A Trade Compliance Specialist ensures that international transactions adhere to regulatory requirements, minimizing legal risks and avoiding penalties. A Risk Analyst focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial and operational risks to protect business assets and enhance decision-making. Both roles are crucial in maintaining secure and compliant global trade operations.
Table of Comparison
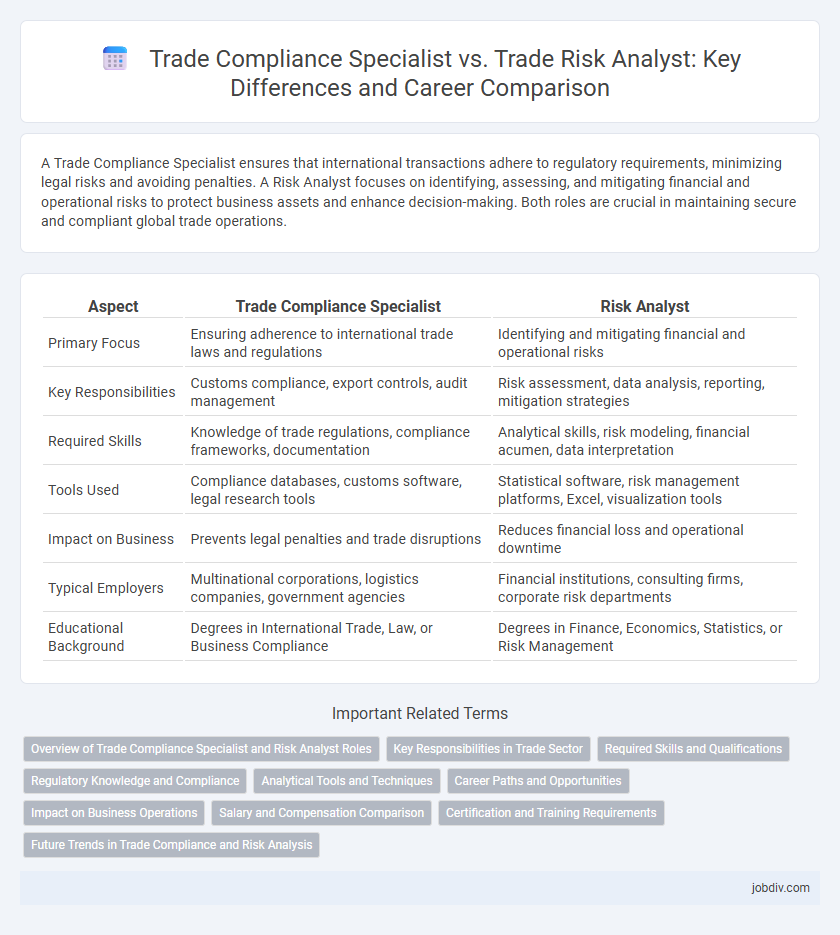
| Aspect | Trade Compliance Specialist | Risk Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Ensuring adherence to international trade laws and regulations | Identifying and mitigating financial and operational risks |
| Key Responsibilities | Customs compliance, export controls, audit management | Risk assessment, data analysis, reporting, mitigation strategies |
| Required Skills | Knowledge of trade regulations, compliance frameworks, documentation | Analytical skills, risk modeling, financial acumen, data interpretation |
| Tools Used | Compliance databases, customs software, legal research tools | Statistical software, risk management platforms, Excel, visualization tools |
| Impact on Business | Prevents legal penalties and trade disruptions | Reduces financial loss and operational downtime |
| Typical Employers | Multinational corporations, logistics companies, government agencies | Financial institutions, consulting firms, corporate risk departments |
| Educational Background | Degrees in International Trade, Law, or Business Compliance | Degrees in Finance, Economics, Statistics, or Risk Management |
Overview of Trade Compliance Specialist and Risk Analyst Roles
Trade Compliance Specialists ensure adherence to international trade regulations, manage documentation, and mitigate risks associated with customs laws and export controls. Risk Analysts identify, assess, and prioritize trade-related risks by analyzing market trends, regulatory changes, and financial data to support decision-making. Both roles are critical in maintaining legal compliance and minimizing financial and operational risks within global trade environments.
Key Responsibilities in Trade Sector
Trade Compliance Specialists ensure adherence to international trade regulations by monitoring shipments, verifying documentation, and managing customs procedures to prevent legal violations. Risk Analysts evaluate potential financial, operational, and regulatory risks within trade transactions, employing data analysis and market intelligence to recommend mitigation strategies. Both roles collaborate to safeguard organizations from trade-related penalties and optimize supply chain integrity.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Trade Compliance Specialists require deep knowledge of international trade laws, customs regulations, and export controls, along with strong attention to detail and proficiency in compliance software. Risk Analysts must excel in data analysis, risk assessment methodologies, and financial modeling, often holding certifications like FRM or CFA to evaluate trade-related risks effectively. Both roles demand strong communication skills and the ability to interpret complex regulatory environments, but Trade Compliance Specialists focus more on legal adherence while Risk Analysts emphasize strategic risk mitigation.
Regulatory Knowledge and Compliance
Trade Compliance Specialists possess in-depth regulatory knowledge of international trade laws, export controls, and customs regulations, ensuring companies adhere to all legal requirements and avoid penalties. Risk Analysts focus on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks, including regulatory risks, by analyzing data and market trends but may lack the detailed compliance expertise required for navigating complex trade regulations. Effective trade management often relies on collaboration where Trade Compliance Specialists provide regulatory insights while Risk Analysts evaluate potential impacts on business operations.
Analytical Tools and Techniques
Trade Compliance Specialists utilize tools like global trade management software and regulatory databases to ensure adherence to import-export laws and sanctions. Risk Analysts apply advanced analytical techniques, including predictive modeling and risk assessment frameworks, to identify and mitigate potential operational and financial risks in trade processes. Both roles leverage data analytics platforms and compliance monitoring systems, but Risk Analysts emphasize quantitative risk evaluation while Trade Compliance Specialists focus on regulatory alignment.
Career Paths and Opportunities
Trade Compliance Specialists focus on ensuring regulatory adherence and managing import-export documentation, positioning themselves for careers in global trade management or customs consulting. Risk Analysts analyze market trends and operational risks, leading to opportunities in financial risk management or strategic planning within trade organizations. Both roles offer growth in multinational corporations, with Trade Compliance Specialists specializing in legal frameworks, while Risk Analysts emphasize data-driven decision-making.
Impact on Business Operations
Trade Compliance Specialists ensure adherence to international trade regulations, minimizing risks of legal penalties and shipment delays. Risk Analysts evaluate potential financial and operational threats, enabling proactive strategies that protect company assets and optimize resource allocation. Both roles significantly influence business continuity, with compliance safeguarding regulatory standing and risk analysis driving informed decision-making.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Trade Compliance Specialists typically earn a median salary ranging from $60,000 to $85,000 annually, reflecting their expertise in regulatory adherence and customs documentation. Risk Analysts, focusing on identifying and mitigating financial and operational risks, command slightly higher compensation, often between $70,000 and $95,000 per year, based on industry and experience level. Compensation packages for both roles may include bonuses, benefits, and performance incentives, with Risk Analysts generally receiving higher variable pay due to their impact on strategic risk management.
Certification and Training Requirements
Trade Compliance Specialists typically require certifications such as Certified Customs Specialist (CCS) or Certified Trade Compliance Professional (CTCP), emphasizing knowledge in customs regulations and export controls. Risk Analysts often pursue certifications like Financial Risk Manager (FRM) or Certified Risk Analyst (CRA), focusing on risk assessment methodologies and financial regulations. Training for Trade Compliance Specialists centers on trade laws and international shipping procedures, while Risk Analysts undergo advanced training in data analysis, risk modeling, and regulatory compliance frameworks.
Future Trends in Trade Compliance and Risk Analysis
Trade Compliance Specialists will increasingly leverage AI-driven regulatory technology to ensure adherence to evolving international trade laws, minimizing violations and penalties. Risk Analysts are expected to integrate predictive analytics and machine learning models to proactively identify and mitigate supply chain disruptions and geopolitical risks. Both roles will converge through advanced data integration platforms, enhancing real-time decision-making and strategic trade risk management.
Trade Compliance Specialist vs Risk Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com