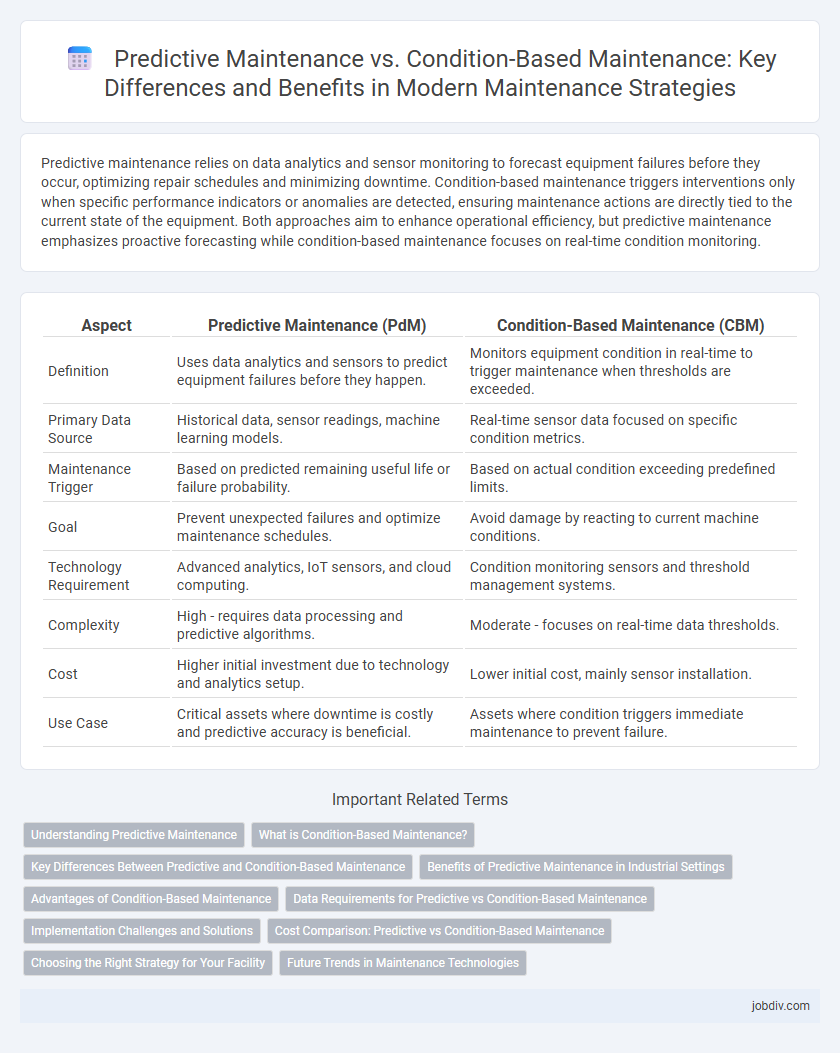
Predictive maintenance relies on data analytics and sensor monitoring to forecast equipment failures before they occur, optimizing repair schedules and minimizing downtime. Condition-based maintenance triggers interventions only when specific performance indicators or anomalies are detected, ensuring maintenance actions are directly tied to the current state of the equipment. Both approaches aim to enhance operational efficiency, but predictive maintenance emphasizes proactive forecasting while condition-based maintenance focuses on real-time condition monitoring.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Predictive Maintenance (PdM) | Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses data analytics and sensors to predict equipment failures before they happen. | Monitors equipment condition in real-time to trigger maintenance when thresholds are exceeded. |
| Primary Data Source | Historical data, sensor readings, machine learning models. | Real-time sensor data focused on specific condition metrics. |
| Maintenance Trigger | Based on predicted remaining useful life or failure probability. | Based on actual condition exceeding predefined limits. |
| Goal | Prevent unexpected failures and optimize maintenance schedules. | Avoid damage by reacting to current machine conditions. |
| Technology Requirement | Advanced analytics, IoT sensors, and cloud computing. | Condition monitoring sensors and threshold management systems. |
| Complexity | High - requires data processing and predictive algorithms. | Moderate - focuses on real-time data thresholds. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to technology and analytics setup. | Lower initial cost, mainly sensor installation. |
| Use Case | Critical assets where downtime is costly and predictive accuracy is beneficial. | Assets where condition triggers immediate maintenance to prevent failure. |
Understanding Predictive Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance utilizes data analytics, machine learning, and sensor data to forecast equipment failures before they occur, enabling proactive repairs and reducing downtime. Unlike Condition-Based Maintenance, which relies solely on current equipment conditions and thresholds, Predictive Maintenance analyzes historical and real-time data trends to predict future asset health. This approach optimizes maintenance schedules, extends asset lifespan, and lowers operational costs by preventing unexpected breakdowns.
What is Condition-Based Maintenance?
Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) involves monitoring equipment health through real-time data analysis such as vibration, temperature, and pressure sensors to determine when maintenance is necessary. This approach reduces downtime by addressing issues only when specific indicators show signs of potential failure. CBM contrasts with Predictive Maintenance by relying more on actual condition signals rather than advanced predictive analytics or machine learning models.
Key Differences Between Predictive and Condition-Based Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance uses data analytics, machine learning, and sensor data to forecast equipment failures before they occur, enabling proactive interventions. Condition-Based Maintenance relies on real-time monitoring of equipment conditions such as vibration, temperature, and pressure to trigger maintenance activities only when specific thresholds are exceeded. The key difference lies in Predictive Maintenance's focus on predicting future failures versus Condition-Based Maintenance's reliance on current equipment state for decision-making.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance in Industrial Settings
Predictive maintenance leverages advanced data analytics and real-time sensor monitoring to forecast equipment failures before they occur, significantly reducing unplanned downtime in industrial settings. It optimizes maintenance schedules based on actual equipment condition and performance trends, enhancing asset lifespan and operational efficiency. This approach minimizes maintenance costs by preventing over-maintenance and prioritizing critical interventions, leading to improved safety and productivity across manufacturing operations.
Advantages of Condition-Based Maintenance
Condition-Based Maintenance offers precise intervention by continuously monitoring equipment health through real-time sensor data, reducing unnecessary maintenance and minimizing unexpected failures. It extends asset lifespan and lowers operational costs by targeting repairs only when specific condition thresholds are met, optimizing resource allocation. This approach enhances safety and efficiency by enabling timely detection of anomalies before critical breakdowns occur.
Data Requirements for Predictive vs Condition-Based Maintenance
Predictive maintenance relies heavily on large volumes of historical and real-time sensor data to analyze patterns and forecast equipment failures before they occur, requiring advanced data storage and processing capabilities. Condition-based maintenance depends primarily on real-time data from specific condition monitoring sensors to trigger maintenance actions only when certain thresholds or anomalies are detected. The data requirements for predictive maintenance are more complex, involving machine learning models and extensive datasets, while condition-based maintenance focuses on immediate and actionable sensor data for timely interventions.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Predictive Maintenance implementation faces challenges like data integration complexity, requiring advanced analytics platforms to handle sensor-generated big data effectively. Condition-Based Maintenance struggles with real-time monitoring accuracy and sensor reliability, solved by investing in high-quality IoT devices and robust calibration procedures. Both approaches benefit from cross-functional teams bridging IT and operations to streamline technology adoption and improve maintenance decision-making.
Cost Comparison: Predictive vs Condition-Based Maintenance
Predictive maintenance typically incurs higher initial costs due to advanced sensor technology and data analytics software but reduces overall expenses by preventing unexpected equipment failures and optimizing maintenance schedules. Condition-based maintenance involves lower upfront investment but may lead to increased reactive repairs and downtime costs as maintenance is performed only after detecting specific equipment conditions. Long-term cost analysis often favors predictive maintenance for critical assets where minimizing operational interruptions and prolonging machinery lifespan are essential.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Facility
Selecting the appropriate maintenance strategy depends on facility-specific factors such as asset criticality, operational complexity, and available data infrastructure. Predictive maintenance leverages real-time sensor data and advanced analytics to forecast equipment failures, reducing unplanned downtime in high-value assets. Condition-based maintenance, driven by threshold indicators like temperature or vibration levels, suits facilities with simpler systems and limited data capabilities seeking cost-effective maintenance interventions.
Future Trends in Maintenance Technologies
Predictive Maintenance leverages advanced AI algorithms and IoT sensor data to forecast equipment failures before they occur, optimizing maintenance schedules and minimizing downtime. Condition-Based Maintenance relies on real-time monitoring of machinery health, using vibration analysis, temperature sensors, and ultrasonic testing to trigger maintenance actions only when necessary. Future trends highlight the integration of machine learning, edge computing, and digital twins to enhance predictive accuracy and enable more precise, data-driven maintenance strategies.
Predictive Maintenance vs Condition-Based Maintenance Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com