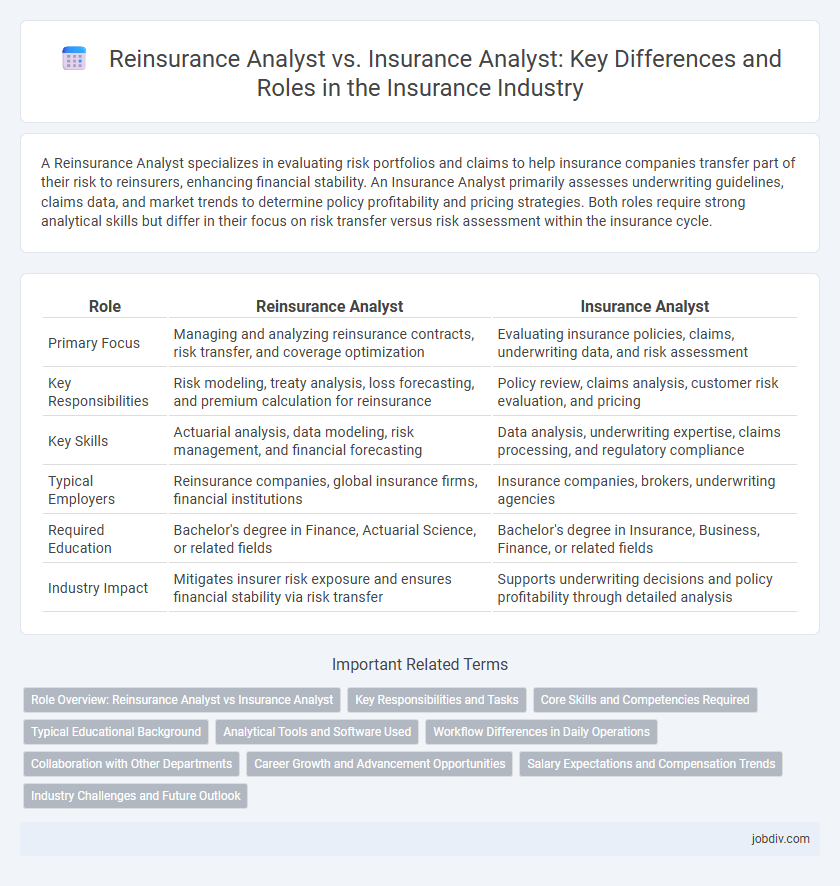
A Reinsurance Analyst specializes in evaluating risk portfolios and claims to help insurance companies transfer part of their risk to reinsurers, enhancing financial stability. An Insurance Analyst primarily assesses underwriting guidelines, claims data, and market trends to determine policy profitability and pricing strategies. Both roles require strong analytical skills but differ in their focus on risk transfer versus risk assessment within the insurance cycle.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Reinsurance Analyst | Insurance Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing and analyzing reinsurance contracts, risk transfer, and coverage optimization | Evaluating insurance policies, claims, underwriting data, and risk assessment |
| Key Responsibilities | Risk modeling, treaty analysis, loss forecasting, and premium calculation for reinsurance | Policy review, claims analysis, customer risk evaluation, and pricing |
| Key Skills | Actuarial analysis, data modeling, risk management, and financial forecasting | Data analysis, underwriting expertise, claims processing, and regulatory compliance |
| Typical Employers | Reinsurance companies, global insurance firms, financial institutions | Insurance companies, brokers, underwriting agencies |
| Required Education | Bachelor's degree in Finance, Actuarial Science, or related fields | Bachelor's degree in Insurance, Business, Finance, or related fields |
| Industry Impact | Mitigates insurer risk exposure and ensures financial stability via risk transfer | Supports underwriting decisions and policy profitability through detailed analysis |
Role Overview: Reinsurance Analyst vs Insurance Analyst
Reinsurance Analysts specialize in evaluating risk transfer between insurance companies and reinsurers, analyzing treaties and facultative agreements to optimize risk-sharing strategies. Insurance Analysts focus on assessing policy performance, underwriting data, and claims trends to improve client risk profiles and pricing accuracy. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but Reinsurance Analysts operate primarily in the secondary risk market, while Insurance Analysts concentrate on primary insurance products and direct customer portfolios.
Key Responsibilities and Tasks
A Reinsurance Analyst primarily evaluates and manages risk transfer agreements between insurance companies and reinsurers, analyzing complex contracts and monitoring financial exposures to ensure optimal risk distribution. An Insurance Analyst focuses on assessing policy performance, underwriting data, and claim trends to support pricing strategies and improve loss ratios within the insurance company. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but the Reinsurance Analyst specializes in external risk mitigation while the Insurance Analyst concentrates on internal risk assessment and policy management.
Core Skills and Competencies Required
A Reinsurance Analyst must excel in risk assessment, actuarial analysis, and contract interpretation to evaluate complex reinsurance treaties and financial exposures accurately. An Insurance Analyst requires strong underwriting knowledge, claims evaluation skills, and proficiency in regulatory compliance to ensure effective policy management and risk mitigation. Both roles demand advanced data analysis capabilities and attention to detail, but Reinsurance Analysts emphasize portfolio risk modeling while Insurance Analysts focus on customer-centered policy assessment.
Typical Educational Background
A Reinsurance Analyst typically holds a degree in finance, actuarial science, or risk management, emphasizing strong quantitative and analytical skills essential for assessing reinsurance contracts and risk exposures. In contrast, an Insurance Analyst often possesses a background in business administration, economics, or insurance studies, focusing on underwriting, claims analysis, and market trends. Both roles benefit from certifications such as the CPCU (Chartered Property Casualty Underwriter) or ARM (Associate in Risk Management) to enhance industry-specific knowledge and career advancement.
Analytical Tools and Software Used
Reinsurance Analysts commonly utilize specialized tools such as AIR Worldwide and RMS for catastrophe modeling and risk assessment, while Insurance Analysts often rely on platforms like Guidewire and SAS for claims management and underwriting analytics. Both roles leverage advanced Excel functions, SQL databases, and statistical software like R or Python for data analysis and predictive modeling. The key distinction lies in the reinsurance focus on catastrophe and portfolio risk modeling, compared to the insurance sector's emphasis on policy pricing, claims trends, and customer data analytics.
Workflow Differences in Daily Operations
Reinsurance analysts primarily focus on assessing and managing risk transfer processes between insurance companies, analyzing reinsurance contracts, and monitoring ceded premium and claims data to optimize risk distribution. Insurance analysts concentrate on underwriting support, claims evaluation, policy pricing, and customer risk assessments within primary insurance operations. Workflow differences largely stem from the reinsurance analyst's emphasis on contract scrutiny and external risk distribution, while insurance analysts engage more deeply in day-to-day policyholder risk evaluation and operational data analysis.
Collaboration with Other Departments
Reinsurance Analysts collaborate closely with underwriting, claims, and finance departments to assess risk transfer strategies and ensure optimal reinsurance coverage aligns with company objectives. Insurance Analysts work alongside underwriting, sales, and actuarial teams to analyze policy performance, pricing, and customer data for accurate risk evaluation and product development. Effective cooperation between reinsurance and insurance analysts enhances data sharing, risk assessment accuracy, and financial stability across the organization.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Reinsurance analysts focus on evaluating risks and financial data related to reinsurance contracts, offering specialized expertise that can lead to advanced positions in risk management or underwriting within global insurance firms. Insurance analysts assess broader insurance products and claims, providing a solid foundation for roles in underwriting, claims management, or insurance product development. Career growth for reinsurance analysts often involves niche opportunities in catastrophe modeling and treaty negotiation, while insurance analysts may progress toward leadership roles in policy design and regulatory compliance.
Salary Expectations and Compensation Trends
Reinsurance analysts typically command higher salary expectations due to their specialized expertise in managing risk transfer and underwriting complex portfolios, with average annual compensation ranging from $80,000 to $120,000. Insurance analysts tend to earn between $65,000 and $90,000, reflecting broader market analysis and claims evaluation responsibilities. Compensation trends indicate increasing demand for reinsurance analysts driven by global risk exposure, pushing salary growth above general insurance analyst roles.
Industry Challenges and Future Outlook
Reinsurance analysts face complex challenges such as evaluating large-scale risks and navigating fluctuating global markets, whereas insurance analysts concentrate on underwriting accuracy and claims forecasting within more localized contexts. Both roles require advanced data analytics skills, but reinsurance analysts must integrate macroeconomic trends and catastrophic event models to manage portfolio risks effectively. The future outlook indicates increasing reliance on artificial intelligence and predictive modeling to enhance risk assessment and decision-making in both reinsurance and insurance sectors.
Reinsurance Analyst vs Insurance Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com