Maintenance Technicians primarily handle routine inspections, repairs, and upkeep of machinery to ensure operational efficiency. Reliability Technicians focus on analyzing equipment data, implementing predictive maintenance strategies, and improving asset longevity to minimize downtime. Both roles are essential for maximizing production uptime and reducing overall maintenance costs in manufacturing environments.
Table of Comparison
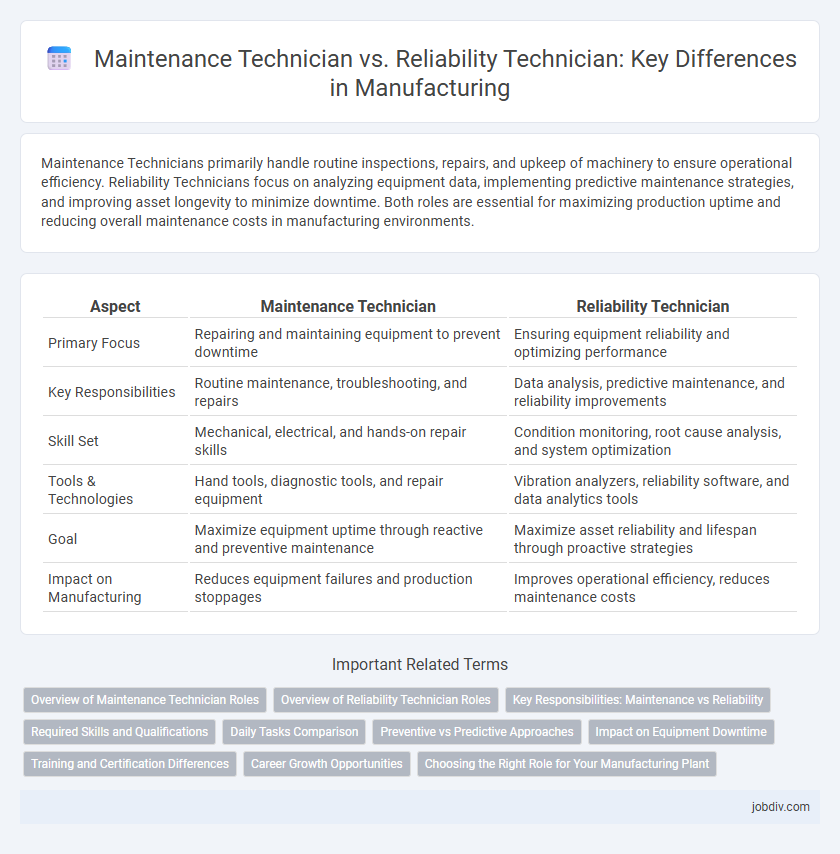
| Aspect | Maintenance Technician | Reliability Technician |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Repairing and maintaining equipment to prevent downtime | Ensuring equipment reliability and optimizing performance |
| Key Responsibilities | Routine maintenance, troubleshooting, and repairs | Data analysis, predictive maintenance, and reliability improvements |
| Skill Set | Mechanical, electrical, and hands-on repair skills | Condition monitoring, root cause analysis, and system optimization |
| Tools & Technologies | Hand tools, diagnostic tools, and repair equipment | Vibration analyzers, reliability software, and data analytics tools |
| Goal | Maximize equipment uptime through reactive and preventive maintenance | Maximize asset reliability and lifespan through proactive strategies |
| Impact on Manufacturing | Reduces equipment failures and production stoppages | Improves operational efficiency, reduces maintenance costs |
Overview of Maintenance Technician Roles
Maintenance Technicians perform routine inspections, troubleshoot mechanical issues, and ensure the smooth operation of manufacturing equipment to minimize downtime. Their responsibilities include preventive maintenance, repairing malfunctions, and maintaining safety standards on the production floor. This role demands hands-on technical skills and a strong understanding of machinery to support continuous manufacturing processes.
Overview of Reliability Technician Roles
Reliability Technicians specialize in predictive and preventive maintenance techniques to enhance equipment uptime and reduce unplanned downtime. They utilize data analysis, condition monitoring, and root cause failure analysis to improve asset reliability and optimize maintenance schedules. Their role bridges operations and maintenance teams by implementing reliability-centered maintenance (RCM) strategies to extend equipment life and increase production efficiency.
Key Responsibilities: Maintenance vs Reliability
Maintenance Technicians focus on repairing and servicing equipment to ensure operational continuity, performing tasks such as troubleshooting, preventive maintenance, and emergency repairs. Reliability Technicians emphasize analyzing equipment performance data, implementing predictive maintenance strategies, and optimizing asset reliability to minimize downtime. Both roles are essential, with Maintenance Technicians addressing immediate operational needs and Reliability Technicians driving long-term equipment efficiency.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Maintenance Technicians require strong mechanical aptitude, electrical knowledge, and proficiency in troubleshooting routine equipment failures, often supported by a technical diploma or associate degree. Reliability Technicians emphasize advanced skills in predictive maintenance techniques, data analysis, and root cause failure analysis, typically necessitating certifications such as Certified Maintenance & Reliability Technician (CMRT) or similar. Both roles demand a solid understanding of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) tools and computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) to optimize equipment uptime and performance.
Daily Tasks Comparison
Maintenance Technicians perform routine inspections, troubleshoot equipment malfunctions, and execute scheduled repairs to ensure machinery operates smoothly. Reliability Technicians analyze equipment performance data, implement predictive maintenance strategies, and focus on minimizing downtime through long-term reliability improvements. Both roles collaborate to enhance operational efficiency but differ in their approaches to daily maintenance activities and fault prevention.
Preventive vs Predictive Approaches
Maintenance Technicians primarily focus on preventive maintenance, conducting scheduled inspections and routine repairs to avoid equipment failures. Reliability Technicians emphasize predictive maintenance, utilizing data analytics and condition-monitoring tools like vibration analysis and thermal imaging to foresee and prevent potential breakdowns. The integration of both preventive and predictive approaches enhances overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) and reduces unplanned downtime in manufacturing operations.
Impact on Equipment Downtime
Maintenance Technicians address immediate equipment failures through corrective repairs, reducing downtime caused by unexpected breakdowns. Reliability Technicians implement predictive maintenance strategies, analyzing data to prevent failures and optimize equipment performance, thereby minimizing unplanned downtime more effectively. Both roles contribute to equipment availability, but Reliability Technicians focus on long-term operational continuity through proactive measures.
Training and Certification Differences
Maintenance Technicians typically require certifications such as OSHA safety training and basic electrical or mechanical certifications, emphasizing hands-on repair skills and routine equipment upkeep. Reliability Technicians often pursue advanced certifications like Certified Maintenance & Reliability Technician (CMRT) or Certified Reliability Engineer (CRE), focusing on predictive maintenance, root cause analysis, and asset management strategies. Training for Reliability Technicians includes data-driven diagnostic methods and system optimization, whereas Maintenance Technicians receive practical instruction centered around troubleshooting and equipment restoration.
Career Growth Opportunities
Maintenance Technicians develop foundational skills in equipment repair and routine servicing, offering immediate hands-on experience crucial for manufacturing operations. Reliability Technicians focus on predictive maintenance strategies and data analysis to enhance equipment longevity, positioning themselves for advanced roles in asset management and process optimization. Career growth for Reliability Technicians typically includes leadership roles in reliability engineering and maintenance planning, reflecting a higher strategic impact within manufacturing organizations.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Manufacturing Plant
Maintenance Technicians perform routine inspections, repairs, and troubleshooting to ensure equipment operates smoothly, focusing on immediate machine functionality. Reliability Technicians analyze data and implement predictive maintenance strategies to minimize downtime and extend asset lifespan, emphasizing long-term operational efficiency. Selecting the right role depends on your manufacturing plant's needs: prioritize Maintenance Technicians for reactive support and Reliability Technicians for proactive, data-driven asset management.
Maintenance Technician vs Reliability Technician Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com