Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive and preventive maintenance involving all employees to maximize equipment effectiveness and minimize downtime. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) focuses on identifying critical assets and applying maintenance strategies based on failure modes and consequences to ensure system reliability. Both approaches aim to enhance asset performance but differ in scope, with TPM fostering a culture of continuous improvement and RCM prioritizing risk-based decision-making.
Table of Comparison
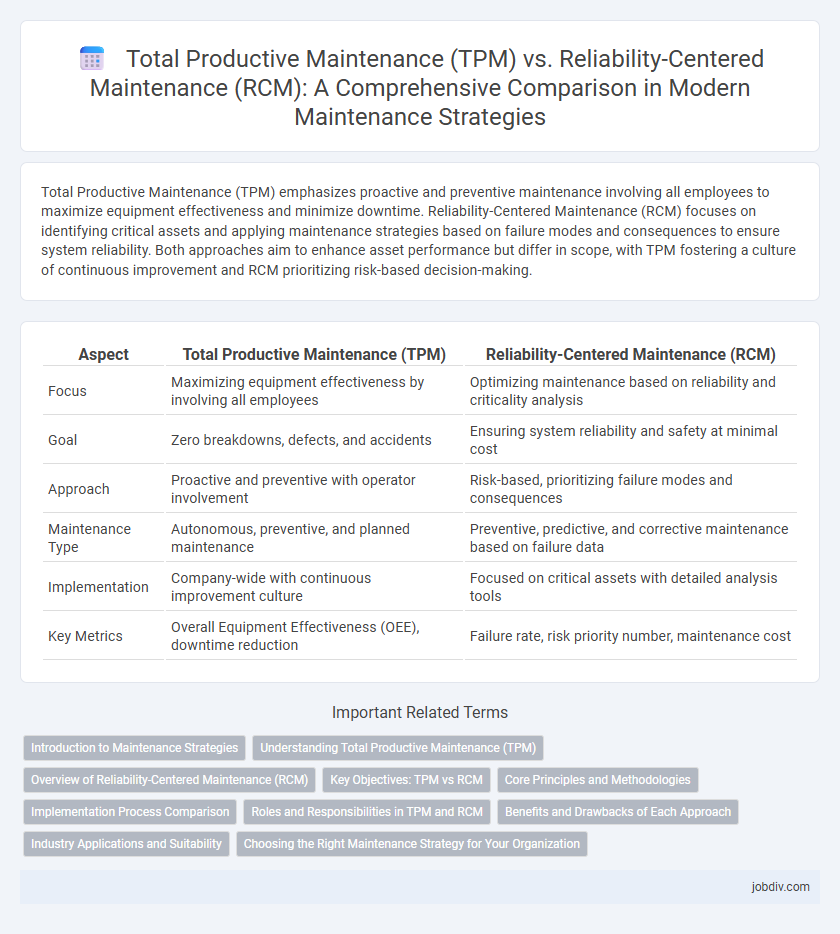
| Aspect | Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) | Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Maximizing equipment effectiveness by involving all employees | Optimizing maintenance based on reliability and criticality analysis |
| Goal | Zero breakdowns, defects, and accidents | Ensuring system reliability and safety at minimal cost |
| Approach | Proactive and preventive with operator involvement | Risk-based, prioritizing failure modes and consequences |
| Maintenance Type | Autonomous, preventive, and planned maintenance | Preventive, predictive, and corrective maintenance based on failure data |
| Implementation | Company-wide with continuous improvement culture | Focused on critical assets with detailed analysis tools |
| Key Metrics | Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), downtime reduction | Failure rate, risk priority number, maintenance cost |
Introduction to Maintenance Strategies
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive and preventive maintenance to maximize equipment effectiveness through operator involvement and continuous improvement. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) prioritizes identifying critical assets and developing tailored maintenance plans based on failure modes and operational context. Both strategies aim to optimize maintenance efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance overall reliability but differ in focus and implementation methodologies.
Understanding Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes proactive and preventive maintenance to maximize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by involving all employees from operators to management. TPM focuses on autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, and continuous improvement to reduce equipment downtime and improve production quality. This holistic approach integrates equipment care into daily operations, fostering a culture of shared responsibility and sustainable productivity.
Overview of Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) is a systematic approach that prioritizes maintenance tasks based on the reliability and criticality of equipment to ensure optimal performance and safety. It focuses on identifying failure modes, their causes, and effects, enabling targeted preventive and predictive maintenance strategies. RCM enhances asset reliability by optimizing maintenance resources and minimizing unplanned downtime through condition-based and scheduled interventions.
Key Objectives: TPM vs RCM
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) aims to maximize equipment effectiveness by involving all employees in proactive and preventive maintenance activities to eliminate breakdowns, reduce downtime, and improve overall productivity. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) focuses on identifying critical equipment functions and failure modes to prioritize maintenance tasks that ensure operational reliability and safety while optimizing costs. TPM emphasizes continuous improvement through workforce engagement, whereas RCM leverages detailed failure analysis to develop tailored maintenance strategies.
Core Principles and Methodologies
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) centers on engaging all employees in proactive equipment maintenance to maximize overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) through autonomous maintenance, planned maintenance, and continuous improvement. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) focuses on identifying critical asset functions, failure modes, and their consequences to develop tailored maintenance strategies that optimize reliability and safety. While TPM emphasizes broad participation and reducing downtime via prevention, RCM prioritizes risk-based decision-making to balance maintenance costs with asset performance.
Implementation Process Comparison
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) implementation emphasizes employee involvement through autonomous maintenance and continuous improvement activities aimed at maximizing equipment effectiveness. In contrast, Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) follows a structured analytical approach, focusing on identifying failure modes, prioritizing maintenance tasks based on risk and reliability data. TPM fosters a culture of proactive maintenance with widespread shop-floor engagement, while RCM relies on detailed engineering analysis to optimize maintenance strategies for critical assets.
Roles and Responsibilities in TPM and RCM
In Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), roles emphasize operator involvement in routine equipment care, encouraging a collaborative approach between maintenance teams and production staff to enhance overall equipment effectiveness. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) assigns responsibilities primarily to maintenance engineers and reliability specialists who analyze failure modes and develop preservation strategies tailored to critical assets. TPM fosters proactive, cross-functional participation for continuous improvement, while RCM focuses on technical expertise to optimize maintenance tasks based on asset reliability and risk assessment.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Each Approach
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) enhances equipment effectiveness by involving all employees in proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and boosting productivity but may require significant cultural shifts and training investments. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) prioritizes maintenance tasks based on failure consequences, optimizing resource allocation and improving asset reliability, yet it demands detailed failure analysis and can be time-consuming to implement. Both approaches aim to minimize unplanned outages, but TPM excels in fostering operator engagement, while RCM offers a more analytical framework for critical asset management.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) excels in manufacturing industries by promoting operator-driven maintenance to maximize equipment uptime and efficiency, making it highly suitable for repetitive production environments. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) is optimal for complex, high-risk industries like aerospace and power generation, where precise failure analysis and risk assessment guide maintenance strategies. TPM focuses on proactive, preventive actions targeting overall equipment effectiveness, while RCM emphasizes reliability and safety through condition-based and predictive maintenance tailored to critical assets.
Choosing the Right Maintenance Strategy for Your Organization
Selecting the appropriate maintenance strategy requires evaluating organizational goals, asset criticality, and resource availability; Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) emphasizes operator involvement and continuous improvement to maximize overall equipment effectiveness, while Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) focuses on failure modes and prioritizes maintenance tasks based on risk and reliability analysis. Companies aiming to reduce downtime and improve workforce engagement may benefit from TPM, whereas those managing complex systems with high safety or operational risks often find RCM more effective. Aligning maintenance strategy with operational objectives and asset characteristics ensures optimized performance and cost-efficiency.
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) vs Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com