Corrective maintenance involves fixing equipment after a fault is detected but before it causes a complete failure, reducing downtime and preventing further damage. Breakdown maintenance occurs only after the equipment has stopped functioning, often leading to longer disruptions and higher repair costs. Choosing corrective maintenance over breakdown maintenance enhances reliability and extends the lifespan of machinery.
Table of Comparison
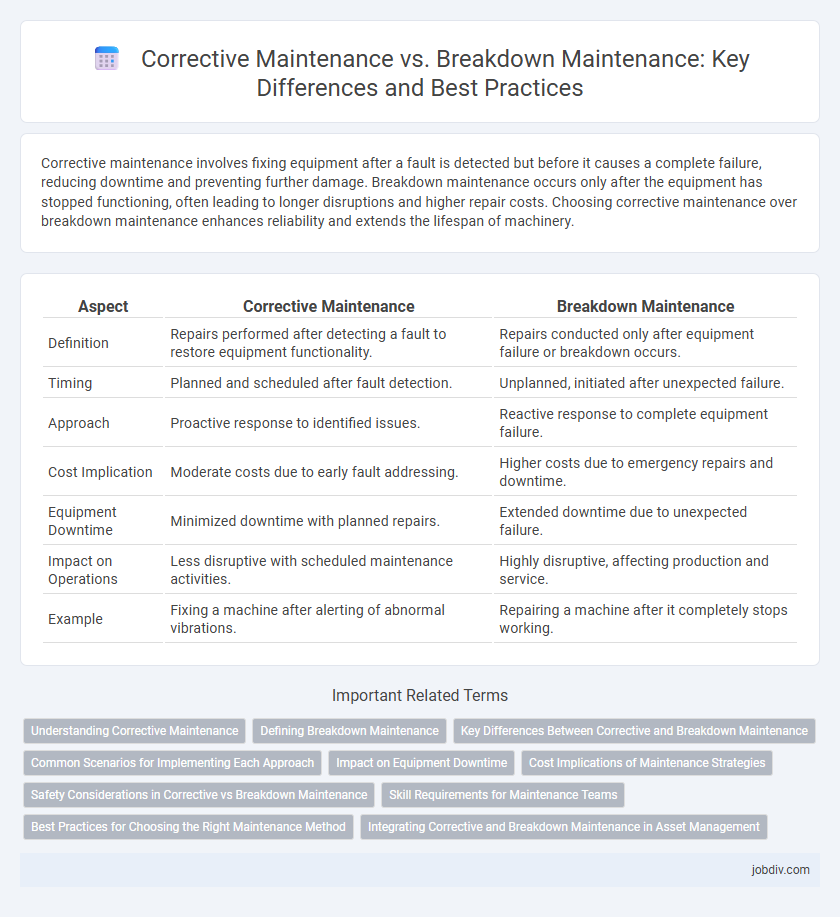
| Aspect | Corrective Maintenance | Breakdown Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repairs performed after detecting a fault to restore equipment functionality. | Repairs conducted only after equipment failure or breakdown occurs. |
| Timing | Planned and scheduled after fault detection. | Unplanned, initiated after unexpected failure. |
| Approach | Proactive response to identified issues. | Reactive response to complete equipment failure. |
| Cost Implication | Moderate costs due to early fault addressing. | Higher costs due to emergency repairs and downtime. |
| Equipment Downtime | Minimized downtime with planned repairs. | Extended downtime due to unexpected failure. |
| Impact on Operations | Less disruptive with scheduled maintenance activities. | Highly disruptive, affecting production and service. |
| Example | Fixing a machine after alerting of abnormal vibrations. | Repairing a machine after it completely stops working. |
Understanding Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance involves identifying and repairing faults after they occur, aiming to restore equipment to its operational condition efficiently. Unlike breakdown maintenance, which reacts only when equipment fails unexpectedly, corrective maintenance includes planned interventions based on fault detection and diagnostic data. This approach minimizes downtime by addressing issues promptly without awaiting total equipment failure.
Defining Breakdown Maintenance
Breakdown maintenance refers to the reactive approach of repairing equipment only after it has failed or broken down, resulting in unplanned downtime and potential production losses. This type of maintenance contrasts with corrective maintenance, which involves identifying and fixing faults before complete failure occurs to prevent extended disruptions. Breakdown maintenance is often more costly and less efficient due to the urgent nature of repairs and the unpredictability of equipment failure.
Key Differences Between Corrective and Breakdown Maintenance
Corrective maintenance involves repairing equipment after a fault is detected during routine inspections, whereas breakdown maintenance occurs only after equipment has completely failed. Corrective maintenance aims to fix minor issues to prevent major failures, contrasting with breakdown maintenance's reactive approach to restore functionality post-failure. The key difference lies in timing and prevention, with corrective maintenance reducing downtime and breakdown maintenance often leading to longer operational interruptions.
Common Scenarios for Implementing Each Approach
Corrective maintenance is commonly applied in scenarios where equipment degradation is detected through regular inspections before complete failure occurs. Breakdown maintenance is typically implemented in non-critical systems where unexpected failures minimally impact production and repair costs are lower than preventive measures. Industries with high equipment redundancy often prefer corrective maintenance to balance downtime and repair expenses, whereas breakdown maintenance suits simple machinery with manageable failure risks.
Impact on Equipment Downtime
Corrective maintenance typically reduces overall equipment downtime by addressing issues before complete failure occurs, enabling timely repairs that prevent extended operational halts. In contrast, breakdown maintenance results in increased downtime as repairs are only performed after equipment failure, often leading to unpredictable and prolonged outages. Optimizing maintenance strategies by prioritizing corrective actions can significantly enhance equipment availability and operational efficiency.
Cost Implications of Maintenance Strategies
Corrective maintenance involves repairing equipment after a failure, often resulting in higher emergency repair costs and extended downtime, which can significantly impact operational budgets. Breakdown maintenance, a subset of corrective maintenance, tends to incur unpredictable expenses due to sudden equipment failures, leading to increased labor costs and potential production losses. Implementing proactive maintenance strategies can reduce the frequency and severity of breakdowns, ultimately optimizing cost efficiency and minimizing financial risks associated with reactive repairs.
Safety Considerations in Corrective vs Breakdown Maintenance
Corrective maintenance involves timely repairs following the detection of faults, prioritizing safety by preventing hazardous failures through controlled interventions. Breakdown maintenance occurs after equipment failure, posing higher safety risks due to unexpected malfunctions and potential accidents during unplanned downtime. Implementing corrective maintenance enhances workplace safety by minimizing the likelihood of sudden breakdowns and associated dangers.
Skill Requirements for Maintenance Teams
Corrective Maintenance requires maintenance teams to have intermediate diagnostic skills to identify and repair known faults promptly, ensuring minimal downtime. Breakdown Maintenance demands advanced troubleshooting capabilities, rapid response proficiency, and robust problem-solving skills to address unexpected system failures efficiently. Skilled technicians must continuously update their technical knowledge to adapt to evolving equipment complexities in both maintenance types.
Best Practices for Choosing the Right Maintenance Method
Corrective maintenance involves repairing equipment after a fault is detected, while breakdown maintenance waits until equipment fails completely before intervention. Best practices for choosing the right maintenance method include analyzing equipment criticality, downtime costs, and available resources to balance operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Implementing condition monitoring and predictive analytics helps decide when corrective maintenance is more beneficial than risking costly breakdown maintenance.
Integrating Corrective and Breakdown Maintenance in Asset Management
Integrating corrective and breakdown maintenance within asset management enhances operational efficiency by ensuring timely repairs and minimizing unexpected downtime. Corrective maintenance addresses identified faults proactively, while breakdown maintenance responds to failures as they occur, creating a comprehensive maintenance strategy. Leveraging real-time monitoring systems and data analytics optimizes resource allocation and extends asset lifecycle, resulting in cost savings and improved reliability.
Corrective Maintenance vs Breakdown Maintenance Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com