Electrical maintenance involves inspecting, testing, and repairing electrical components and systems to ensure safe and reliable operation, focusing on wiring, circuits, and electrical equipment. Mechanical maintenance targets machinery and mechanical systems, including lubrication, adjustments, and part replacements to prevent wear and tear and ensure optimal performance. Both types of maintenance are essential for minimizing downtime and extending the lifespan of equipment.
Table of Comparison
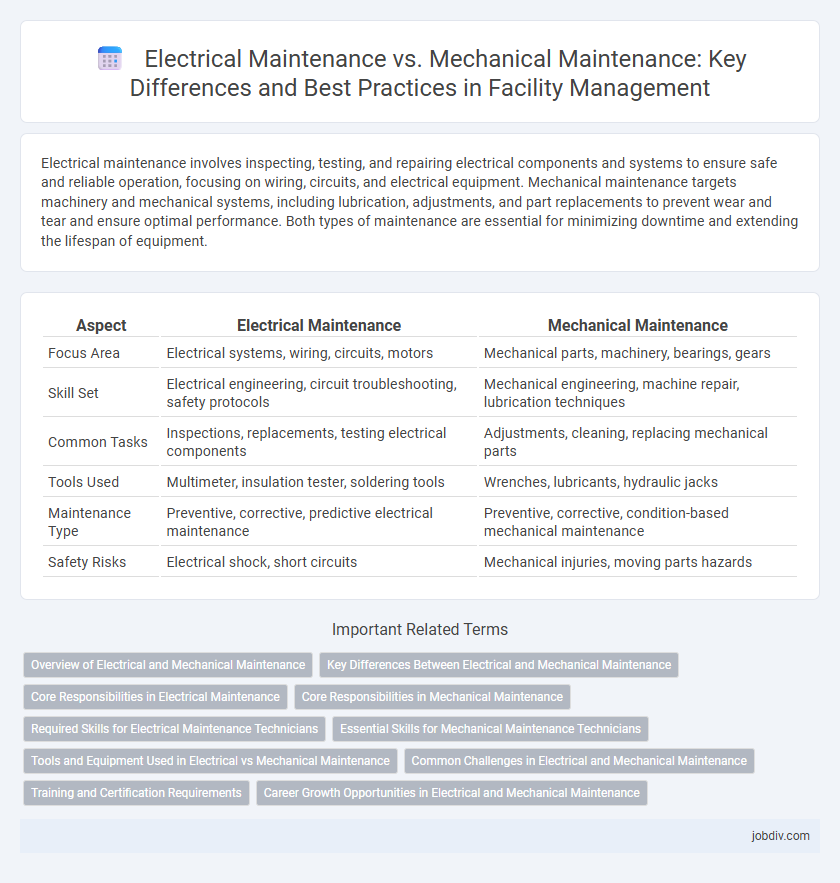
| Aspect | Electrical Maintenance | Mechanical Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Focus Area | Electrical systems, wiring, circuits, motors | Mechanical parts, machinery, bearings, gears |
| Skill Set | Electrical engineering, circuit troubleshooting, safety protocols | Mechanical engineering, machine repair, lubrication techniques |
| Common Tasks | Inspections, replacements, testing electrical components | Adjustments, cleaning, replacing mechanical parts |
| Tools Used | Multimeter, insulation tester, soldering tools | Wrenches, lubricants, hydraulic jacks |
| Maintenance Type | Preventive, corrective, predictive electrical maintenance | Preventive, corrective, condition-based mechanical maintenance |
| Safety Risks | Electrical shock, short circuits | Mechanical injuries, moving parts hazards |
Overview of Electrical and Mechanical Maintenance
Electrical maintenance involves the inspection, testing, and repair of electrical systems and equipment to ensure safe and efficient operation, focusing on components such as wiring, circuit breakers, and transformers. Mechanical maintenance centers on the upkeep of mechanical systems including engines, pumps, and HVAC units, emphasizing lubrication, alignment, and replacement of worn parts. Both disciplines are critical in industrial settings to prevent downtime, enhance equipment longevity, and comply with safety regulations.
Key Differences Between Electrical and Mechanical Maintenance
Electrical maintenance primarily involves the inspection, testing, and repair of electrical systems such as wiring, circuit breakers, transformers, and motors, ensuring safe and efficient power distribution. Mechanical maintenance focuses on machinery components like gears, bearings, belts, and hydraulic systems, emphasizing lubrication, alignment, and wear prevention to maintain equipment functionality. The key differences lie in the technical expertise required--electrical maintenance demands knowledge of circuitry and electrical safety, whereas mechanical maintenance requires skills in mechanical systems and physical troubleshooting.
Core Responsibilities in Electrical Maintenance
Electrical maintenance centers on inspecting, testing, and repairing electrical systems, including wiring, circuit breakers, transformers, and motors to ensure safety and functionality. Core responsibilities involve preventative maintenance to avoid electrical failures, troubleshooting outages, and compliance with electrical codes and safety standards. Skilled technicians utilize diagnostic tools and perform regular system updates to maintain uninterrupted power supply and equipment reliability.
Core Responsibilities in Mechanical Maintenance
Core responsibilities in mechanical maintenance include inspecting, repairing, and servicing machinery components such as motors, bearings, gears, and conveyor systems to ensure optimal performance and prevent breakdowns. Routine lubrication, alignment, and calibration of mechanical equipment are crucial for minimizing wear and extending asset lifespan. Mechanical maintenance also involves troubleshooting mechanical failures and implementing corrective measures to maintain production efficiency and safety standards.
Required Skills for Electrical Maintenance Technicians
Electrical maintenance technicians require expertise in circuit analysis, electrical schematics, and safety protocols to troubleshoot and repair electrical systems effectively. Proficiency in using diagnostic tools like multimeters, oscilloscopes, and insulation testers is essential to ensure accurate fault detection and preventive maintenance. Strong knowledge of electrical codes, wiring standards, and control systems enables technicians to maintain reliable equipment operation and prevent downtime.
Essential Skills for Mechanical Maintenance Technicians
Mechanical maintenance technicians require in-depth knowledge of machinery components, such as bearings, gears, and hydraulics, to ensure optimal equipment performance. Proficiency in diagnostic tools and techniques for troubleshooting mechanical failures is essential to minimize downtime and prevent costly repairs. Strong understanding of preventive maintenance schedules and the ability to interpret technical schematics are critical skills that differentiate mechanical maintenance from electrical maintenance roles.
Tools and Equipment Used in Electrical vs Mechanical Maintenance
Electrical maintenance relies heavily on specialized tools such as multimeters, insulation testers, clamp meters, and wire strippers designed for precise voltage measurement, circuit analysis, and safe handling of live wires. In contrast, mechanical maintenance primarily utilizes equipment like torque wrenches, hydraulic lifts, bearing pullers, and alignment tools essential for assembly, disassembly, and adjustment of mechanical components. Both fields emphasize safety and efficiency but require distinct toolsets tailored to the electrical systems or mechanical machinery they service.
Common Challenges in Electrical and Mechanical Maintenance
Common challenges in electrical and mechanical maintenance include diagnosing complex system faults, managing equipment downtime, and ensuring safety compliance. Both types face difficulties in accessing accurate, real-time data for predictive maintenance to reduce unexpected failures. Additionally, balancing skilled workforce availability with the fast-paced operational demands often hampers maintenance efficiency and reliability.
Training and Certification Requirements
Electrical maintenance demands specialized training in electrical systems, high-voltage safety protocols, and certification such as OSHA or NFPA 70E compliance to ensure safe handling of live circuits. Mechanical maintenance requires knowledge of machinery operation, hydraulics, and pneumatic systems, often validated through certifications like Certified Maintenance & Reliability Technician (CMRT) or Industrial Maintenance Technician programs. Both fields emphasize ongoing training but differ significantly in technical skill sets and regulatory standards for certification.
Career Growth Opportunities in Electrical and Mechanical Maintenance
Electrical maintenance offers robust career growth opportunities in industries like power generation, telecommunications, and automation, driven by the increasing reliance on complex electrical systems and renewable energy technologies. Mechanical maintenance provides expansive career prospects in manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace sectors, emphasizing skills in machinery diagnostics, hydraulics, and robotics. Both fields demand continuous learning and certification, but electrical maintenance professionals often experience faster advancement due to the evolving nature of electrical components and control systems.
Electrical Maintenance vs Mechanical Maintenance Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com