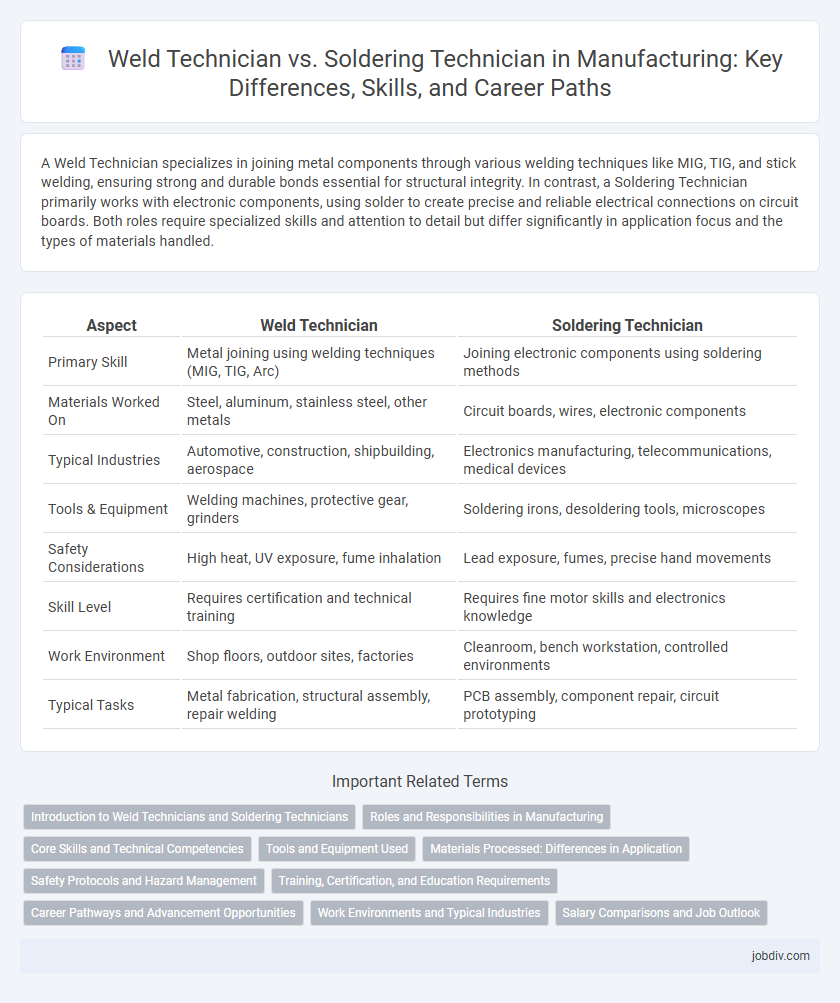
A Weld Technician specializes in joining metal components through various welding techniques like MIG, TIG, and stick welding, ensuring strong and durable bonds essential for structural integrity. In contrast, a Soldering Technician primarily works with electronic components, using solder to create precise and reliable electrical connections on circuit boards. Both roles require specialized skills and attention to detail but differ significantly in application focus and the types of materials handled.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Weld Technician | Soldering Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Skill | Metal joining using welding techniques (MIG, TIG, Arc) | Joining electronic components using soldering methods |
| Materials Worked On | Steel, aluminum, stainless steel, other metals | Circuit boards, wires, electronic components |
| Typical Industries | Automotive, construction, shipbuilding, aerospace | Electronics manufacturing, telecommunications, medical devices |
| Tools & Equipment | Welding machines, protective gear, grinders | Soldering irons, desoldering tools, microscopes |
| Safety Considerations | High heat, UV exposure, fume inhalation | Lead exposure, fumes, precise hand movements |
| Skill Level | Requires certification and technical training | Requires fine motor skills and electronics knowledge |
| Work Environment | Shop floors, outdoor sites, factories | Cleanroom, bench workstation, controlled environments |
| Typical Tasks | Metal fabrication, structural assembly, repair welding | PCB assembly, component repair, circuit prototyping |
Introduction to Weld Technicians and Soldering Technicians
Weld technicians specialize in joining metal parts using heat and pressure techniques such as MIG, TIG, and arc welding, essential for structural integrity in manufacturing. Soldering technicians focus on assembling electronic components by melting solder to create reliable electrical connections on circuit boards. Both roles require precise skill sets and adherence to safety standards to ensure high-quality production outputs.
Roles and Responsibilities in Manufacturing
Weld Technicians specialize in joining metal parts using techniques such as MIG, TIG, and arc welding, ensuring structural integrity and compliance with engineering specifications. Soldering Technicians focus on assembling electronic components by melting solder to create reliable electrical connections on printed circuit boards and small metal parts. Both roles require precision, quality control, and adherence to safety standards but differ significantly in application and material handling within manufacturing.
Core Skills and Technical Competencies
Weld Technicians excel in core skills such as interpreting blueprints, operating welding machines, and applying various welding techniques like MIG, TIG, and stick welding with precision and safety compliance. Soldering Technicians specialize in fine motor skills, proficiency with soldering irons and reflow ovens, and expertise in electronic components assembly, ensuring reliable electrical connectivity and minimal thermal damage. Both roles require thorough understanding of metallurgy principles, quality control standards, and troubleshooting techniques specific to their distinct fabrication processes.
Tools and Equipment Used
Weld technicians primarily use equipment such as MIG welders, TIG welders, plasma cutters, and welding helmets designed for high-intensity heat and metal fusion processes. Soldering technicians rely on precision tools like soldering irons, hot air rework stations, flux, solder wire, and magnifying lenses to join electronic components without damaging sensitive circuitry. Both roles require specialized protective gear, but the tool complexity and thermal requirements differ significantly based on the materials and scale of the manufacturing task.
Materials Processed: Differences in Application
Weld technicians primarily work with metals such as steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, using processes like MIG, TIG, and arc welding to join thick materials in structural and heavy-duty applications. Soldering technicians focus on joining delicate components, often in electronics, using low-temperature solder alloys like tin-lead or lead-free solders on materials such as copper, gold, and circuit boards. The key difference lies in the material thickness and thermal requirements, with welding suited for robust metal fabrication and soldering optimized for precision electrical connections.
Safety Protocols and Hazard Management
Weld Technicians implement stringent safety protocols involving protective gear such as helmets with auto-darkening lenses, flame-resistant clothing, and respirators to guard against intense heat, UV radiation, and fumes. Soldering Technicians prioritize ventilation systems and electrostatic discharge (ESD) controls to mitigate inhalation of flux fumes and prevent damage to sensitive electronic components. Both roles conduct regular hazard assessments and utilize industry-standard procedures to minimize risk exposure during their respective metal joining processes.
Training, Certification, and Education Requirements
Weld Technicians typically require specialized training programs that include hands-on welding techniques, metallurgy, and safety protocols, often paired with certifications such as AWS (American Welding Society) credentials to demonstrate proficiency. Soldering Technicians focus on electronic assembly skills, circuit board repair, and precise temperature control, with certifications from IPC (Institute for Printed Circuits) being highly valued in the electronics manufacturing industry. Both roles demand a strong foundation in technical education, but Welding generally requires more extensive formal training due to the complexity of materials and structural applications.
Career Pathways and Advancement Opportunities
Weld technicians often advance by specializing in advanced welding techniques, obtaining certifications like AWS CWI, and transitioning into roles such as welding inspectors or supervisors. Soldering technicians typically progress by developing expertise in precision electronics soldering, achieving IPC certification, and moving into quality control or process engineering positions. Both career paths offer opportunities for leadership roles and demand continuous skill development aligned with industry standards.
Work Environments and Typical Industries
Weld technicians typically work in heavy industries such as construction, shipbuilding, and automotive manufacturing, often operating in outdoor or industrial settings with exposure to high heat and intense physical conditions. Soldering technicians are commonly employed in electronics manufacturing, aerospace, and medical device industries, working in controlled cleanroom environments requiring precision and attention to delicate components. Both roles demand specialized skills but differ significantly in their work environments and the types of products they help create.
Salary Comparisons and Job Outlook
Weld technicians typically earn higher salaries than soldering technicians due to the complexity and demand for welding skills in industries such as construction and aerospace, with average annual wages ranging from $45,000 to $65,000 compared to soldering technicians' $35,000 to $50,000. Job outlook for weld technicians is robust, driven by infrastructure projects and manufacturing growth, projecting a 6% employment increase over the next decade, while soldering technicians face a more moderate growth rate of around 3% due to automation advancements in electronics assembly. Skill specialization and certifications in welding technology often lead to better earnings and job stability compared to soldering roles.
Weld Technician vs Soldering Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com