Bookkeepers maintain accurate daily financial records by tracking transactions, receipts, and invoices, ensuring data integrity for smaller businesses. Accountants analyze these records to prepare financial statements, conduct audits, and provide strategic tax advice, contributing to long-term financial planning. The distinction lies in bookkeepers handling detailed record-keeping, while accountants interpret and leverage data for business growth.
Table of Comparison
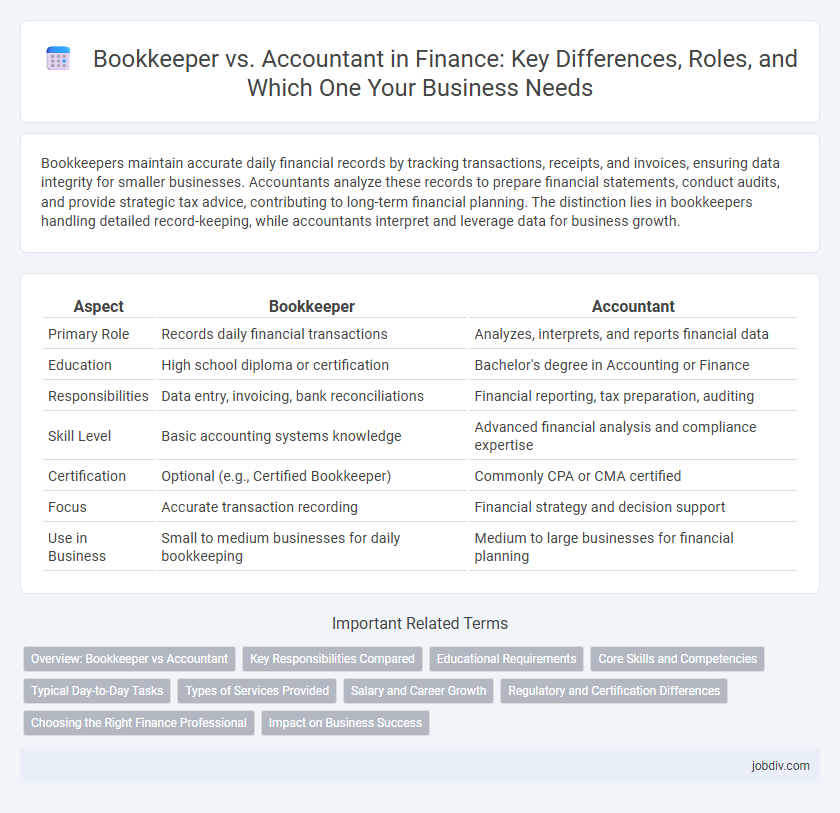
| Aspect | Bookkeeper | Accountant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Records daily financial transactions | Analyzes, interprets, and reports financial data |
| Education | High school diploma or certification | Bachelor's degree in Accounting or Finance |
| Responsibilities | Data entry, invoicing, bank reconciliations | Financial reporting, tax preparation, auditing |
| Skill Level | Basic accounting systems knowledge | Advanced financial analysis and compliance expertise |
| Certification | Optional (e.g., Certified Bookkeeper) | Commonly CPA or CMA certified |
| Focus | Accurate transaction recording | Financial strategy and decision support |
| Use in Business | Small to medium businesses for daily bookkeeping | Medium to large businesses for financial planning |
Overview: Bookkeeper vs Accountant
Bookkeepers manage day-to-day financial transactions, including recording sales, purchases, and payments, ensuring accurate ledgers and reconciliations. Accountants analyze this financial data to prepare reports, perform audits, and provide strategic insights for tax planning and business growth. While bookkeepers handle routine data entry, accountants apply expertise to interpret financial information and ensure regulatory compliance.
Key Responsibilities Compared
Bookkeepers primarily handle daily financial transactions, including recording sales, purchases, receipts, and payments to maintain accurate ledgers and ensure up-to-date financial data. Accountants analyze financial records, prepare financial statements, conduct audits, and provide strategic tax planning to optimize financial performance and compliance. Both roles are essential for maintaining financial integrity, but accountants focus more on interpretation, reporting, and regulatory adherence.
Educational Requirements
Bookkeepers typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, often supplemented by certification programs such as the Certified Bookkeeper credential. Accountants generally need a bachelor's degree in accounting or finance, with many pursuing advanced certifications like the CPA (Certified Public Accountant) to enhance their qualifications. The educational gap reflects the complexity and scope of tasks, with accountants handling more analytical and regulatory responsibilities than bookkeepers.
Core Skills and Competencies
Bookkeepers excel in transaction recording, maintaining ledgers, and reconciling accounts, emphasizing accuracy and attention to detail in financial documentation. Accountants possess advanced competencies in financial analysis, tax preparation, regulatory compliance, and strategic planning, enabling them to interpret data for decision-making. Both roles require proficiency in accounting software, but accountants typically hold certifications such as CPA, reflecting deeper expertise in complex financial reporting.
Typical Day-to-Day Tasks
Bookkeepers manage daily financial transactions such as recording sales, purchases, receipts, and payments to maintain accurate ledgers. Accountants analyze these financial records to prepare reports, ensure regulatory compliance, and assist with budgeting and tax planning. While bookkeepers focus on data entry and transaction tracking, accountants handle complex financial analysis and strategic decision-making.
Types of Services Provided
Bookkeepers primarily manage daily financial transactions, including recording sales, expenses, and payroll, ensuring accurate and up-to-date ledgers. Accountants offer advanced services such as preparing financial statements, tax planning, auditing, and providing strategic financial advice to optimize business growth. Both roles play crucial parts in maintaining financial health but differ in scope and complexity of services delivered.
Salary and Career Growth
Bookkeepers typically earn between $35,000 and $50,000 annually, managing daily financial transactions, while accountants command higher salaries, often ranging from $60,000 to $90,000, due to advanced responsibilities like financial analysis and tax preparation. Career growth for bookkeepers is generally limited to senior bookkeeping or office manager roles, whereas accountants can advance to senior accountant, financial manager, or CFO positions. The higher salary potential and broader career trajectory make accounting a preferred path for long-term professional development in finance.
Regulatory and Certification Differences
Bookkeepers primarily handle daily transaction recording and do not require formal certification, whereas accountants must obtain certifications such as CPA (Certified Public Accountant) to perform audits, tax planning, and financial analysis under regulatory standards. Accountants adhere to stringent regulations set by bodies like the AICPA and IRS, ensuring compliance with GAAP and tax laws, while bookkeepers operate under less regulatory oversight. The certification process for accountants involves rigorous exams and continuing education to maintain compliance and expertise in financial reporting and regulatory requirements.
Choosing the Right Finance Professional
Bookkeepers manage daily financial transactions and maintain accurate records, ensuring data is organized and up-to-date for business operations. Accountants analyze financial reports, prepare tax returns, and advise on financial planning and compliance, providing strategic insights for long-term growth. Choosing the right finance professional depends on your business needs: bookkeepers handle routine data entry, while accountants offer expert financial analysis and decision-making support.
Impact on Business Success
Bookkeepers maintain accurate and organized financial records, ensuring transaction data is consistently recorded to provide a clear financial snapshot. Accountants analyze these records to prepare financial statements, manage tax filings, and offer strategic financial advice that drives informed decision-making and business growth. The combined efforts of bookkeeping and accounting enhance financial accuracy, compliance, and strategic planning, directly impacting profitability and long-term business success.
Bookkeeper vs Accountant Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com