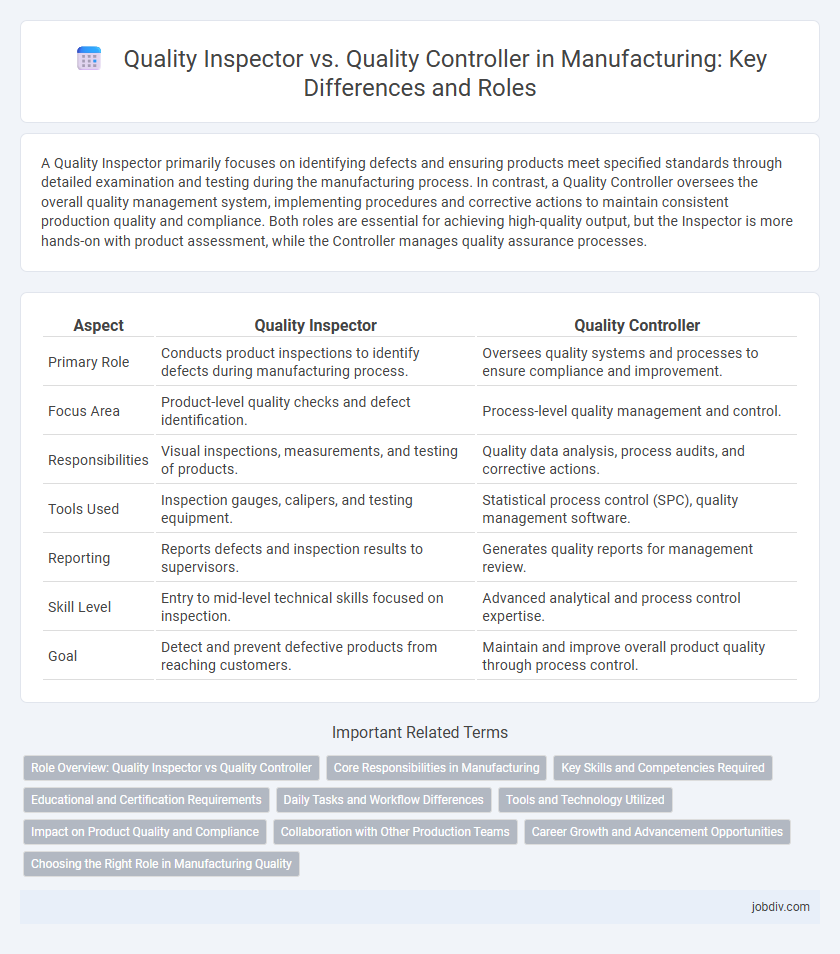
A Quality Inspector primarily focuses on identifying defects and ensuring products meet specified standards through detailed examination and testing during the manufacturing process. In contrast, a Quality Controller oversees the overall quality management system, implementing procedures and corrective actions to maintain consistent production quality and compliance. Both roles are essential for achieving high-quality output, but the Inspector is more hands-on with product assessment, while the Controller manages quality assurance processes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Quality Inspector | Quality Controller |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Conducts product inspections to identify defects during manufacturing process. | Oversees quality systems and processes to ensure compliance and improvement. |
| Focus Area | Product-level quality checks and defect identification. | Process-level quality management and control. |
| Responsibilities | Visual inspections, measurements, and testing of products. | Quality data analysis, process audits, and corrective actions. |
| Tools Used | Inspection gauges, calipers, and testing equipment. | Statistical process control (SPC), quality management software. |
| Reporting | Reports defects and inspection results to supervisors. | Generates quality reports for management review. |
| Skill Level | Entry to mid-level technical skills focused on inspection. | Advanced analytical and process control expertise. |
| Goal | Detect and prevent defective products from reaching customers. | Maintain and improve overall product quality through process control. |
Role Overview: Quality Inspector vs Quality Controller
Quality Inspectors focus on examining products during and after production to ensure compliance with quality standards, using tools to identify defects and deviations. Quality Controllers develop and implement quality control processes, analyze inspection data, and enforce corrective actions to maintain consistent product quality. Both roles collaborate to minimize defects and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements in manufacturing environments.
Core Responsibilities in Manufacturing
Quality Inspectors conduct detailed examinations of products and materials during various stages of manufacturing to ensure compliance with industry standards and specifications. Quality Controllers develop and implement quality management systems, analyze inspection data, and oversee corrective actions to maintain overall product quality and process efficiency. Both roles collaborate closely to identify defects, minimize production errors, and uphold regulatory requirements in manufacturing environments.
Key Skills and Competencies Required
Quality Inspectors require strong attention to detail, proficiency in inspection tools, and knowledge of product specifications to identify defects and ensure compliance with standards. Quality Controllers demand advanced analytical skills, expertise in quality management systems (QMS), and the ability to interpret data for continuous process improvement. Both roles necessitate effective communication and problem-solving abilities to maintain manufacturing quality and uphold regulatory requirements.
Educational and Certification Requirements
Quality Inspectors typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, with on-the-job training or technical certifications such as ASQ Certified Quality Inspector (CQI) enhancing their qualifications. Quality Controllers often hold a bachelor's degree in engineering, manufacturing, or quality management fields, supplemented by advanced certifications like ASQ Certified Quality Engineer (CQE) or Six Sigma Black Belt. The higher educational background and specialized certifications enable Quality Controllers to design and implement quality systems, whereas Quality Inspectors focus on executing inspections and identifying defects.
Daily Tasks and Workflow Differences
Quality Inspectors perform routine checks on raw materials, in-process components, and finished products to detect defects and ensure compliance with specifications, documenting findings for traceability. Quality Controllers analyze inspection data, coordinate corrective actions, and oversee quality assurance processes to maintain production standards and minimize variability. Inspectors focus on hands-on evaluation during production, while Controllers manage workflow integration and enforce quality improvement strategies.
Tools and Technology Utilized
Quality Inspectors utilize handheld measurement tools, visual inspection systems, and digital gauges to identify product defects and ensure compliance with manufacturing standards. Quality Controllers leverage advanced statistical software, automated quality management systems (QMS), and real-time data analytics tools to monitor process performance and implement continuous improvement strategies. The integration of AI-driven inspection technologies and IoT sensors enables both roles to enhance accuracy, reduce errors, and streamline quality assurance workflows in manufacturing environments.
Impact on Product Quality and Compliance
Quality Inspectors play a crucial role in identifying defects and ensuring products meet specified criteria during various production stages, directly preventing defective items from reaching customers and enhancing overall product quality. Quality Controllers oversee the implementation of quality processes and standards, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and continuous improvement initiatives that maintain consistent product excellence. The combined impact of these roles results in reduced product recalls, improved customer satisfaction, and adherence to industry regulations critical for manufacturing success.
Collaboration with Other Production Teams
Quality Inspectors collaborate closely with production teams by performing on-site inspections to ensure products meet specified standards, providing immediate feedback for process adjustments. Quality Controllers coordinate with multiple departments, analyzing inspection data to implement systemic quality improvements across production lines. This collaborative dynamic enhances overall manufacturing efficiency and reduces defect rates.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
Quality Inspectors primarily focus on identifying defects and ensuring products meet specified standards, providing a foundational role essential for entry into manufacturing quality assurance. Quality Controllers take on broader responsibilities, including process optimization and compliance oversight, positioning themselves for managerial roles and strategic decision-making within quality management systems. Advancing from a Quality Inspector to a Quality Controller often leads to enhanced career growth, higher salary potential, and opportunities in leadership and continuous improvement initiatives.
Choosing the Right Role in Manufacturing Quality
Choosing the right role in manufacturing quality depends on understanding the distinct responsibilities of a Quality Inspector and a Quality Controller. Quality Inspectors focus on identifying product defects through visual examinations and testing during production, ensuring compliance with predefined standards. Quality Controllers analyze inspection data to implement process improvements and maintain overall quality systems, driving continuous enhancement in manufacturing operations.
Quality Inspector vs Quality Controller Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com