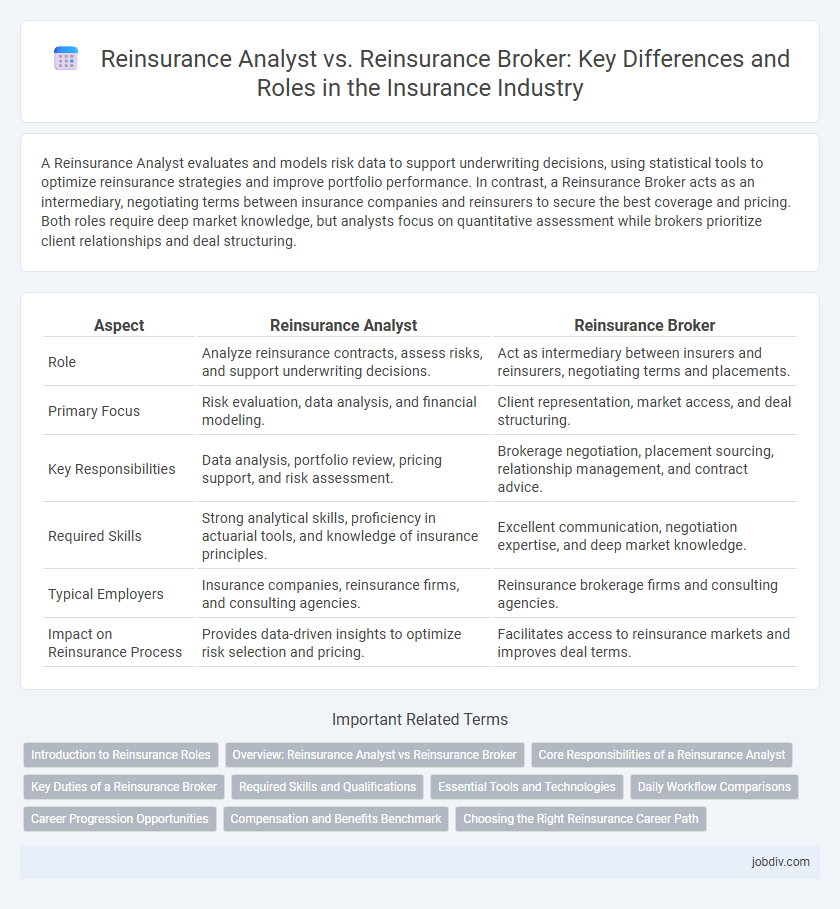
A Reinsurance Analyst evaluates and models risk data to support underwriting decisions, using statistical tools to optimize reinsurance strategies and improve portfolio performance. In contrast, a Reinsurance Broker acts as an intermediary, negotiating terms between insurance companies and reinsurers to secure the best coverage and pricing. Both roles require deep market knowledge, but analysts focus on quantitative assessment while brokers prioritize client relationships and deal structuring.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reinsurance Analyst | Reinsurance Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Analyze reinsurance contracts, assess risks, and support underwriting decisions. | Act as intermediary between insurers and reinsurers, negotiating terms and placements. |
| Primary Focus | Risk evaluation, data analysis, and financial modeling. | Client representation, market access, and deal structuring. |
| Key Responsibilities | Data analysis, portfolio review, pricing support, and risk assessment. | Brokerage negotiation, placement sourcing, relationship management, and contract advice. |
| Required Skills | Strong analytical skills, proficiency in actuarial tools, and knowledge of insurance principles. | Excellent communication, negotiation expertise, and deep market knowledge. |
| Typical Employers | Insurance companies, reinsurance firms, and consulting agencies. | Reinsurance brokerage firms and consulting agencies. |
| Impact on Reinsurance Process | Provides data-driven insights to optimize risk selection and pricing. | Facilitates access to reinsurance markets and improves deal terms. |
Introduction to Reinsurance Roles
Reinsurance analysts evaluate risk portfolios and pricing models to support underwriting decisions, ensuring financial stability in insurance markets. Reinsurance brokers act as intermediaries, negotiating terms and placing reinsurance contracts between insurers and reinsurers to optimize coverage and cost. Both roles require deep knowledge of reinsurance structures, market dynamics, and regulatory frameworks to effectively manage risk transfer.
Overview: Reinsurance Analyst vs Reinsurance Broker
A Reinsurance Analyst evaluates risk exposure, pricing, and financial data to support insurance companies in optimizing their reinsurance strategies. A Reinsurance Broker acts as an intermediary between insurers and reinsurers, negotiating terms and placing reinsurance contracts to secure the best coverage and rates. While analysts focus on data-driven risk assessment and portfolio management, brokers emphasize market relationships and transaction facilitation within the reinsurance industry.
Core Responsibilities of a Reinsurance Analyst
A Reinsurance Analyst primarily evaluates risk portfolios, assesses contract terms, and supports underwriting decisions by analyzing data trends and financial impacts. They ensure accuracy in pricing models, monitor claim experience, and prepare detailed reports for risk management teams. Unlike a Reinsurance Broker who negotiates and places reinsurance treaties between insurers and reinsurers, the analyst focuses on data-driven risk assessment and internal strategy optimization.
Key Duties of a Reinsurance Broker
A Reinsurance Broker acts as an intermediary between insurance companies and reinsurers, negotiating terms and securing reinsurance coverage tailored to the client's risk profile. Key duties include assessing market conditions, evaluating reinsurance capacity, and advising insurers on optimal treaty structures to mitigate risks. They also facilitate contract placement, manage renewals, and maintain client relationships to ensure continuous and effective reinsurance support.
Required Skills and Qualifications
A Reinsurance Analyst requires strong analytical skills, proficiency in data modeling, and expertise in risk assessment, typically holding a degree in finance, actuarial science, or insurance. A Reinsurance Broker needs exceptional negotiation abilities, industry networking, and in-depth knowledge of market trends, often supported by certifications like Chartered Insurance Broker (CIB). Both roles demand understanding of reinsurance contracts, regulatory compliance, and effective communication, but the analyst focuses more on quantitative analysis while the broker emphasizes relationship management and deal structuring.
Essential Tools and Technologies
Reinsurance analysts rely heavily on advanced data analytics software, predictive modeling tools, and risk assessment platforms such as SAS, R, and Python to evaluate ceded risk portfolios and optimize treaty structures. Reinsurance brokers utilize specialized CRM systems, market intelligence tools, and digital contract management software like Salesforce, AcordX, and ClickNotices to efficiently negotiate terms and streamline client communications. Both roles increasingly adopt AI-driven solutions and cloud-based platforms to enhance accuracy, operational efficiency, and data integration within the reinsurance ecosystem.
Daily Workflow Comparisons
Reinsurance analysts primarily focus on risk assessment, data modeling, and loss forecasting using complex actuarial and financial tools to support underwriting and pricing decisions. Reinsurance brokers, on the other hand, engage in client relationship management, market research, and negotiation with reinsurers to secure optimal coverage terms and premium rates. While analysts emphasize quantitative analysis and reporting, brokers prioritize communication, strategy, and deal facilitation in their daily workflow.
Career Progression Opportunities
Reinsurance analysts typically advance by deepening expertise in risk assessment, pricing models, and data analysis, often progressing to senior analyst or risk management roles within insurance companies or reinsurers. Reinsurance brokers have career growth opportunities through client relationship management, deal negotiation, and market development, with potential advancement to senior broker, brokerage manager, or executive leadership positions. Both paths demand strong industry knowledge, but analysts focus on technical evaluation while brokers excel in strategic sales and networking, shaping distinct yet complementary career trajectories in the reinsurance sector.
Compensation and Benefits Benchmark
Reinsurance Analysts typically earn a structured salary with performance bonuses tied to risk assessment accuracy and portfolio management, aligning compensation with company profitability. Reinsurance Brokers receive commission-based compensation plus base salary, incentivizing client acquisition and deal closure, often resulting in higher variable pay. Benchmark data shows Brokers generally achieve higher total compensation ceilings due to commission structures, while Analysts benefit from more stable earnings and comprehensive benefits packages including health insurance, retirement plans, and professional development support.
Choosing the Right Reinsurance Career Path
A Reinsurance Analyst specializes in evaluating risk data, financial reports, and treaty structures to advise insurance companies on optimizing their reinsurance programs. A Reinsurance Broker acts as an intermediary between insurers and reinsurers, negotiating contracts and securing coverage terms that best fit client needs. Choosing the right career path depends on whether one prefers analytical roles focused on risk assessment or client-facing roles centered around negotiation and relationship management in the reinsurance industry.
Reinsurance Analyst vs Reinsurance Broker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com