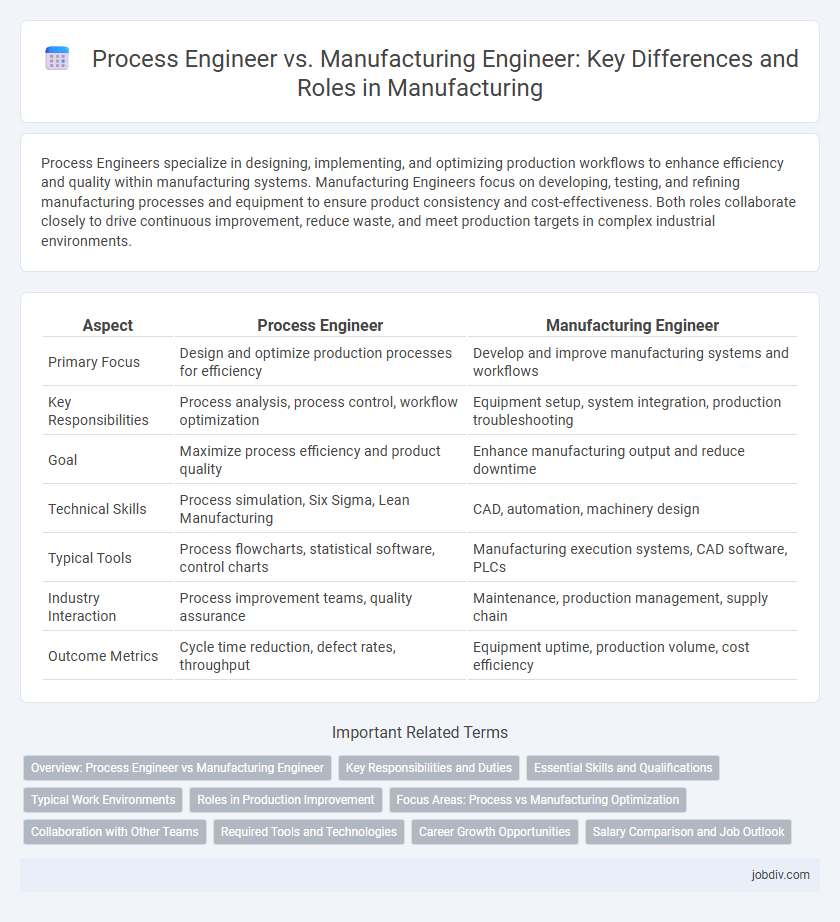
Process Engineers specialize in designing, implementing, and optimizing production workflows to enhance efficiency and quality within manufacturing systems. Manufacturing Engineers focus on developing, testing, and refining manufacturing processes and equipment to ensure product consistency and cost-effectiveness. Both roles collaborate closely to drive continuous improvement, reduce waste, and meet production targets in complex industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Process Engineer | Manufacturing Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design and optimize production processes for efficiency | Develop and improve manufacturing systems and workflows |
| Key Responsibilities | Process analysis, process control, workflow optimization | Equipment setup, system integration, production troubleshooting |
| Goal | Maximize process efficiency and product quality | Enhance manufacturing output and reduce downtime |
| Technical Skills | Process simulation, Six Sigma, Lean Manufacturing | CAD, automation, machinery design |
| Typical Tools | Process flowcharts, statistical software, control charts | Manufacturing execution systems, CAD software, PLCs |
| Industry Interaction | Process improvement teams, quality assurance | Maintenance, production management, supply chain |
| Outcome Metrics | Cycle time reduction, defect rates, throughput | Equipment uptime, production volume, cost efficiency |
Overview: Process Engineer vs Manufacturing Engineer
Process engineers specialize in designing, implementing, and optimizing manufacturing processes to improve efficiency, quality, and safety. Manufacturing engineers focus on developing, evaluating, and refining production systems and equipment to streamline manufacturing operations and reduce costs. Both roles collaborate closely to enhance product throughput and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Process Engineers design and optimize manufacturing workflows to improve efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness by analyzing production data and implementing process control systems. Manufacturing Engineers focus on developing and maintaining manufacturing equipment, ensuring machinery reliability, and streamlining production line setup to enhance operational performance. Both roles collaborate closely to troubleshoot production issues and drive continuous improvement initiatives within industrial environments.
Essential Skills and Qualifications
Process engineers require expertise in process design, optimization, and control, with strong analytical skills and proficiency in software tools like MATLAB and AutoCAD. Manufacturing engineers must excel in production planning, quality control, and equipment maintenance, often needing knowledge of Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma methodologies. Both roles demand a bachelor's degree in engineering disciplines such as industrial, mechanical, or chemical engineering, alongside experience in problem-solving and project management.
Typical Work Environments
Process engineers primarily operate in production facilities, focusing on optimizing manufacturing processes, troubleshooting equipment, and improving workflow efficiency. Manufacturing engineers work in both factory floors and design offices, balancing hands-on machinery oversight with process design and quality control responsibilities. Both roles require collaboration with cross-functional teams but differ in their everyday environments, with process engineers more embedded in direct production zones.
Roles in Production Improvement
Process engineers specialize in analyzing and optimizing production workflows to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality through process design and control. Manufacturing engineers focus on implementing and maintaining machinery, equipment, and systems to streamline manufacturing operations and ensure consistent output. Both roles collaborate to drive continuous improvement and operational excellence in manufacturing environments.
Focus Areas: Process vs Manufacturing Optimization
Process Engineers concentrate on optimizing specific production processes by analyzing workflows, improving efficiency, and reducing defects through detailed process control techniques. Manufacturing Engineers focus on end-to-end manufacturing systems, integrating equipment, technology, and labor to enhance overall plant productivity and streamline production lines. Both roles prioritize continuous improvement but differ in scope, with Process Engineers targeting micro-level process enhancements and Manufacturing Engineers driving macro-level manufacturing optimization.
Collaboration with Other Teams
Process engineers collaborate closely with quality assurance and production teams to optimize workflows and ensure product consistency, while manufacturing engineers work alongside design, procurement, and maintenance departments to implement efficient manufacturing systems. Both roles require seamless communication to align process improvements with equipment capabilities and supply chain demands. Effective collaboration between process and manufacturing engineers drives innovation, reduces downtime, and enhances overall production efficiency.
Required Tools and Technologies
Process engineers primarily utilize tools such as process simulation software (e.g., Aspen HYSYS, MATLAB) and statistical process control (SPC) systems to optimize manufacturing workflows and improve process efficiency. Manufacturing engineers focus on technologies like CAD/CAM software (e.g., AutoCAD, SolidWorks), robotics, and automation systems to design and enhance production lines. Both roles require proficiency in data analysis tools and an understanding of Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT and advanced manufacturing sensors.
Career Growth Opportunities
Process Engineers typically focus on improving production efficiency, quality control, and implementing process innovations, which can lead to roles in operations management or continuous improvement leadership. Manufacturing Engineers concentrate on designing and optimizing manufacturing systems and equipment, with career paths advancing toward plant management or industrial engineering departments. Both career tracks offer strong growth potential in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and electronics manufacturing, where expertise in lean manufacturing and automation is highly valued.
Salary Comparison and Job Outlook
Process engineers typically earn between $70,000 and $95,000 annually, focusing on optimizing production processes and improving efficiency. Manufacturing engineers average salaries ranging from $65,000 to $90,000, emphasizing equipment maintenance and production system design. Job outlook for both roles remains strong, with predicted growth rates of 6-8% over the next decade due to increasing automation and demand for improved manufacturing practices.
Process Engineer vs Manufacturing Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com