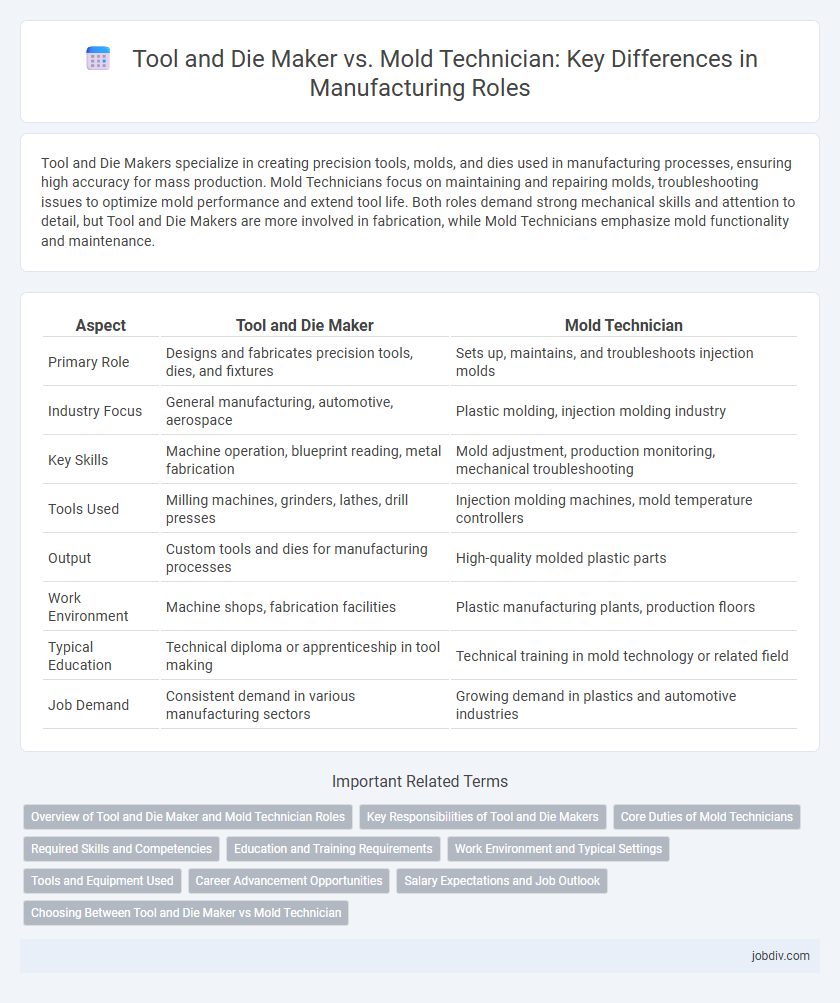
Tool and Die Makers specialize in creating precision tools, molds, and dies used in manufacturing processes, ensuring high accuracy for mass production. Mold Technicians focus on maintaining and repairing molds, troubleshooting issues to optimize mold performance and extend tool life. Both roles demand strong mechanical skills and attention to detail, but Tool and Die Makers are more involved in fabrication, while Mold Technicians emphasize mold functionality and maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tool and Die Maker | Mold Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Designs and fabricates precision tools, dies, and fixtures | Sets up, maintains, and troubleshoots injection molds |
| Industry Focus | General manufacturing, automotive, aerospace | Plastic molding, injection molding industry |
| Key Skills | Machine operation, blueprint reading, metal fabrication | Mold adjustment, production monitoring, mechanical troubleshooting |
| Tools Used | Milling machines, grinders, lathes, drill presses | Injection molding machines, mold temperature controllers |
| Output | Custom tools and dies for manufacturing processes | High-quality molded plastic parts |
| Work Environment | Machine shops, fabrication facilities | Plastic manufacturing plants, production floors |
| Typical Education | Technical diploma or apprenticeship in tool making | Technical training in mold technology or related field |
| Job Demand | Consistent demand in various manufacturing sectors | Growing demand in plastics and automotive industries |
Overview of Tool and Die Maker and Mold Technician Roles
Tool and die makers specialize in designing, fabricating, and repairing precision tools, dies, and molds used in manufacturing processes to shape materials. Mold technicians focus on assembling, maintaining, and troubleshooting molds to ensure smooth production runs and product quality. Both roles require expertise in machining, blueprint reading, and quality control, with tool and die makers emphasizing tool creation and mold technicians concentrating on mold functionality.
Key Responsibilities of Tool and Die Makers
Tool and Die Makers specialize in fabricating precision tools, dies, and molds essential for manufacturing processes, ensuring accuracy in metal stamping and forming operations. Their key responsibilities include reading blueprints and technical drawings, setting up and operating machine tools such as grinders and lathes, and performing precise measurements to maintain strict tolerances. These professionals also conduct troubleshooting and maintenance of tools to optimize production efficiency and product quality.
Core Duties of Mold Technicians
Mold Technicians specialize in designing, assembling, and repairing molds used in manufacturing processes, ensuring precision and quality in molded parts production. They work closely with CAD models and use CNC machines to fabricate and adjust mold components. Core duties include troubleshooting mold issues, maintaining mold functionality, and optimizing mold performance for high-volume manufacturing efficiency.
Required Skills and Competencies
Tool and die makers require advanced skills in blueprint reading, precision machining, and metal fabrication to create custom tools and dies used in manufacturing processes. Mold technicians focus on competencies in mold design, maintenance, and troubleshooting, specializing in injection molding and polymer processing. Both roles demand proficiency in CNC programming, attention to detail, and problem-solving abilities to ensure production accuracy and efficiency.
Education and Training Requirements
Tool and Die Makers typically require a high school diploma followed by an apprenticeship or vocational training in precision machining, focusing on interpreting blueprints and operating manual and CNC machines. Mold Technicians often need specialized training in polymer science and mold design, which can be obtained through technical schools or community college programs emphasizing mold construction and troubleshooting. Both roles benefit from hands-on experience but differ in their educational focus, with Tool and Die Makers concentrating on metalworking skills and Mold Technicians on molding processes and materials.
Work Environment and Typical Settings
Tool and die makers primarily work in manufacturing plants, machine shops, and tool rooms where precision machining and metalworking are critical. Mold technicians often operate in injection molding facilities or plastic part production environments, focusing on maintaining and adjusting molds to ensure product quality. Both roles require a controlled, clean workspace with safety protocols due to the use of heavy machinery and tooling equipment.
Tools and Equipment Used
Tool and Die Makers primarily use precision machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, and grinders to fabricate and repair dies, molds, and fixtures with tight tolerances. Mold Technicians specialize in operating injection molding presses, temperature controllers, and hydraulic systems to assemble, adjust, and maintain molds for plastic production. Both roles require proficiency in computer-aided design (CAD) software and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to ensure accuracy and quality in manufacturing processes.
Career Advancement Opportunities
Tool and Die Makers have broader career advancement opportunities due to their expertise in creating and repairing precision tools and dies used across various manufacturing sectors, often leading to supervisory or engineering roles. Mold Technicians, specializing in the maintenance and troubleshooting of molds for plastic or metal parts, typically advance into roles such as mold designers, quality control specialists, or production managers within specialized molding facilities. Both career paths benefit from certifications and continuous skill development, but Tool and Die Makers generally have a wider range of advancement options in diverse manufacturing environments.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Tool and Die Makers earn an average annual salary of $56,000, with demand driven by the automotive and aerospace industries requiring precision tooling. Mold Technicians typically earn slightly less, averaging $52,000 per year, as they specialize in maintaining and repairing molds for plastic injection molding processes. Both professions face steady job outlooks, with employment expected to grow around 5% over the next decade due to ongoing manufacturing automation and the need for skilled tradespeople.
Choosing Between Tool and Die Maker vs Mold Technician
Choosing between a Tool and Die Maker and a Mold Technician depends on the specific manufacturing processes involved and the complexity of the parts being produced. Tool and Die Makers specialize in fabricating precision tools, dies, and fixtures primarily used in stamping and forming operations, while Mold Technicians focus on designing, maintaining, and repairing molds used in injection molding and casting processes. Understanding the production requirements and material characteristics can guide manufacturers in selecting the appropriate skilled professional to optimize tooling efficiency and product quality.
Tool and Die Maker vs Mold Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com