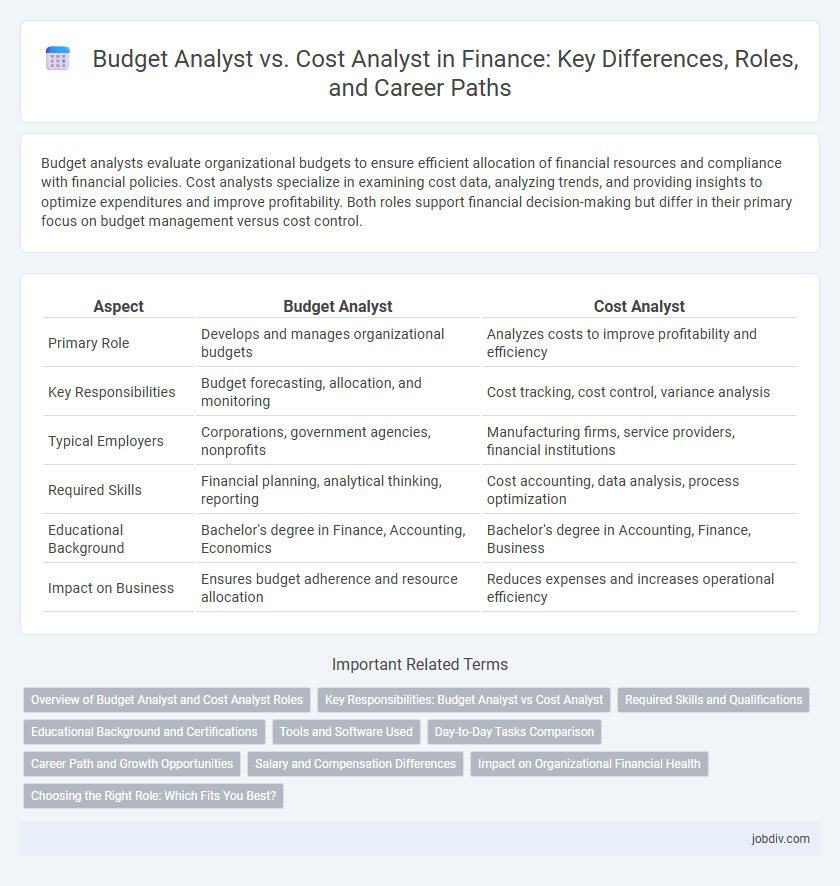
Budget analysts evaluate organizational budgets to ensure efficient allocation of financial resources and compliance with financial policies. Cost analysts specialize in examining cost data, analyzing trends, and providing insights to optimize expenditures and improve profitability. Both roles support financial decision-making but differ in their primary focus on budget management versus cost control.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Budget Analyst | Cost Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Develops and manages organizational budgets | Analyzes costs to improve profitability and efficiency |
| Key Responsibilities | Budget forecasting, allocation, and monitoring | Cost tracking, cost control, variance analysis |
| Typical Employers | Corporations, government agencies, nonprofits | Manufacturing firms, service providers, financial institutions |
| Required Skills | Financial planning, analytical thinking, reporting | Cost accounting, data analysis, process optimization |
| Educational Background | Bachelor's degree in Finance, Accounting, Economics | Bachelor's degree in Accounting, Finance, Business |
| Impact on Business | Ensures budget adherence and resource allocation | Reduces expenses and increases operational efficiency |
Overview of Budget Analyst and Cost Analyst Roles
Budget analysts specialize in preparing budget reports and monitoring organizational spending to ensure compliance with financial plans and regulations. Cost analysts focus on analyzing production costs and recommending efficiency improvements to optimize operational expenditures. Both roles require strong analytical skills and knowledge of financial data to support strategic decision-making in finance management.
Key Responsibilities: Budget Analyst vs Cost Analyst
Budget analysts develop, coordinate, and monitor an organization's financial plans to ensure efficient allocation of resources and adherence to budgetary constraints. Cost analysts focus on evaluating, analyzing, and controlling costs related to production, operations, and projects to improve profitability and reduce expenses. Both roles require detailed financial reporting, data analysis, and collaboration with various departments to support informed decision-making.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Budget analysts require strong analytical skills, proficiency in financial software, and a solid understanding of budgeting principles along with a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, or related fields. Cost analysts need expertise in cost accounting, data analysis, and manufacturing processes, often holding certifications like CMA (Certified Management Accountant) and experience with ERP systems. Both roles demand attention to detail, critical thinking, and effective communication skills to interpret financial data and support strategic decision-making.
Educational Background and Certifications
Budget analysts typically hold a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, economics, or public administration, with many pursuing certifications such as Certified Government Financial Manager (CGFM) or Certified Public Accountant (CPA) to enhance their expertise. Cost analysts often have educational backgrounds in finance, accounting, or industrial engineering, and certifications like Certified Management Accountant (CMA) or Certified Cost Technician (CCT) are common for advancing skills in cost control and analysis. Both roles benefit from strong analytical abilities and knowledge of financial software, but their certifications align specifically with budget planning versus cost management functions.
Tools and Software Used
Budget analysts primarily utilize software such as Microsoft Excel, SAP, Oracle Hyperion, and IBM Planning Analytics for forecasting, budgeting, and financial reporting. Cost analysts rely heavily on tools like Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, and cost management systems including Apptio and Prophix to conduct cost analysis and track expenditure efficiency. Both roles require proficiency in ERP systems like Oracle Financials and SAP ERP to integrate financial data across business units effectively.
Day-to-Day Tasks Comparison
Budget Analysts focus on developing, preparing, and managing an organization's overall financial plans by reviewing budget proposals and monitoring expenditures to ensure alignment with financial goals. Cost Analysts specialize in analyzing production costs, evaluating cost efficiency, and providing detailed reports that help management control expenses and improve profitability. Both roles require strong analytical skills but differ with Budget Analysts emphasizing budget forecasting and compliance, while Cost Analysts concentrate on cost measurement and reduction strategies.
Career Path and Growth Opportunities
Budget Analysts typically advance by gaining expertise in financial planning, moving toward senior financial management or director roles, with strong opportunities in government and corporate sectors. Cost Analysts focus on controlling expenses and improving cost efficiency, often progressing to cost management or operations analysis positions, with growth in manufacturing, healthcare, and engineering industries. Both career paths benefit from certifications like CPA or CMA, enhancing prospects for higher-level managerial roles.
Salary and Compensation Differences
Budget analysts typically earn an average salary ranging from $60,000 to $85,000 annually, reflecting their responsibility for designing and monitoring organizational budgets. Cost analysts generally have a slightly lower salary range, averaging between $55,000 and $80,000 per year, as their primary focus centers on analyzing and reducing operational expenses. Compensation differences also depend on industry, experience, and location, with budget analysts often receiving higher bonuses and benefits in corporate finance roles.
Impact on Organizational Financial Health
Budget Analysts optimize organizational financial health by forecasting revenues and expenditures, ensuring funds are allocated efficiently to meet strategic goals. Cost Analysts enhance financial performance by scrutinizing production and operational costs, identifying inefficiencies, and recommending cost-saving measures. Both roles collaboratively support sustainable financial decision-making through precise budget control and detailed cost management.
Choosing the Right Role: Which Fits You Best?
Budget Analysts specialize in developing, analyzing, and managing financial plans to ensure organizational fiscal efficiency, while Cost Analysts focus on examining cost data to control expenses and improve profitability. Choosing the right role depends on your interest in strategic financial planning versus detailed cost control and analysis. Understanding your strengths in either forecasting budgets or scrutinizing cost structures helps align your career with the optimal finance specialization.
Budget Analyst vs Cost Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com