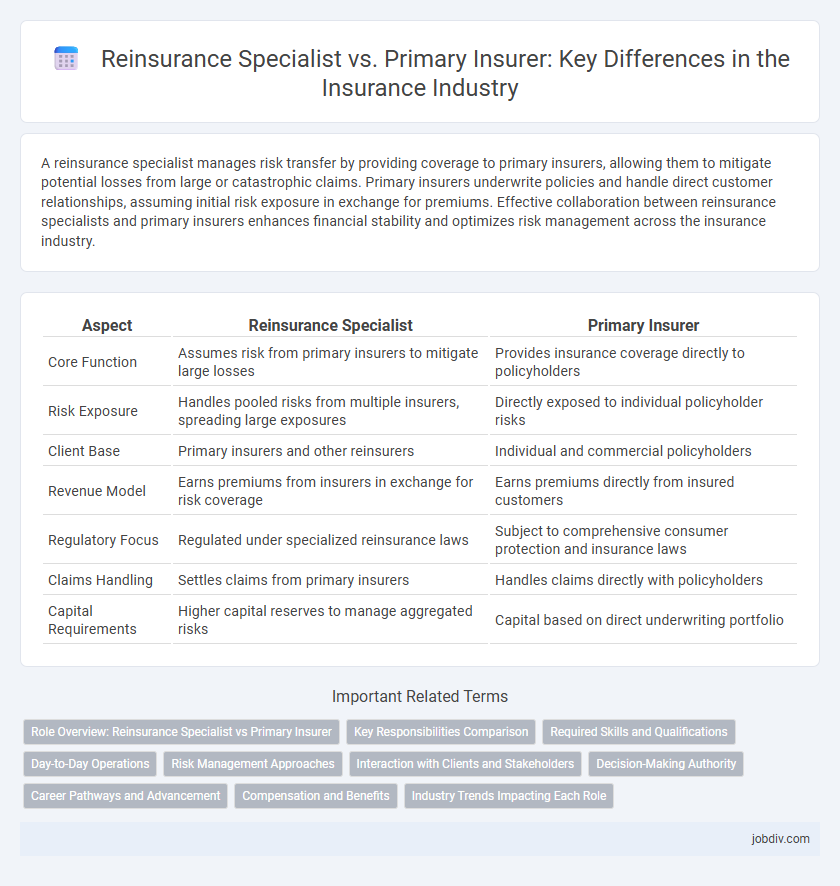
A reinsurance specialist manages risk transfer by providing coverage to primary insurers, allowing them to mitigate potential losses from large or catastrophic claims. Primary insurers underwrite policies and handle direct customer relationships, assuming initial risk exposure in exchange for premiums. Effective collaboration between reinsurance specialists and primary insurers enhances financial stability and optimizes risk management across the insurance industry.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reinsurance Specialist | Primary Insurer |
|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Assumes risk from primary insurers to mitigate large losses | Provides insurance coverage directly to policyholders |
| Risk Exposure | Handles pooled risks from multiple insurers, spreading large exposures | Directly exposed to individual policyholder risks |
| Client Base | Primary insurers and other reinsurers | Individual and commercial policyholders |
| Revenue Model | Earns premiums from insurers in exchange for risk coverage | Earns premiums directly from insured customers |
| Regulatory Focus | Regulated under specialized reinsurance laws | Subject to comprehensive consumer protection and insurance laws |
| Claims Handling | Settles claims from primary insurers | Handles claims directly with policyholders |
| Capital Requirements | Higher capital reserves to manage aggregated risks | Capital based on direct underwriting portfolio |
Role Overview: Reinsurance Specialist vs Primary Insurer
A Reinsurance Specialist manages risk by securing insurance for insurance companies, enabling primary insurers to underwrite larger policies and stabilize loss exposure. Primary Insurers directly provide coverage to policyholders, handling claims, premiums, and client relationships. The Reinsurance Specialist's expertise lies in structuring reinsurance treaties and negotiating terms, while Primary Insurers focus on underwriting and customer service.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Reinsurance specialists assess and manage risk portfolios by underwriting insurance policies for other insurers, facilitating risk transfer and mitigating large-scale losses. Primary insurers focus on underwriting policies directly for individual or corporate policyholders, handling claims processing, and providing customer service. The reinsurance role emphasizes risk assessment across multiple insurers, while primary insurers concentrate on policy issuance and claims management for their insured clients.
Required Skills and Qualifications
A Reinsurance Specialist must possess advanced analytical skills, deep expertise in risk assessment, and proficiency in complex financial modeling to evaluate reinsurance treaties and manage large-scale risk portfolios. In contrast, a Primary Insurer typically requires strong underwriting experience, customer relationship management abilities, and regulatory compliance knowledge to directly assess and price insurance policies for individual clients. Both roles demand a solid understanding of insurance principles, strong attention to detail, and proficiency in industry-specific software, but the Reinsurance Specialist leans more towards strategic risk mitigation while the Primary Insurer focuses on policy issuance and claims management.
Day-to-Day Operations
Reinsurance specialists manage risk transfer agreements and evaluate exposure by analyzing portfolios from multiple primary insurers, ensuring financial stability and loss mitigation. Primary insurers handle direct customer policies, underwriting, claims processing, and customer service on a daily basis to maintain policyholder satisfaction and regulatory compliance. Both roles require detailed data analysis but differ primarily in their operational scope, with reinsurers focusing on broader risk aggregation and primary insurers concentrating on individual policy management.
Risk Management Approaches
Reinsurance specialists and primary insurers employ distinct risk management approaches to mitigate exposure and enhance financial stability. Reinsurance specialists primarily focus on transferring part of the risk portfolios from primary insurers through treaty or facultative reinsurance agreements, enabling risk diversification and capital relief. Primary insurers concentrate on underwriting accuracy, claims management, and pricing strategies to assess and retain manageable risk levels before ceding excess exposure to reinsurers.
Interaction with Clients and Stakeholders
Reinsurance specialists primarily engage with primary insurers to assess risk portfolios and structure coverage agreement terms, ensuring capital stability and risk mitigation. Primary insurers interact directly with clients, managing underwriting, policy issuance, and claims processing while relying on reinsurers for financial backing and risk transfer. Effective communication and collaboration between reinsurance specialists and primary insurers enhance client service, optimize risk management, and improve overall policyholder satisfaction.
Decision-Making Authority
Reinsurance specialists possess decision-making authority primarily in evaluating risk transfer agreements and negotiating terms between primary insurers and reinsurers. Primary insurers hold direct decision-making power over underwriting policies, client risk assessments, and premium setting, which significantly impact initial risk exposure. Effective collaboration between reinsurance specialists and primary insurers ensures balanced risk management and financial stability across insurance portfolios.
Career Pathways and Advancement
A Reinsurance Specialist typically advances by gaining expertise in risk assessment, treaty negotiation, and portfolio management within the reinsurance sector, often progressing to senior roles such as reinsurance manager or underwriter. In contrast, career pathways for a Primary Insurer focus on underwriting, claims management, and product development, leading to positions like underwriting manager or claims director. Both roles require deep industry knowledge, but reinsurance specialists tend to develop more strategic skills related to risk distribution and capital optimization, while primary insurers emphasize customer-facing operations and policy administration.
Compensation and Benefits
Reinsurance specialists typically receive compensation packages that include higher base salaries and performance bonuses reflecting the complex risk assessments and negotiations they manage. Primary insurers offer benefits focused on broader employee wellness, including comprehensive health plans and retirement contributions, to support their larger, more diverse workforce. Both roles may receive stock options and profit-sharing incentives, but reinsurance specialists often benefit from tailored financial rewards linked directly to treaty profitability and risk mitigation outcomes.
Industry Trends Impacting Each Role
Reinsurance specialists navigate evolving industry trends such as increased demand for catastrophe risk modeling and the integration of advanced analytics to optimize risk transfer strategies. Primary insurers face mounting regulatory pressures and the need to enhance underwriting accuracy through AI technologies to remain competitive in a saturated market. Both roles are influenced by the growing importance of cyber risk coverage and the shift toward more tailored, data-driven insurance products.
Reinsurance Specialist vs Primary Insurer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com