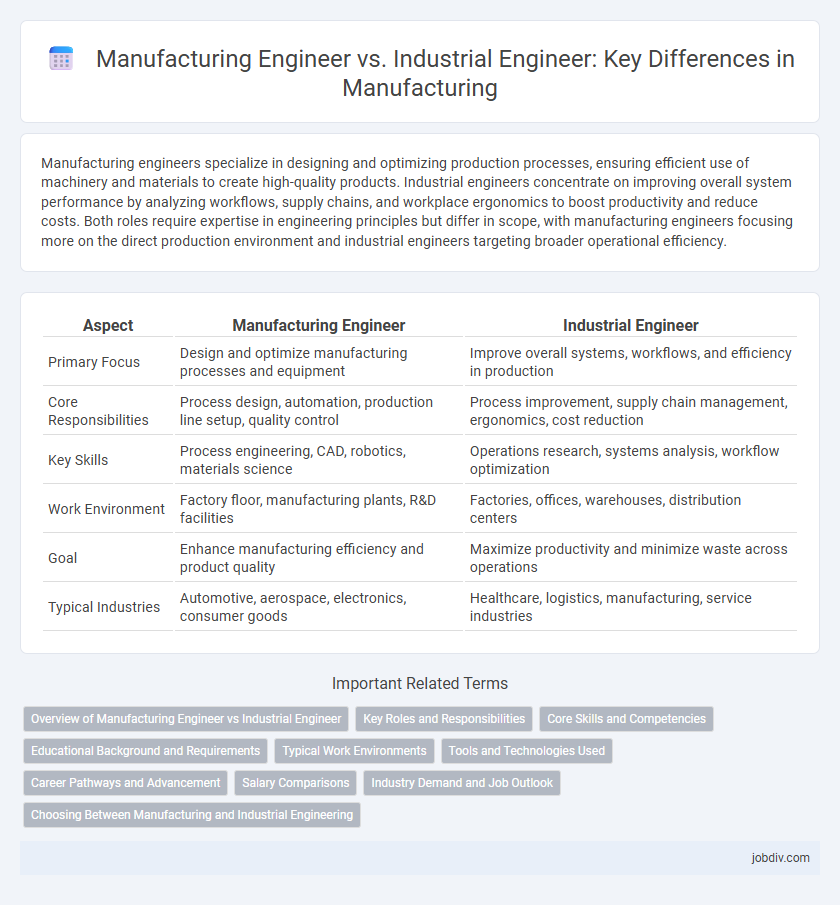
Manufacturing engineers specialize in designing and optimizing production processes, ensuring efficient use of machinery and materials to create high-quality products. Industrial engineers concentrate on improving overall system performance by analyzing workflows, supply chains, and workplace ergonomics to boost productivity and reduce costs. Both roles require expertise in engineering principles but differ in scope, with manufacturing engineers focusing more on the direct production environment and industrial engineers targeting broader operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Manufacturing Engineer | Industrial Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design and optimize manufacturing processes and equipment | Improve overall systems, workflows, and efficiency in production |
| Core Responsibilities | Process design, automation, production line setup, quality control | Process improvement, supply chain management, ergonomics, cost reduction |
| Key Skills | Process engineering, CAD, robotics, materials science | Operations research, systems analysis, workflow optimization |
| Work Environment | Factory floor, manufacturing plants, R&D facilities | Factories, offices, warehouses, distribution centers |
| Goal | Enhance manufacturing efficiency and product quality | Maximize productivity and minimize waste across operations |
| Typical Industries | Automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods | Healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, service industries |
Overview of Manufacturing Engineer vs Industrial Engineer
Manufacturing Engineers specialize in designing and improving production processes, focusing on machinery, automation, and workflow optimization to enhance product quality and efficiency. Industrial Engineers concentrate on optimizing complex systems, including supply chains, workforce management, and facility layout, aiming to reduce costs and improve overall operational performance. Both roles overlap in process improvement but differ in emphasis, with Manufacturing Engineers targeting production technology and Industrial Engineers focusing on system integration and resource management.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Manufacturing Engineers specialize in designing, developing, and improving production processes to enhance efficiency, quality, and safety on the factory floor. Industrial Engineers focus on optimizing complex systems and workflows by analyzing and integrating human factors, logistics, and operational procedures to reduce costs and improve overall productivity. Both roles collaborate to streamline manufacturing operations, with Manufacturing Engineers emphasizing process innovation and Industrial Engineers concentrating on systemic optimization.
Core Skills and Competencies
Manufacturing Engineers specialize in process design, automation, and quality control to optimize production efficiency and product consistency. Industrial Engineers focus on systems integration, workflow optimization, and resource management to enhance overall operational performance and reduce waste. Both roles require strong problem-solving skills, proficiency in CAD and data analysis, and knowledge of Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma methodologies.
Educational Background and Requirements
Manufacturing engineers typically hold degrees in manufacturing engineering, mechanical engineering, or industrial engineering, emphasizing hands-on knowledge of production processes, automation, and quality control. Industrial engineers often have a broader educational background in industrial engineering, focusing on optimizing complex systems, workflow, and efficiency across various industries. Both roles require strong foundations in mathematics, physics, and engineering principles, but manufacturing engineers prioritize manufacturing-specific coursework while industrial engineers study systems analysis and operations research.
Typical Work Environments
Manufacturing Engineers typically work in production plants and assembly lines, focusing on designing, improving, and implementing manufacturing processes to increase efficiency and product quality. Industrial Engineers operate in a broader range of environments, including factories, warehouses, and corporate offices, optimizing complex systems related to human factors, supply chains, and workflow management. Both roles require collaboration with multidisciplinary teams but differ in the scope of process improvement and environment specialization.
Tools and Technologies Used
Manufacturing engineers primarily utilize CAD/CAM software, CNC machines, and robotics to design and optimize production processes, emphasizing automation and precision. Industrial engineers employ simulation software, statistical analysis tools, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to improve workflow efficiency and resource allocation across manufacturing operations. Both disciplines integrate IoT sensors and data analytics platforms to enhance process monitoring and decision-making in smart factories.
Career Pathways and Advancement
Manufacturing Engineers specialize in optimizing production processes, focusing on designing efficient systems and troubleshooting machinery to enhance manufacturing operations. Industrial Engineers concentrate on improving overall organizational efficiency by analyzing workflows, supply chains, and quality control to reduce costs and increase productivity. Career advancement for Manufacturing Engineers often leads to roles in process development or plant management, while Industrial Engineers may progress toward operations management, supply chain leadership, or consulting positions.
Salary Comparisons
Manufacturing Engineers earn an average annual salary of approximately $75,000, focusing on optimizing production processes and equipment efficiency. Industrial Engineers typically have a median salary around $80,000, with roles emphasizing system improvements and operational workflows across industries. Salary variations depend on factors such as experience, location, and industry sector within the manufacturing field.
Industry Demand and Job Outlook
Manufacturing engineers and industrial engineers both play critical roles in optimizing production processes, yet job outlooks differ based on industry demand and specialization. Manufacturing engineers are increasingly sought after in advanced manufacturing sectors like automotive and aerospace due to their expertise in automation and production technology. Industrial engineers maintain strong demand across diverse manufacturing and service industries focused on improving efficiency, supply chain management, and operational cost reduction.
Choosing Between Manufacturing and Industrial Engineering
Manufacturing engineers specialize in optimizing production processes, focusing on machinery, tools, and workflow efficiency to enhance product quality and reduce costs. Industrial engineers emphasize system-wide improvements by analyzing supply chains, logistics, and human factors to maximize overall operational efficiency. Choosing between manufacturing and industrial engineering depends on whether the priority lies in direct production optimization or comprehensive process and system integration within manufacturing environments.
Manufacturing Engineer vs Industrial Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com