Asset maintenance involves preserving the performance and longevity of individual equipment and machinery, ensuring operational efficiency and minimizing costly downtime. Infrastructure maintenance focuses on the upkeep and repair of foundational systems like roads, bridges, and utilities, essential for overall operational support and safety. Both approaches are critical in a comprehensive maintenance strategy, balancing detailed equipment care with broader system reliability.
Table of Comparison
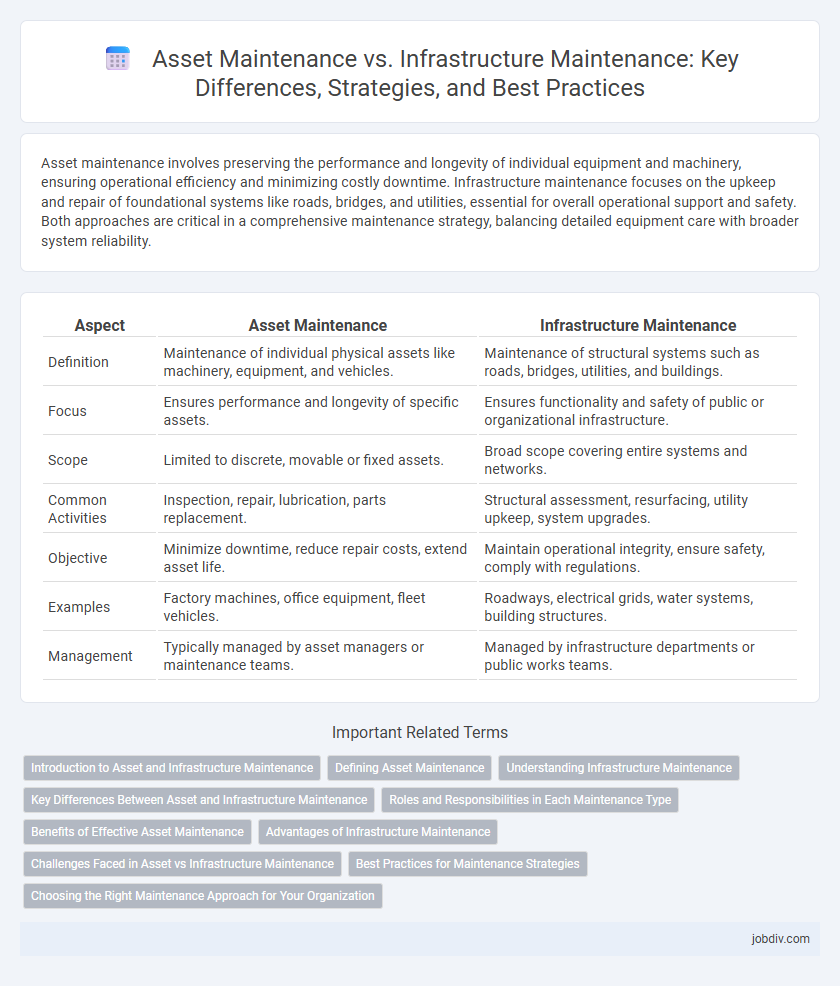
| Aspect | Asset Maintenance | Infrastructure Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintenance of individual physical assets like machinery, equipment, and vehicles. | Maintenance of structural systems such as roads, bridges, utilities, and buildings. |
| Focus | Ensures performance and longevity of specific assets. | Ensures functionality and safety of public or organizational infrastructure. |
| Scope | Limited to discrete, movable or fixed assets. | Broad scope covering entire systems and networks. |
| Common Activities | Inspection, repair, lubrication, parts replacement. | Structural assessment, resurfacing, utility upkeep, system upgrades. |
| Objective | Minimize downtime, reduce repair costs, extend asset life. | Maintain operational integrity, ensure safety, comply with regulations. |
| Examples | Factory machines, office equipment, fleet vehicles. | Roadways, electrical grids, water systems, building structures. |
| Management | Typically managed by asset managers or maintenance teams. | Managed by infrastructure departments or public works teams. |
Introduction to Asset and Infrastructure Maintenance
Asset maintenance involves the systematic care and repair of physical equipment to maximize operational efficiency and lifespan. Infrastructure maintenance focuses on preserving essential systems such as roads, utilities, and communication networks to ensure safety and functionality. Both types of maintenance require strategic planning, routine inspections, and timely interventions to prevent costly failures and downtime.
Defining Asset Maintenance
Asset maintenance involves the systematic inspection, servicing, and repair of physical assets such as machinery, equipment, and vehicles to ensure optimal performance and extend their operational lifespan. It focuses on preserving individual asset functionality through scheduled preventive measures or corrective actions based on condition monitoring and failure analysis. This contrasts with infrastructure maintenance, which targets the upkeep of foundational systems like roads, bridges, and utility networks critical for overall operational support.
Understanding Infrastructure Maintenance
Infrastructure maintenance involves the regular inspection, repair, and upgrading of foundational systems such as roads, bridges, utilities, and communication networks to ensure functionality and safety. Unlike asset maintenance, which targets specific machinery or equipment, infrastructure maintenance addresses large-scale public and commercial systems critical for operational continuity. Effective infrastructure maintenance strategies reduce downtime, extend lifespan, and optimize performance by proactively managing structural integrity and utility services.
Key Differences Between Asset and Infrastructure Maintenance
Asset maintenance targets individual equipment and machinery to ensure operational efficiency and prolong service life, focusing on components like motors, pumps, and HVAC systems. Infrastructure maintenance involves the upkeep of foundational systems such as roads, bridges, utilities, and building structures to guarantee safety, compliance, and reliability. Key differences include the scale of maintenance, with asset maintenance being equipment-specific and infrastructure maintenance addressing broader structural systems critical for overall facility function.
Roles and Responsibilities in Each Maintenance Type
Asset maintenance primarily involves managing and preserving individual equipment, machinery, and tools to ensure operational efficiency, with responsibilities including routine inspections, repairs, and performance tracking by maintenance technicians and asset managers. Infrastructure maintenance focuses on the upkeep of physical structures such as buildings, roads, and utilities, requiring coordination among civil engineers, facility managers, and specialized contractors to address structural integrity, safety compliance, and long-term sustainability. Clear delineation of roles ensures optimized resource allocation, preventive maintenance scheduling, and reduced downtime across both maintenance domains.
Benefits of Effective Asset Maintenance
Effective asset maintenance extends equipment lifespan, reduces unexpected downtimes, and minimizes repair costs by ensuring optimal performance and early detection of issues. Unlike broader infrastructure maintenance, asset maintenance targets individual machinery or components, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability. Prioritizing asset maintenance leads to significant cost savings and improved safety across production environments.
Advantages of Infrastructure Maintenance
Infrastructure maintenance enhances system reliability by preventing large-scale failures and reducing downtime across connected assets. It optimizes resource allocation through centralized monitoring and predictive analytics, leading to cost savings and extended service life. Proactive infrastructure maintenance supports sustainability and resilience in critical facilities like transportation networks, utilities, and communication systems.
Challenges Faced in Asset vs Infrastructure Maintenance
Asset maintenance faces challenges such as unpredictable equipment failures, high costs of spare parts, and the need for specialized skills to repair complex machinery. Infrastructure maintenance struggles with aging structures, weather-related deterioration, and the extensive coordination required for large-scale repairs impacting public safety and service continuity. Both require strategic planning but differ significantly in resource allocation, with asset maintenance focusing on individual components and infrastructure demanding systemic, long-term interventions.
Best Practices for Maintenance Strategies
Asset maintenance prioritizes the upkeep of individual equipment and machinery to ensure operational efficiency and longevity, while infrastructure maintenance focuses on preserving physical structures such as roads, bridges, and utilities to guarantee safety and functionality. Best practices for maintenance strategies include implementing predictive maintenance using IoT sensors and data analytics, scheduling regular inspections, and employing condition-based monitoring to reduce downtime and optimize resource allocation. Integrating computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) enhances tracking, reporting, and decision-making for both asset and infrastructure maintenance.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Approach for Your Organization
Asset maintenance focuses on preserving the functionality and longevity of individual equipment and machinery, while infrastructure maintenance targets the upkeep of foundational systems such as buildings, roads, and utilities. Selecting the appropriate maintenance approach depends on factors like organizational priorities, operational impact, and lifecycle costs associated with assets versus infrastructure components. Implementing a tailored strategy that balances both asset reliability and infrastructure integrity ensures optimized resource allocation and sustainable organizational performance.
Asset Maintenance vs Infrastructure Maintenance Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com