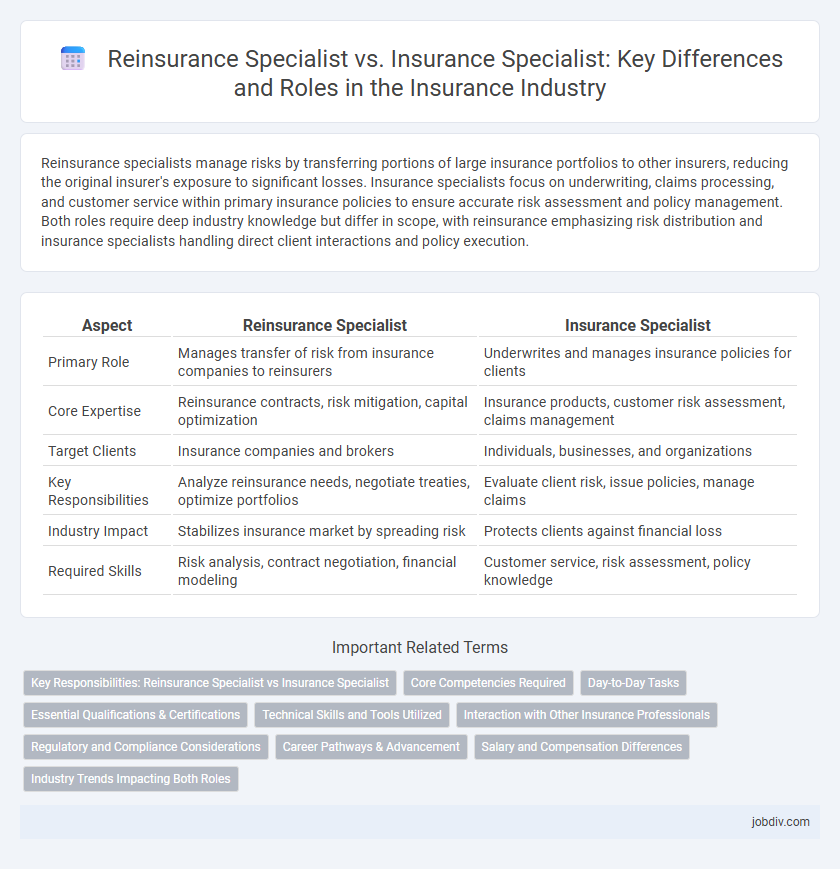
Reinsurance specialists manage risks by transferring portions of large insurance portfolios to other insurers, reducing the original insurer's exposure to significant losses. Insurance specialists focus on underwriting, claims processing, and customer service within primary insurance policies to ensure accurate risk assessment and policy management. Both roles require deep industry knowledge but differ in scope, with reinsurance emphasizing risk distribution and insurance specialists handling direct client interactions and policy execution.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reinsurance Specialist | Insurance Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manages transfer of risk from insurance companies to reinsurers | Underwrites and manages insurance policies for clients |
| Core Expertise | Reinsurance contracts, risk mitigation, capital optimization | Insurance products, customer risk assessment, claims management |
| Target Clients | Insurance companies and brokers | Individuals, businesses, and organizations |
| Key Responsibilities | Analyze reinsurance needs, negotiate treaties, optimize portfolios | Evaluate client risk, issue policies, manage claims |
| Industry Impact | Stabilizes insurance market by spreading risk | Protects clients against financial loss |
| Required Skills | Risk analysis, contract negotiation, financial modeling | Customer service, risk assessment, policy knowledge |
Key Responsibilities: Reinsurance Specialist vs Insurance Specialist
Reinsurance Specialists manage risk transfer by negotiating and structuring reinsurance contracts, analyzing ceded premiums, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, whereas Insurance Specialists focus on underwriting policies, assessing client risk profiles, and processing claims to maintain profitability and customer satisfaction. Reinsurance Specialists often work with actuaries and legal teams to optimize risk pools and capital efficiency, while Insurance Specialists collaborate directly with clients and agents to tailor coverage solutions. The distinction lies in the Reinsurance Specialist's role in mitigating insurer exposure through strategic partnerships, compared to the Insurance Specialist's role in frontline policy management and claims adjudication.
Core Competencies Required
Reinsurance specialists possess core competencies in risk assessment, contract negotiation, and treaty management, enabling them to effectively mitigate large-scale risks through strategic partnerships with other insurers. Insurance specialists excel in underwriting, claims processing, and customer service, focusing on individual policyholder needs and regulatory compliance. Both roles demand strong analytical skills, industry knowledge, and proficiency in data analysis software to optimize risk management and operational efficiency.
Day-to-Day Tasks
Reinsurance Specialists manage risk transfer by negotiating and structuring reinsurance agreements, analyzing treaty terms, and conducting loss reserve reviews to protect the insurer's financial stability. Insurance Specialists focus on underwriting policies, assessing client risk profiles, processing claims, and ensuring compliance with regulatory guidelines. Their daily activities diverge as Reinsurance Specialists handle complex risk-sharing arrangements, whereas Insurance Specialists concentrate on policy issuance and direct customer interactions.
Essential Qualifications & Certifications
Reinsurance Specialists typically require advanced knowledge of risk assessment, underwriting, and contract negotiation, supported by certifications such as the Associate in Reinsurance (ARe) designation. Insurance Specialists often hold credentials like the Chartered Property Casualty Underwriter (CPCU) or Associate in Risk Management (ARM) that emphasize comprehensive understanding of insurance policies and claims management. Essential qualifications for both roles include proficiency in actuarial analysis, regulatory compliance, and strong analytical skills tailored to their specific focus areas within the insurance sector.
Technical Skills and Tools Utilized
Reinsurance Specialists master complex risk assessment models and treaties, leveraging software like RMS and AIR for catastrophe modeling and risk quantification, while Insurance Specialists concentrate on underwriting platforms such as Guidewire and Duck Creek to evaluate individual policy risks. Proficiency in actuarial analysis, statistical software like SAS, and familiarity with regulatory compliance tools are crucial for both roles, yet Reinsurance Specialists often require deeper insights into treaty negotiation and portfolio aggregation. Expertise in claims management systems is more critical for Insurance Specialists, who directly handle policy issuance, endorsements, and claims processing.
Interaction with Other Insurance Professionals
Reinsurance specialists collaborate closely with underwriting teams, risk managers, and actuaries to structure coverage that mitigates potential losses for primary insurers. Insurance specialists engage directly with brokers, claims adjusters, and policyholders to develop, sell, and service insurance products tailored to client needs. Interaction between reinsurance and insurance professionals ensures balanced risk distribution and efficient claims management within the insurance ecosystem.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Reinsurance specialists navigate complex regulatory frameworks governing the transfer of risk between insurance companies, ensuring compliance with international treaties and national insurance laws. Insurance specialists focus on adherence to consumer protection regulations, underwriting standards, and claims practices within direct insurance operations. Both roles require staying current with evolving regulatory environments to mitigate legal risks and ensure organizational compliance.
Career Pathways & Advancement
Reinsurance specialists focus on assessing and managing risks transferred between insurance companies, requiring in-depth knowledge of underwriting, risk analysis, and contract negotiation, which positions them for senior roles in risk management and underwriting departments. Insurance specialists handle policy creation, claims processing, and customer service, developing expertise in regulatory compliance and client relations, often advancing to leadership roles in sales, underwriting, or claims management. Both career paths demand strong analytical skills and industry knowledge, but reinsurance specialists typically progress towards strategic risk consultancy, while insurance specialists move towards operational management and client-focused leadership.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Reinsurance specialists typically earn higher salaries compared to insurance specialists due to the complexity and scale of managing insurance risks transferred between companies, with average annual compensation ranging from $90,000 to $140,000. Insurance specialists, focusing on underwriting, claims, or policy management, generally receive salaries between $50,000 and $80,000, reflecting their more direct client-facing and operational roles. Differences in bonuses, profit-sharing, and commission structures further contribute to the compensation gap, as reinsurance roles often involve higher-value transactions and performance-based incentives.
Industry Trends Impacting Both Roles
Industry trends such as the rise of climate-related risks and increasing regulatory demands are reshaping the roles of both reinsurance specialists and insurance specialists. Advances in data analytics and artificial intelligence enhance risk assessment accuracy, requiring these professionals to adapt their strategies for underwriting and claims management. Collaboration between reinsurance and insurance experts grows crucial as market volatility and emerging risks drive the need for integrated risk mitigation solutions.
Reinsurance Specialist vs Insurance Specialist Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com