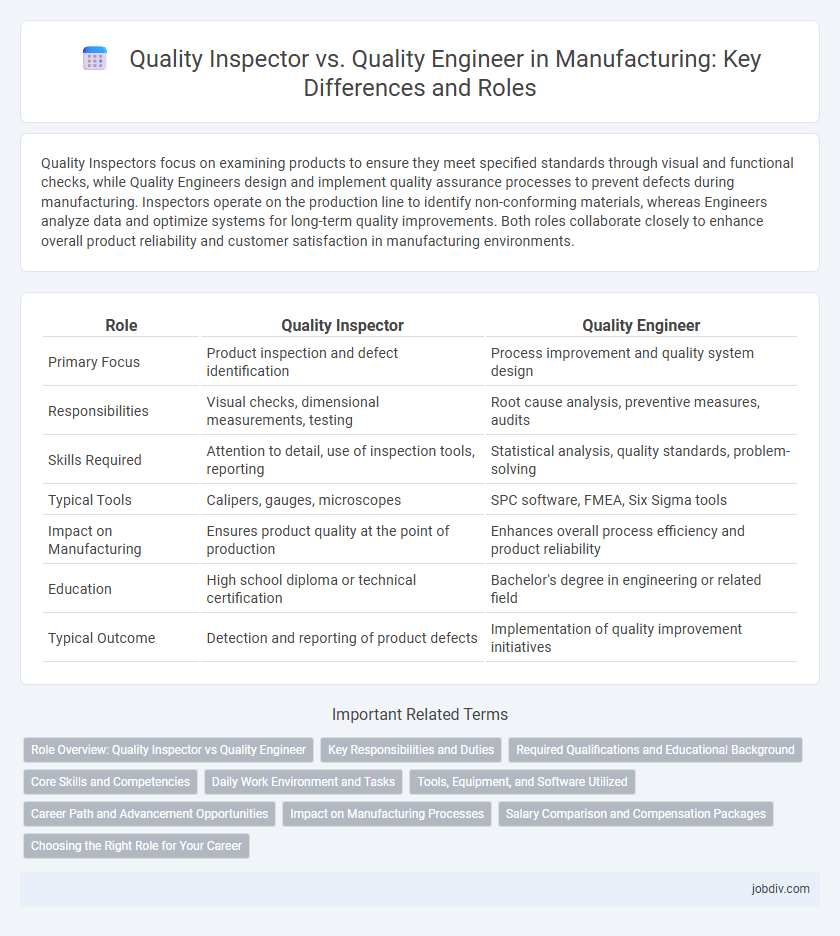
Quality Inspectors focus on examining products to ensure they meet specified standards through visual and functional checks, while Quality Engineers design and implement quality assurance processes to prevent defects during manufacturing. Inspectors operate on the production line to identify non-conforming materials, whereas Engineers analyze data and optimize systems for long-term quality improvements. Both roles collaborate closely to enhance overall product reliability and customer satisfaction in manufacturing environments.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Quality Inspector | Quality Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Product inspection and defect identification | Process improvement and quality system design |
| Responsibilities | Visual checks, dimensional measurements, testing | Root cause analysis, preventive measures, audits |
| Skills Required | Attention to detail, use of inspection tools, reporting | Statistical analysis, quality standards, problem-solving |
| Typical Tools | Calipers, gauges, microscopes | SPC software, FMEA, Six Sigma tools |
| Impact on Manufacturing | Ensures product quality at the point of production | Enhances overall process efficiency and product reliability |
| Education | High school diploma or technical certification | Bachelor's degree in engineering or related field |
| Typical Outcome | Detection and reporting of product defects | Implementation of quality improvement initiatives |
Role Overview: Quality Inspector vs Quality Engineer
Quality Inspectors conduct hands-on product evaluations and perform routine tests to ensure compliance with manufacturing standards, focusing on defect identification and immediate issue resolution. Quality Engineers develop and implement quality control systems, analyze production processes, and drive continuous improvement initiatives to enhance overall product reliability and efficiency. Both roles collaborate to uphold stringent quality standards but differ in scope, with Inspectors executing on the ground inspections and Engineers providing strategic quality improvements.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
Quality Inspectors primarily focus on executing inspection procedures, identifying defects, and ensuring products meet specified standards through routine testing and documentation. Quality Engineers develop and implement quality control systems, analyze data for process improvements, and collaborate with production teams to enhance manufacturing efficiency and product reliability. Both roles play critical parts in maintaining product quality, with Inspectors concentrating on operational compliance and Engineers on systemic quality advancements.
Required Qualifications and Educational Background
Quality Inspectors typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, with specialized certifications like ASQ Certified Quality Inspector enhancing their expertise in product evaluation and defect identification. Quality Engineers usually hold a bachelor's degree in engineering, manufacturing, or a related field, often complemented by professional certifications such as Six Sigma or ASQ Certified Quality Engineer to drive process improvements and quality system development. The educational background of Quality Engineers equips them with in-depth knowledge of statistical analysis, quality management systems (QMS), and engineering principles, distinguishing their role from Quality Inspectors focused on operational inspection tasks.
Core Skills and Competencies
Quality Inspectors specialize in detecting defects and ensuring products meet specified standards through detailed visual and dimensional inspections, proficiency in measurement tools, and adherence to quality control procedures. Quality Engineers focus on designing, implementing, and improving quality management systems using statistical analysis, root cause analysis, and process optimization techniques to enhance product reliability and efficiency. Both roles require strong attention to detail and knowledge of industry regulations, but engineers emphasize problem-solving and continuous improvement, while inspectors concentrate on tactical quality verification.
Daily Work Environment and Tasks
Quality Inspectors conduct routine inspections and tests on manufacturing products to ensure compliance with specifications and standards, focusing on identifying defects and documenting results. Quality Engineers design and implement quality control systems, analyze production data, and collaborate with cross-functional teams to improve processes and prevent defects. Inspectors spend most of their day on the production floor performing hands-on assessments, while Engineers balance office work involving data analysis, report generation, and process optimization strategies.
Tools, Equipment, and Software Utilized
Quality Inspectors primarily utilize measurement tools such as calipers, micrometers, and optical comparators to perform visual and dimensional inspections, alongside statistical process control (SPC) software for data recording. Quality Engineers employ advanced software solutions like Six Sigma analytics, Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) platforms, and Computer-Aided Design (CAD) systems to enhance quality planning and process improvement. Equipment-wise, Engineers integrate automated testing machinery and quality management systems (QMS) to analyze product reliability and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Quality Inspectors primarily focus on monitoring product quality through inspections and testing, gaining expertise in identifying defects and ensuring compliance with standards. Quality Engineers advance by designing and implementing quality systems, analyzing processes, and driving continuous improvement initiatives, offering broader technical and leadership roles. Career progression typically leads Inspectors to supervisory positions, while Engineers often advance into senior management, quality assurance leadership, or specialized engineering roles.
Impact on Manufacturing Processes
Quality Inspectors primarily focus on identifying defects and ensuring products meet specified standards, directly affecting the consistency and reliability of manufacturing outputs. Quality Engineers design and implement process improvements and quality control systems, resulting in enhanced efficiency, reduced waste, and higher overall product quality. Together, their roles drive continuous improvement in manufacturing processes, leading to increased customer satisfaction and cost savings.
Salary Comparison and Compensation Packages
Quality Engineers usually earn higher salaries than Quality Inspectors, with median annual wages of approximately $85,000 compared to $50,000 in manufacturing sectors. Compensation packages for Quality Engineers often include performance bonuses, stock options, and advanced benefits due to their involvement in process improvements and strategy, while Quality Inspectors typically receive standard benefits and hourly wages. Geographic location, company size, and industry specialization further influence the salary disparity between these key quality assurance roles.
Choosing the Right Role for Your Career
Quality Inspectors focus on identifying defects in manufactured products through rigorous testing and inspection protocols, ensuring compliance with industry standards. Quality Engineers develop and implement quality management systems, analyze process data, and drive continuous improvement initiatives to enhance product reliability and efficiency. Choosing between these roles depends on your interest in hands-on inspection work versus strategic quality planning and process optimization in manufacturing environments.
Quality Inspector vs Quality Engineer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com