Production operators focus on operating machinery and monitoring production lines to ensure efficient manufacturing processes, often handling raw materials and equipment settings. Assembly technicians specialize in putting together components and parts according to detailed schematics or instructions, emphasizing precision and tight quality control. Both roles are critical in manufacturing, but operators are more process-oriented, while assembly technicians prioritize hands-on construction and accuracy.
Table of Comparison
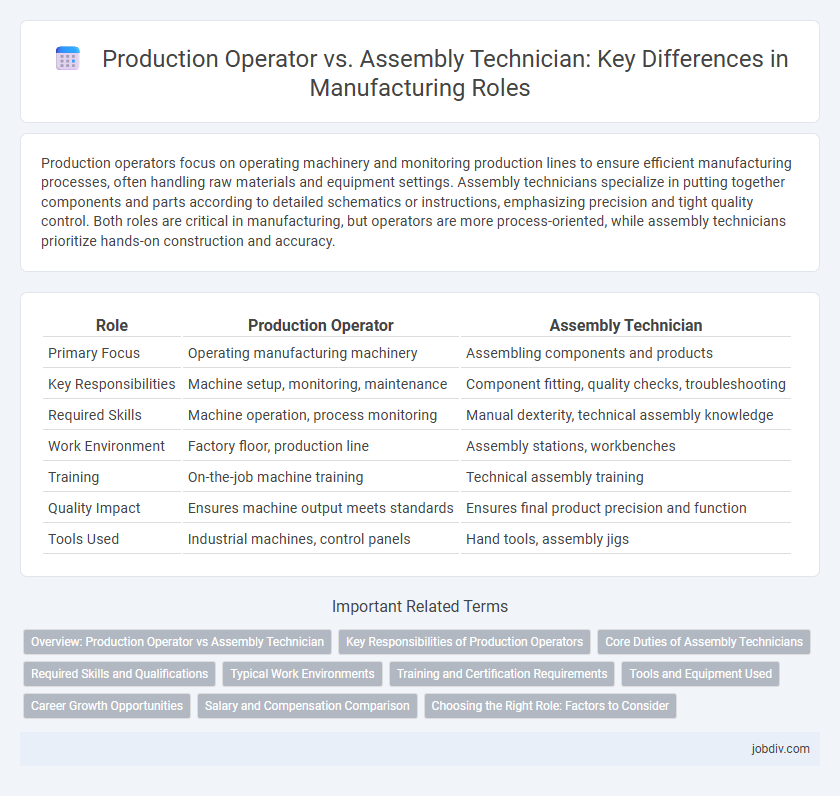
| Role | Production Operator | Assembly Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Operating manufacturing machinery | Assembling components and products |
| Key Responsibilities | Machine setup, monitoring, maintenance | Component fitting, quality checks, troubleshooting |
| Required Skills | Machine operation, process monitoring | Manual dexterity, technical assembly knowledge |
| Work Environment | Factory floor, production line | Assembly stations, workbenches |
| Training | On-the-job machine training | Technical assembly training |
| Quality Impact | Ensures machine output meets standards | Ensures final product precision and function |
| Tools Used | Industrial machines, control panels | Hand tools, assembly jigs |
Overview: Production Operator vs Assembly Technician
Production Operators oversee the entire manufacturing process, ensuring machinery runs efficiently and products meet quality standards, while Assembly Technicians specialize in assembling components and subassemblies according to detailed specifications. Production Operators often handle equipment setup, monitoring, and troubleshooting, whereas Assembly Technicians focus on precise manual or semi-automated assembly tasks. Both roles require attention to detail and adherence to safety protocols but differ in scope and technical responsibilities within the production line.
Key Responsibilities of Production Operators
Production Operators are responsible for operating and maintaining machinery, ensuring efficient production line workflow, and monitoring quality control standards to meet manufacturing specifications. They perform routine equipment inspections, troubleshoot minor mechanical issues, and adhere to safety protocols to minimize downtime and maintain product consistency. Unlike Assembly Technicians who focus on component assembly and fine adjustments, Production Operators oversee the entire production process from material handling to final output.
Core Duties of Assembly Technicians
Assembly technicians specialize in constructing, testing, and inspecting components to ensure product quality and adherence to specifications. Their core duties include reading blueprints, using hand and power tools, and performing precise measurements to maintain assembly accuracy. They collaborate with engineers to troubleshoot production issues, optimize assembly processes, and uphold safety standards on the manufacturing floor.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Production Operators require proficiency in operating machinery, understanding production processes, and maintaining safety standards, with qualifications often including a high school diploma or equivalent. Assembly Technicians need strong manual dexterity, attention to detail, and experience with component fitting or soldering, typically supported by technical training or vocational certification. Both roles demand teamwork, problem-solving capabilities, and adherence to quality control protocols specific to manufacturing environments.
Typical Work Environments
Production Operators typically work in fast-paced manufacturing plants where they handle machinery, monitor production lines, and ensure product quality in environments that may involve noise, temperature variations, and strict safety protocols. Assembly Technicians often operate in more controlled settings such as clean rooms or electronics assembly areas, focusing on precise, hands-on tasks that require attention to detail and may involve repetitive manual assembly or testing. Both roles demand adherence to safety standards, but the work environment for Production Operators tends to be more industrial, while Assembly Technicians often work in specialized or technical manufacturing sectors.
Training and Certification Requirements
Production Operators typically require on-the-job training focused on operating machinery and following safety protocols, with certifications such as OSHA or basic forklift operation enhancing competency. Assembly Technicians often need specialized training in interpreting blueprints, using hand tools, and quality control processes, with certifications like IPC-A-610 for electronics assembly or Six Sigma providing an advantage. Both roles prioritize hands-on experience, but Assembly Technicians usually require more technical certifications specific to product assembly and precision.
Tools and Equipment Used
Production Operators primarily use automated machinery, conveyor systems, and control panels to monitor and manage manufacturing processes, ensuring efficient mass production. Assembly Technicians rely on hand tools, pneumatic tools, and precision instruments such as torque wrenches and soldering irons to assemble components accurately according to specifications. Both roles require familiarity with safety equipment and calibration tools to maintain quality standards and workplace safety.
Career Growth Opportunities
Production Operators often have broader exposure to various manufacturing processes, enabling diverse skill development that can lead to roles in quality control, process optimization, or supervisory positions. Assembly Technicians typically specialize in specific product assembly, providing deep technical expertise that supports advancement into technical support, equipment maintenance, or team lead roles within production lines. Career growth for both positions may also include opportunities in Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma certification pathways to enhance operational efficiency and leadership prospects.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Production Operators typically earn an average salary ranging from $32,000 to $45,000 annually, reflecting entry-level manufacturing roles with operational responsibilities. Assembly Technicians often receive higher compensation, with salaries between $38,000 and $52,000 per year, due to specialized skills in assembling complex components. Benefits packages for Assembly Technicians may include performance bonuses and skill-based incentives, enhancing overall remuneration compared to Production Operators.
Choosing the Right Role: Factors to Consider
Choosing between a Production Operator and an Assembly Technician depends on specific manufacturing processes, required technical skills, and precision levels. Production Operators typically handle machine operation, monitoring, and quality control, requiring strong mechanical aptitude and adherence to safety protocols. Assembly Technicians focus on component fitting, part assembly, and detailed inspection, demanding fine motor skills, attention to detail, and knowledge of assembly procedures.
Production Operator vs Assembly Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com