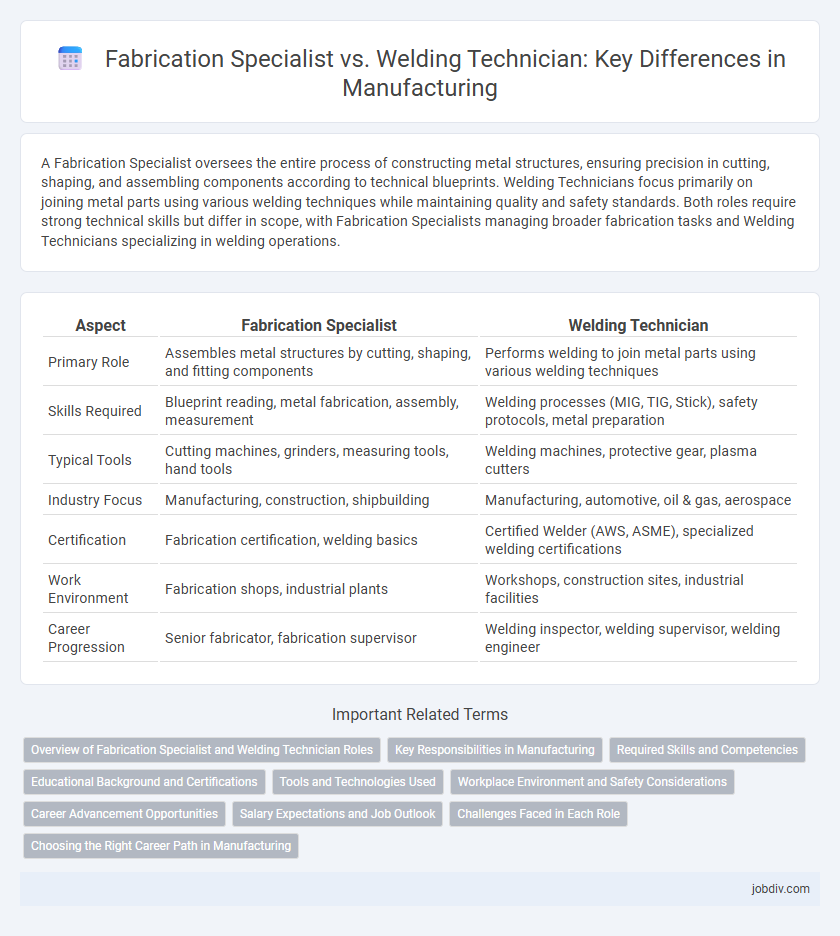
A Fabrication Specialist oversees the entire process of constructing metal structures, ensuring precision in cutting, shaping, and assembling components according to technical blueprints. Welding Technicians focus primarily on joining metal parts using various welding techniques while maintaining quality and safety standards. Both roles require strong technical skills but differ in scope, with Fabrication Specialists managing broader fabrication tasks and Welding Technicians specializing in welding operations.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fabrication Specialist | Welding Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Assembles metal structures by cutting, shaping, and fitting components | Performs welding to join metal parts using various welding techniques |
| Skills Required | Blueprint reading, metal fabrication, assembly, measurement | Welding processes (MIG, TIG, Stick), safety protocols, metal preparation |
| Typical Tools | Cutting machines, grinders, measuring tools, hand tools | Welding machines, protective gear, plasma cutters |
| Industry Focus | Manufacturing, construction, shipbuilding | Manufacturing, automotive, oil & gas, aerospace |
| Certification | Fabrication certification, welding basics | Certified Welder (AWS, ASME), specialized welding certifications |
| Work Environment | Fabrication shops, industrial plants | Workshops, construction sites, industrial facilities |
| Career Progression | Senior fabricator, fabrication supervisor | Welding inspector, welding supervisor, welding engineer |
Overview of Fabrication Specialist and Welding Technician Roles
Fabrication specialists focus on assembling metal structures by interpreting blueprints, measuring materials, and operating machinery to create customized components, often requiring proficiency in cutting, shaping, and fitting metals. Welding technicians specialize in joining metal parts using various welding techniques such as MIG, TIG, and arc welding, ensuring strong, durable bonds and adherence to safety standards. Both roles demand knowledge of metallurgy, precision, and adherence to industry regulations within manufacturing environments.
Key Responsibilities in Manufacturing
Fabrication specialists focus on interpreting blueprints, cutting, shaping, and assembling metal components to create finished products or structural frameworks in manufacturing. Welding technicians specialize in joining metal parts using various welding techniques, ensuring strong, precise welds that meet industry standards and safety regulations. Both roles require attention to detail, but fabrication specialists manage overall assembly processes, while welding technicians concentrate on metal fusion and joint quality control.
Required Skills and Competencies
Fabrication Specialists must possess advanced skills in reading blueprints, precision measuring, and operating CNC machinery, emphasizing material selection and assembly techniques. Welding Technicians require expertise in various welding methods such as MIG, TIG, and arc welding, along with knowledge of metallurgy, safety standards, and weld inspection protocols. Both roles demand strong problem-solving abilities, attention to detail, and adherence to industry quality standards.
Educational Background and Certifications
Fabrication Specialists typically hold degrees or diplomas in mechanical engineering, manufacturing technology, or industrial design, with certifications such as Certified Manufacturing Engineer (CMfgE) enhancing their credentials. Welding Technicians usually have vocational training or associate degrees in welding technology, complemented by certifications like Certified Welding Inspector (CWI) or American Welding Society (AWS) welding certifications. Both roles require specialized knowledge, but Fabrication Specialists emphasize design and process planning, while Welding Technicians focus on welding techniques and standards compliance.
Tools and Technologies Used
Fabrication specialists utilize advanced CNC machines, plasma cutters, and hydraulic presses to shape and assemble metal components with precision. Welding technicians employ specialized welding equipment such as MIG, TIG, and arc welding machines, alongside diagnostic tools like weld inspection gauges and thermal imaging cameras to ensure strong, defect-free joints. Both roles require proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software and adherence to industry safety standards to optimize manufacturing workflows.
Workplace Environment and Safety Considerations
Fabrication Specialists typically work in controlled workshop environments where precision and adherence to design specifications are critical, often involving tasks such as cutting, shaping, and assembling metal components. Welding Technicians operate in more varied settings, including construction sites and industrial plants, requiring strict compliance with safety protocols to manage hazards like intense heat, fumes, and potential electrical risks. Both roles demand rigorous use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and continuous hazard assessment to ensure workplace safety and minimize injury risks.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Fabrication Specialists often have broader skills in metalworking, assembly, and production processes, enabling them to pursue roles in production management or quality control. Welding Technicians typically advance by obtaining certifications in specialized welding techniques, opening doors to positions such as welding inspectors or welding supervisors. Career advancement for both roles benefits from continuous training in new technologies like robotic welding and computer-aided fabrication.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Fabrication Specialists earn an average salary ranging from $45,000 to $70,000 annually, with demand driven by industries like construction and automotive manufacturing. Welding Technicians typically command salaries between $40,000 and $65,000, supported by steady job growth due to infrastructure development and pipefitting needs. Both roles benefit from technical skills and certification, but Fabrication Specialists generally have a broader scope, leading to higher salary potential and diverse employment opportunities.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
Fabrication specialists often encounter challenges related to interpreting complex blueprints and ensuring precision in assembling metal structures, which demands advanced technical skills and attention to detail. Welding technicians face difficulties in maintaining weld quality under varying environmental conditions and handling different metals and welding techniques, requiring both physical endurance and specialized knowledge. Both roles require stringent safety compliance and adaptation to evolving manufacturing technologies to meet production standards.
Choosing the Right Career Path in Manufacturing
Selecting the right career path in manufacturing depends on understanding the distinct roles of a Fabrication Specialist and a Welding Technician. Fabrication Specialists focus on designing, assembling, and testing metal structures, requiring strong skills in blueprint reading and CNC machinery. Welding Technicians specialize in joining metal parts using various welding techniques, emphasizing precision and safety standards to ensure structural integrity.
Fabrication Specialist vs Welding Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com