Extrusion operators specialize in shaping raw materials by forcing them through a die to create continuous profiles, while injection molding operators manage machines that inject molten material into molds to produce complex, detailed parts. Both roles require precise control of temperature, pressure, and machine settings to ensure product quality but differ in the type of machinery and material handling techniques involved. Expertise in troubleshooting and maintaining specific equipment is essential to optimize efficiency and minimize defects in their respective processes.
Table of Comparison
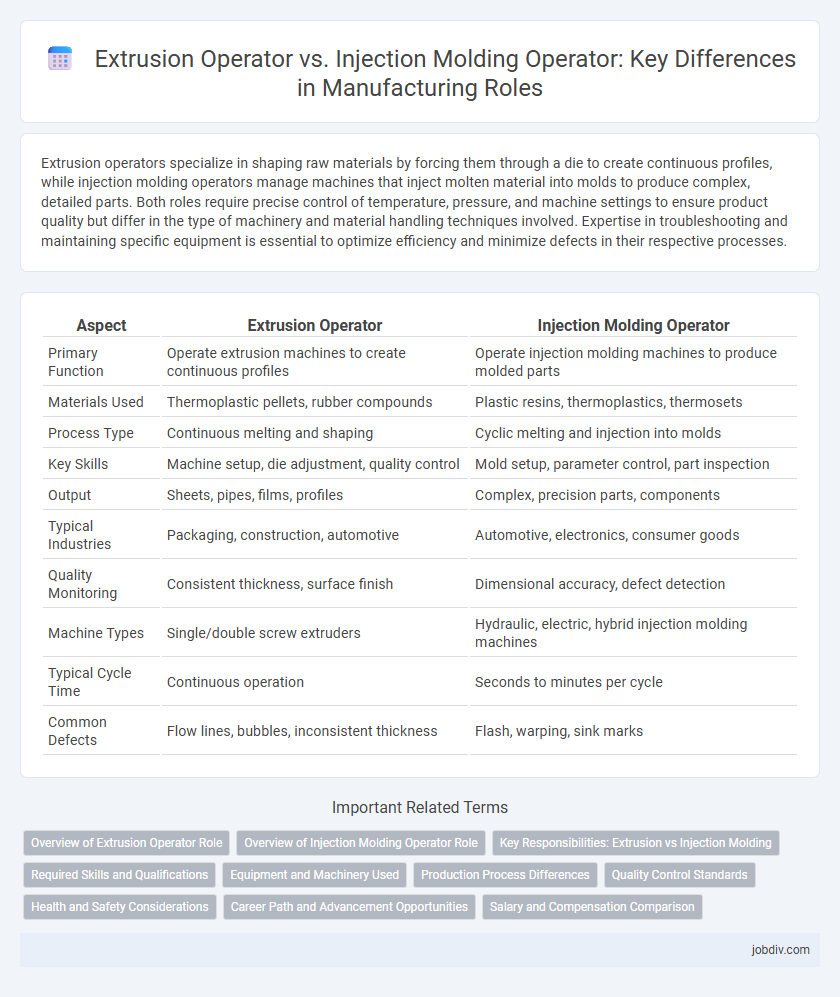
| Aspect | Extrusion Operator | Injection Molding Operator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Operate extrusion machines to create continuous profiles | Operate injection molding machines to produce molded parts |
| Materials Used | Thermoplastic pellets, rubber compounds | Plastic resins, thermoplastics, thermosets |
| Process Type | Continuous melting and shaping | Cyclic melting and injection into molds |
| Key Skills | Machine setup, die adjustment, quality control | Mold setup, parameter control, part inspection |
| Output | Sheets, pipes, films, profiles | Complex, precision parts, components |
| Typical Industries | Packaging, construction, automotive | Automotive, electronics, consumer goods |
| Quality Monitoring | Consistent thickness, surface finish | Dimensional accuracy, defect detection |
| Machine Types | Single/double screw extruders | Hydraulic, electric, hybrid injection molding machines |
| Typical Cycle Time | Continuous operation | Seconds to minutes per cycle |
| Common Defects | Flow lines, bubbles, inconsistent thickness | Flash, warping, sink marks |
Overview of Extrusion Operator Role
Extrusion Operators in manufacturing specialize in feeding raw materials into extruders to create continuous profiles such as pipes, sheets, or films, ensuring precise temperature and pressure controls for quality output. They monitor machine functions, conduct routine maintenance, and adjust settings to meet product specifications and minimize waste. Mastery of extrusion processes and safety protocols distinguishes them from Injection Molding Operators, who primarily handle plastic injection machines for molded parts.
Overview of Injection Molding Operator Role
Injection molding operators specialize in setting up, operating, and maintaining injection molding machines that produce plastic parts by injecting molten material into molds. They monitor machine parameters, adjust settings for quality control, and troubleshoot issues to ensure consistent production efficiency. Skilled in interpreting technical specifications, they collaborate closely with quality assurance teams to meet strict manufacturing standards in automotive, medical, and consumer goods industries.
Key Responsibilities: Extrusion vs Injection Molding
Extrusion Operators primarily manage the continuous process of pushing raw materials through a shaped die to create products like pipes, sheets, or profiles, ensuring consistent material flow and temperature control. Injection Molding Operators focus on injecting molten plastic into molds to produce precise, often complex parts, maintaining mold temperature, injection pressure, and cycle timing for quality output. Both roles require monitoring machine parameters and conducting quality inspections, but extrusion emphasizes steady extrusion rates and die maintenance, while injection molding centers on mold setup and troubleshooting molding defects.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Extrusion operators must have a deep understanding of material properties, machine setup, and process control to produce consistent, high-quality products using extrusion equipment. Injection molding operators require expertise in mold setup, temperature and pressure control, and troubleshooting to ensure precise molding cycles and defect-free parts. Both roles demand strong technical skills, attention to detail, and familiarity with safety protocols and quality assurance standards in manufacturing environments.
Equipment and Machinery Used
Extrusion Operators utilize extrusion machines that heat and force raw materials through a shaped die to create continuous profiles, commonly involving single or twin-screw extruders. Injection Molding Operators work with injection molding machines that inject molten material into molds under high pressure to form discrete parts, often featuring clamping units and hydraulic or electric screw-driven systems. Both roles require precise control of temperature, pressure, and machine settings specific to the equipment type for efficient production and quality consistency.
Production Process Differences
Extrusion operators manage continuous manufacturing by forcing heated raw materials through a die to create long, uniform shapes such as pipes or sheets, emphasizing steady flow control and die maintenance. Injection molding operators handle the batch process of injecting molten plastic into molds to form complex, precise parts, requiring careful mold setup and cycle time optimization. Production in extrusion prioritizes speed and material uniformity, while injection molding focuses on mold accuracy and repeatability for intricate components.
Quality Control Standards
Extrusion operators ensure product consistency by closely monitoring temperature, pressure, and material flow to meet strict quality control standards. Injection molding operators focus on maintaining precise mold temperatures, cycle times, and material viscosity to minimize defects and ensure dimensional accuracy. Both roles implement rigorous inspection protocols and utilize statistical process control (SPC) tools to uphold manufacturing quality and reduce variability.
Health and Safety Considerations
Extrusion operators face risks such as exposure to high temperatures, molten materials, and mechanical hazards requiring strict use of heat-resistant gloves and protective eyewear. Injection molding operators must manage dangers from high-pressure machines and hot molds, necessitating rigorous lockout/tagout procedures and personal protective equipment to prevent burns and crush injuries. Both roles demand comprehensive safety training and adherence to workplace protocols to minimize accidents and ensure healthy working environments.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Extrusion operators typically develop expertise in continuous production processes involving polymers, enabling advancement into roles such as process technician or production supervisor within plastic extrusion manufacturing. Injection molding operators gain skills in precision mold control and machine setup, with career paths leading to quality control specialist or mold maintenance technician. Both roles offer opportunities for cross-training and advancement into manufacturing engineering or plant management positions, depending on the facility size and technology complexity.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Extrusion Operators typically earn an average hourly wage between $18 and $24, while Injection Molding Operators have a similar range, often from $19 to $25 per hour depending on experience and location. Bonuses and overtime pay can significantly increase total compensation in both roles, with benefits packages including health insurance and retirement plans being standard in manufacturing environments. Salary differences often reflect the complexity of the machinery operated and production output efficiency, making Injection Molding Operators slightly more compensated on average due to higher technical demands.
Extrusion Operator vs Injection Molding Operator Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com