HVAC maintenance ensures optimal indoor air quality and temperature control by regularly cleaning filters, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting ductwork, which prevents system breakdowns and improves energy efficiency. Electrical maintenance involves inspecting wiring, testing circuit breakers, and verifying electrical panel integrity to prevent fire hazards and ensure reliable power distribution. Both types of maintenance are critical for safety and operational efficiency but focus on different systems and specialized skill sets.
Table of Comparison
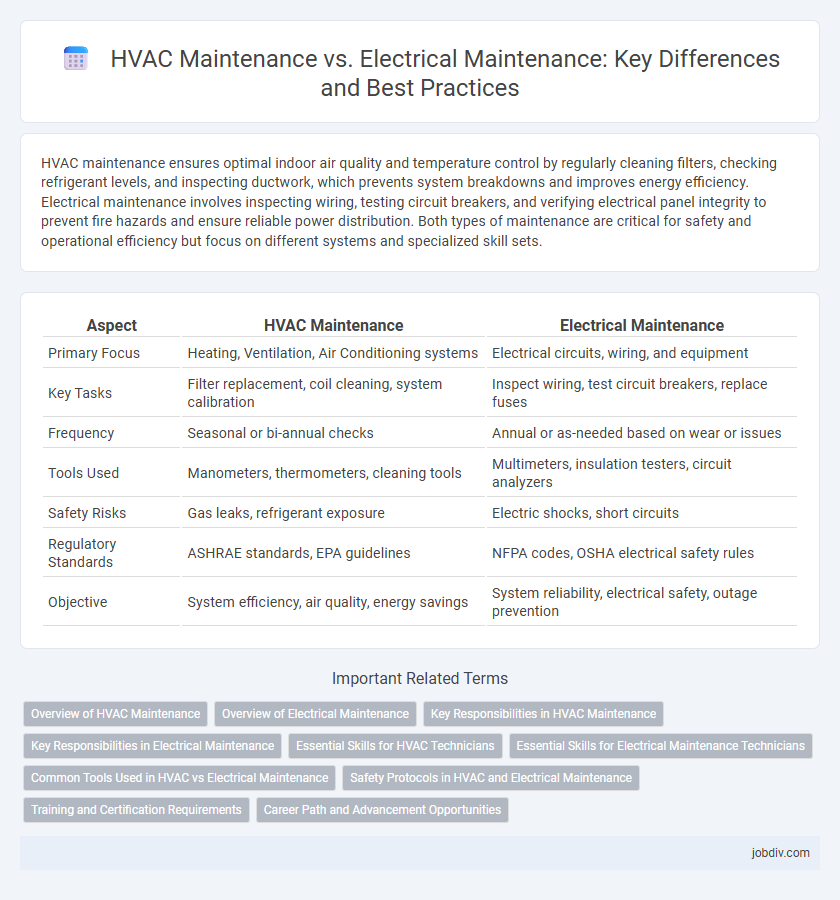
| Aspect | HVAC Maintenance | Electrical Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning systems | Electrical circuits, wiring, and equipment |
| Key Tasks | Filter replacement, coil cleaning, system calibration | Inspect wiring, test circuit breakers, replace fuses |
| Frequency | Seasonal or bi-annual checks | Annual or as-needed based on wear or issues |
| Tools Used | Manometers, thermometers, cleaning tools | Multimeters, insulation testers, circuit analyzers |
| Safety Risks | Gas leaks, refrigerant exposure | Electric shocks, short circuits |
| Regulatory Standards | ASHRAE standards, EPA guidelines | NFPA codes, OSHA electrical safety rules |
| Objective | System efficiency, air quality, energy savings | System reliability, electrical safety, outage prevention |
Overview of HVAC Maintenance
HVAC maintenance involves regular inspection, cleaning, and servicing of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and indoor air quality. Tasks include filter replacement, refrigerant level checks, thermostat calibration, and duct cleaning, which help prevent system breakdowns and extend equipment lifespan. Proper HVAC maintenance reduces energy costs, enhances comfort, and minimizes the risk of costly repairs compared to electrical maintenance, which focuses primarily on wiring, circuits, and power systems.
Overview of Electrical Maintenance
Electrical maintenance involves regular inspection, testing, and repair of electrical systems to ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Key components include circuit breakers, wiring, transformers, and control panels, requiring skilled technicians to prevent downtime and hazards like electrical fires or power outages. Consistent electrical maintenance reduces operational costs by identifying faults early and extending the lifespan of electrical equipment.
Key Responsibilities in HVAC Maintenance
HVAC maintenance key responsibilities include inspecting and cleaning air filters, checking refrigerant levels, and ensuring the proper functioning of thermostats and ventilation systems to optimize indoor air quality and energy efficiency. Technicians also conduct routine inspections of heating and cooling units, lubricate moving parts, and identify potential issues to prevent system breakdowns. These tasks differ from electrical maintenance, which primarily involves troubleshooting wiring, circuit breakers, and electrical panels to ensure safety and continuous power supply.
Key Responsibilities in Electrical Maintenance
Electrical maintenance focuses on inspecting, testing, and repairing electrical systems, including wiring, circuit breakers, and transformers, to ensure safe and efficient power distribution. Key responsibilities involve troubleshooting electrical faults, performing preventive maintenance to reduce downtime, and adhering to safety regulations to prevent electrical hazards. This specialized maintenance contrasts with HVAC maintenance, which centers on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system functionality.
Essential Skills for HVAC Technicians
HVAC technicians require a deep understanding of refrigeration cycles, electrical systems, and airflow dynamics to efficiently diagnose and repair heating, ventilation, and air conditioning units. Proficiency in using specialized tools such as multimeters, refrigerant leak detectors, and thermometers is vital for ensuring system performance and safety. Strong troubleshooting skills, combined with knowledge of electrical wiring and HVAC controls, differentiate HVAC maintenance expertise from general electrical maintenance tasks.
Essential Skills for Electrical Maintenance Technicians
Electrical maintenance technicians require expertise in circuit analysis, wiring diagnostics, and safety protocol adherence to ensure reliable system performance. Proficiency in using multimeters, oscilloscopes, and thermal imaging devices is crucial for accurate fault detection and troubleshooting. Strong knowledge of electrical codes, schematic interpretation, and preventive maintenance schedules distinguishes their role from HVAC maintenance professionals.
Common Tools Used in HVAC vs Electrical Maintenance
Common tools used in HVAC maintenance include refrigerant gauges, leak detectors, multimeters, and vacuum pumps, essential for diagnosing and repairing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Electrical maintenance commonly relies on multimeters, circuit testers, wire strippers, and insulated screwdrivers to ensure circuit integrity and safety. Both fields utilize multimeters extensively, but HVAC maintenance emphasizes tools for handling refrigerants and airflow, while electrical maintenance focuses more on wiring and circuit components.
Safety Protocols in HVAC and Electrical Maintenance
HVAC maintenance prioritizes safety protocols such as regular inspection of ventilation systems, leak detection in refrigerants, and ensuring proper grounding of electrical components to prevent fire hazards. Electrical maintenance emphasizes adherence to lockout-tagout procedures, insulation testing, and circuit breaker functionality checks to minimize electrical shock and short circuit risks. Both maintenance types require strict compliance with OSHA standards and use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to safeguard technicians during routine servicing.
Training and Certification Requirements
HVAC maintenance technicians require specialized certifications such as EPA Section 608 for refrigerant handling and often undergo rigorous training in system diagnostics, airflow optimization, and safety protocols. In contrast, electrical maintenance professionals must acquire certifications like OSHA safety training and NFPA 70E compliance to ensure safe handling of electrical systems and adherence to industry standards. Both fields demand ongoing education to stay current with evolving technologies and regulatory requirements, emphasizing the importance of skilled, certified personnel for system reliability and safety.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
HVAC maintenance careers offer specialized skills in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, with advancement opportunities into supervisory roles, energy management, and system design. Electrical maintenance professionals gain expertise in electrical systems and controls, often progressing to higher-paying roles such as electrical engineers, project managers, or facility maintenance supervisors. Both fields provide strong job stability, but electrical maintenance typically requires broader technical knowledge, which can enhance long-term career growth and advancement potential.
HVAC Maintenance vs Electrical Maintenance Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com