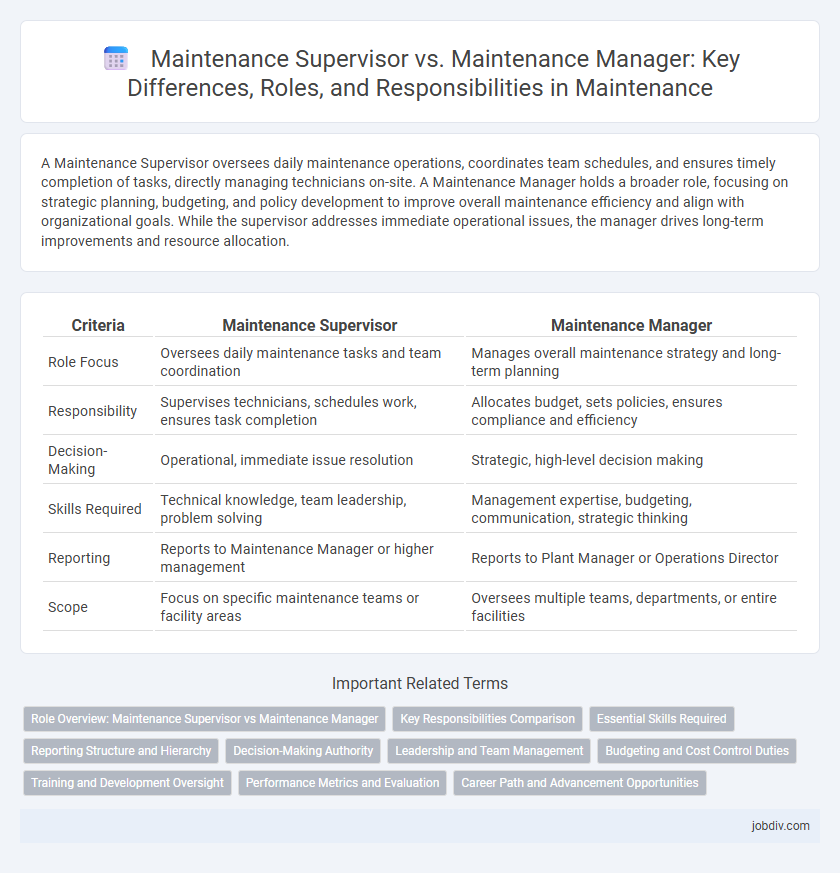
A Maintenance Supervisor oversees daily maintenance operations, coordinates team schedules, and ensures timely completion of tasks, directly managing technicians on-site. A Maintenance Manager holds a broader role, focusing on strategic planning, budgeting, and policy development to improve overall maintenance efficiency and align with organizational goals. While the supervisor addresses immediate operational issues, the manager drives long-term improvements and resource allocation.
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Maintenance Supervisor | Maintenance Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Oversees daily maintenance tasks and team coordination | Manages overall maintenance strategy and long-term planning |
| Responsibility | Supervises technicians, schedules work, ensures task completion | Allocates budget, sets policies, ensures compliance and efficiency |
| Decision-Making | Operational, immediate issue resolution | Strategic, high-level decision making |
| Skills Required | Technical knowledge, team leadership, problem solving | Management expertise, budgeting, communication, strategic thinking |
| Reporting | Reports to Maintenance Manager or higher management | Reports to Plant Manager or Operations Director |
| Scope | Focus on specific maintenance teams or facility areas | Oversees multiple teams, departments, or entire facilities |
Role Overview: Maintenance Supervisor vs Maintenance Manager
A Maintenance Supervisor oversees daily maintenance tasks, coordinates technicians, and ensures equipment reliability through hands-on management and scheduling. The Maintenance Manager focuses on strategic planning, budgeting, and improving maintenance processes to align with organizational goals. Both roles require technical expertise, but the manager emphasizes leadership and resource allocation, while the supervisor handles direct team supervision and task execution.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
A Maintenance Supervisor primarily oversees daily maintenance tasks, coordinates team schedules, and ensures adherence to safety protocols, focusing on operational efficiency and immediate problem resolution. In contrast, a Maintenance Manager develops long-term maintenance strategies, manages budgets, and liaises with other departments to align maintenance objectives with organizational goals. While supervisors handle hands-on team leadership, managers emphasize planning, resource allocation, and performance analysis.
Essential Skills Required
Maintenance Supervisors require strong technical expertise, team leadership, and hands-on problem-solving skills to coordinate daily maintenance tasks and ensure safety compliance. Maintenance Managers need advanced strategic planning abilities, budget management, and excellent communication skills to oversee maintenance operations and drive continuous improvement. Both roles demand proficiency in asset management systems and a deep understanding of preventive maintenance methodologies.
Reporting Structure and Hierarchy
A Maintenance Supervisor typically reports to the Maintenance Manager, operating as the frontline leader overseeing daily maintenance tasks and crew performance. The Maintenance Manager holds a higher hierarchical position, responsible for strategic planning, budget management, and liaising with upper management. This clear reporting structure ensures streamlined communication and efficient workflow within the maintenance department.
Decision-Making Authority
Maintenance Supervisors oversee daily repair tasks and coordinate teams, holding decision-making authority limited to immediate operational issues and workflow adjustments. Maintenance Managers possess broader decision-making authority, including strategic planning, budget allocation, vendor negotiations, and policy implementation to optimize maintenance processes. The scope of authority for Maintenance Managers significantly impacts long-term maintenance efficiency and resource management across facilities.
Leadership and Team Management
Maintenance Supervisors lead frontline teams by assigning daily tasks, monitoring equipment conditions, and ensuring adherence to safety protocols, emphasizing direct team engagement and hands-on problem solving. Maintenance Managers oversee broader operational strategies, resource allocation, and interdepartmental coordination, focusing on leadership development, performance metrics, and long-term maintenance planning. Both roles require strong leadership skills, but Supervisors manage immediate team dynamics while Managers drive overall departmental efficiency and strategic goals.
Budgeting and Cost Control Duties
A Maintenance Supervisor typically oversees day-to-day budgeting by managing labor costs and coordinating routine maintenance expenses within set limits. In contrast, a Maintenance Manager takes a strategic role in budgeting, developing comprehensive cost control plans, allocating resources across departments, and analyzing financial data to optimize maintenance expenditures. Effective budgeting and cost control by the Maintenance Manager directly impact the organization's operational efficiency and asset longevity.
Training and Development Oversight
Maintenance Supervisors directly oversee hands-on training sessions, ensuring technicians acquire practical skills in equipment repair and safety protocols. Maintenance Managers develop comprehensive training programs aligned with organizational goals, integrating advanced techniques and compliance standards to enhance workforce competency. Both roles collaborate to monitor training effectiveness and promote continuous professional development.
Performance Metrics and Evaluation
Maintenance Supervisors directly oversee daily team tasks, focusing on real-time performance metrics such as equipment uptime, response times, and task completion rates. Maintenance Managers analyze broader performance evaluations, including overall maintenance costs, strategic asset reliability, and long-term productivity trends. Performance metrics for supervisors emphasize operational efficiency, while managers prioritize data-driven decision-making and process improvements to enhance organizational maintenance outcomes.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Maintenance Supervisors typically oversee daily operations and team management on-site, serving as a crucial stepping stone for hands-on leadership experience. Maintenance Managers hold broader responsibilities, including strategic planning, budgeting, and cross-department coordination, making the role ideal for professionals aiming to advance into executive positions. Career advancement often progresses from Maintenance Supervisor to Maintenance Manager, with opportunities expanding into facilities management or operations leadership roles.
Maintenance Supervisor vs Maintenance Manager Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com