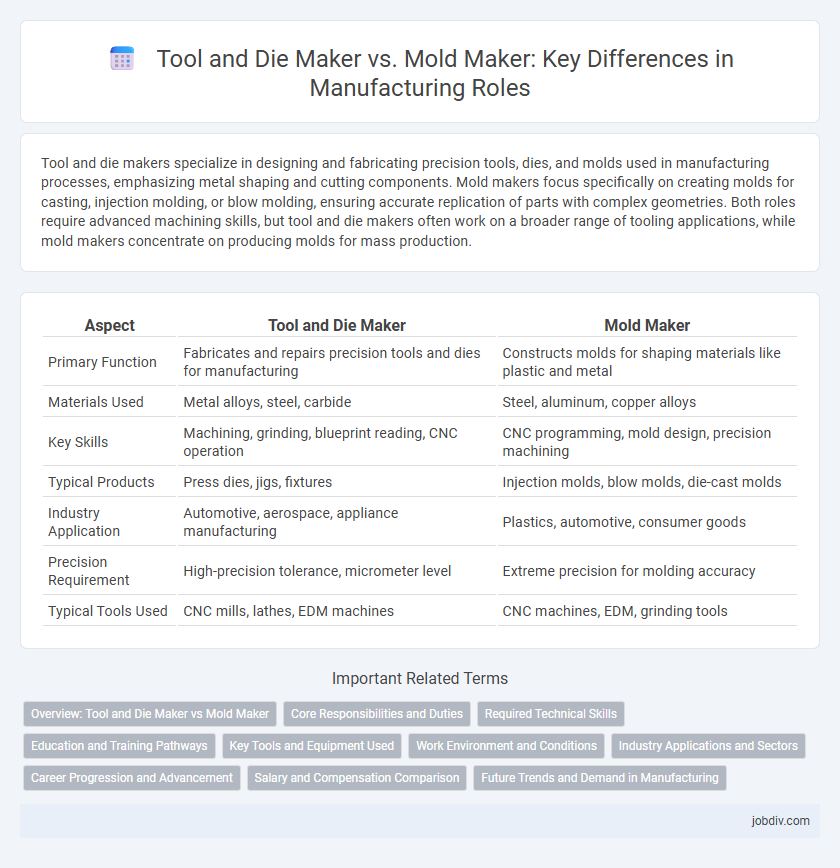
Tool and die makers specialize in designing and fabricating precision tools, dies, and molds used in manufacturing processes, emphasizing metal shaping and cutting components. Mold makers focus specifically on creating molds for casting, injection molding, or blow molding, ensuring accurate replication of parts with complex geometries. Both roles require advanced machining skills, but tool and die makers often work on a broader range of tooling applications, while mold makers concentrate on producing molds for mass production.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Tool and Die Maker | Mold Maker |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Fabricates and repairs precision tools and dies for manufacturing | Constructs molds for shaping materials like plastic and metal |
| Materials Used | Metal alloys, steel, carbide | Steel, aluminum, copper alloys |
| Key Skills | Machining, grinding, blueprint reading, CNC operation | CNC programming, mold design, precision machining |
| Typical Products | Press dies, jigs, fixtures | Injection molds, blow molds, die-cast molds |
| Industry Application | Automotive, aerospace, appliance manufacturing | Plastics, automotive, consumer goods |
| Precision Requirement | High-precision tolerance, micrometer level | Extreme precision for molding accuracy |
| Typical Tools Used | CNC mills, lathes, EDM machines | CNC machines, EDM, grinding tools |
Overview: Tool and Die Maker vs Mold Maker
Tool and Die Makers specialize in creating precision tools, dies, and metal forms used in manufacturing processes, focusing on shaping or cutting metal materials. Mold Makers design and fabricate molds primarily for casting or injection molding, producing complex parts often from plastics or metals. Both roles require expertise in machining and metallurgy, but Mold Makers concentrate on creating cavities and cores used for mass production.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
Tool and die makers specialize in fabricating precision tools, dies, and fixtures used in manufacturing processes, ensuring accurate shape and size for mass production. Mold makers focus on designing and constructing molds for casting or injection molding, creating cavities that form parts from molten or plastic materials. Both roles require expertise in interpreting blueprints and operating CNC machines, but tool and die makers emphasize cutting and shaping tools, while mold makers concentrate on mold assembly and maintenance.
Required Technical Skills
Tool and Die Makers require advanced skills in precision machining, blueprint reading, and knowledge of metalworking techniques to create and repair tools, dies, and fixtures. Mold Makers specialize in CAD software proficiency, mold design, and injection molding process understanding to manufacture molds for casting or molding plastics and metals. Both roles demand expertise in CNC programming, quality control, and materials science to ensure accurate and durable production components.
Education and Training Pathways
Tool and Die Makers typically require a combination of vocational training and apprenticeships that focus on precision metalworking, blueprint reading, and CNC machining, often completing a 4-5 year apprenticeship program. Mold Makers undergo similar technical training but place more emphasis on understanding mold design, injection molding processes, and material properties, frequently acquiring specialized certifications in polymer science or plastics manufacturing. Both careers benefit from hands-on experience and ongoing education through community colleges or technical institutes offering programs in manufacturing technology and CAD/CAM software.
Key Tools and Equipment Used
Tool and die makers primarily use precision grinders, milling machines, and CNC lathes to create jigs, dies, and fixtures essential for stamping and forging processes. Mold makers focus on injection molding machines, EDM (electrical discharge machining) equipment, and polishing tools to produce detailed molds for plastic and metal casting. Both specialists rely on CAD/CAM software for designing and programming the manufacturing of accurate, high-quality components.
Work Environment and Conditions
Tool and Die Makers typically work in clean, temperature-controlled factories, often standing for long periods and handling heavy machinery with precision. Mold Makers face similar industrial settings but may encounter more exposure to chemicals and heat due to the mold casting processes. Both roles demand adherence to strict safety protocols and involve working with metalworking tools in environments requiring attention to detail and physical stamina.
Industry Applications and Sectors
Tool and die makers specialize in producing precision tools, dies, and molds for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery, ensuring accurate metal forming and cutting processes. Mold makers focus primarily on creating molds for plastic injection molding, serving sectors like consumer goods, medical devices, and packaging industries. Both roles are essential in manufacturing, with tool and die makers supporting metal fabrication and mold makers enabling high-volume plastic part production.
Career Progression and Advancement
Tool and die makers often advance by mastering precision machining and gaining expertise in complex dies used for mass production, leading to roles such as tool designer or manufacturing engineer. Mold makers focus on creating molds for plastic injection molding, with career progression typically involving specialization in mold design or project management within manufacturing settings. Both careers benefit from continuous skills development in CAD software and materials science to enhance advancement opportunities in the manufacturing industry.
Salary and Compensation Comparison
Tool and Die Makers typically earn an average annual salary ranging from $50,000 to $70,000, reflecting their expertise in creating and repairing precision tools and dies used in manufacturing processes. Mold Makers often command salaries between $55,000 and $75,000, given their specialized skills in designing and producing molds for plastic, metal, or composite materials. Compensation packages for both roles may include overtime pay, bonuses, and benefits, with variations depending on experience, industry, and geographic location.
Future Trends and Demand in Manufacturing
Tool and Die Makers and Mold Makers are experiencing growing demand driven by advancements in automation, additive manufacturing, and precision engineering within the manufacturing sector. The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies such as AI-powered CNC machines is increasing the need for skilled professionals who can design and maintain complex tooling systems. Emerging trends emphasize sustainability and lightweight materials, prompting both roles to adapt skills for innovative mold and die solutions that improve production efficiency and product quality.
Tool and Die Maker vs Mold Maker Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com