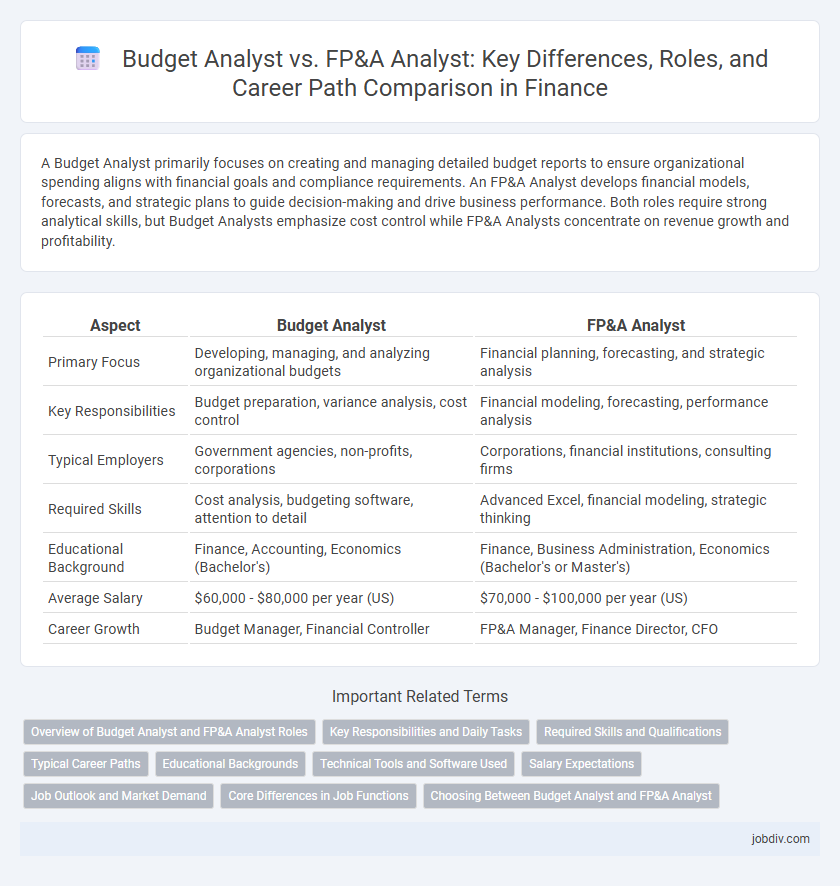
A Budget Analyst primarily focuses on creating and managing detailed budget reports to ensure organizational spending aligns with financial goals and compliance requirements. An FP&A Analyst develops financial models, forecasts, and strategic plans to guide decision-making and drive business performance. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but Budget Analysts emphasize cost control while FP&A Analysts concentrate on revenue growth and profitability.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Budget Analyst | FP&A Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Developing, managing, and analyzing organizational budgets | Financial planning, forecasting, and strategic analysis |
| Key Responsibilities | Budget preparation, variance analysis, cost control | Financial modeling, forecasting, performance analysis |
| Typical Employers | Government agencies, non-profits, corporations | Corporations, financial institutions, consulting firms |
| Required Skills | Cost analysis, budgeting software, attention to detail | Advanced Excel, financial modeling, strategic thinking |
| Educational Background | Finance, Accounting, Economics (Bachelor's) | Finance, Business Administration, Economics (Bachelor's or Master's) |
| Average Salary | $60,000 - $80,000 per year (US) | $70,000 - $100,000 per year (US) |
| Career Growth | Budget Manager, Financial Controller | FP&A Manager, Finance Director, CFO |
Overview of Budget Analyst and FP&A Analyst Roles
Budget Analysts primarily focus on developing, managing, and monitoring organizational budgets to ensure fiscal responsibility and compliance with financial policies. FP&A Analysts concentrate on financial forecasting, variance analysis, and strategic planning to support decision-making and drive business growth. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but FP&A Analysts often engage more with future financial modeling and performance optimization.
Key Responsibilities and Daily Tasks
Budget Analysts primarily focus on developing, managing, and monitoring organizational budgets to ensure financial efficiency and compliance. FP&A Analysts concentrate on financial forecasting, variance analysis, and preparing detailed reports to support strategic decision-making. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but FP&A Analysts engage more in scenario modeling and long-term financial planning.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Budget Analysts require strong proficiency in financial forecasting, budgeting software like Oracle or SAP, and expertise in variance analysis to ensure accurate budget development and control. FP&A Analysts need advanced skills in data modeling, Excel, and financial reporting tools such as Power BI or Tableau, alongside a deep understanding of corporate finance principles to support strategic decision-making. Both roles demand analytical thinking, attention to detail, and a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, or economics, with FP&A positions often favoring candidates with an MBA or CFA certification.
Typical Career Paths
Budget analysts often progress to senior budgeting roles, financial controllers, or government finance managers due to their expertise in cost management and public sector budgeting. FP&A analysts typically advance into roles such as finance managers, strategic planners, or corporate finance directors, leveraging their skills in financial modeling, forecasting, and data-driven decision-making. Both paths offer opportunities to transition into CFO or other executive finance positions, depending on experience and industry specialization.
Educational Backgrounds
Budget Analysts often hold degrees in finance, accounting, economics, or public administration, with strong skills in budgeting, financial reporting, and cost analysis. FP&A Analysts typically have educational backgrounds in finance, business administration, economics, or statistics, emphasizing financial modeling, forecasting, and strategic planning. Both roles benefit from certifications such as CPA, CFA, or CMA to enhance expertise and career advancement opportunities.
Technical Tools and Software Used
Budget Analysts primarily utilize tools like Microsoft Excel, Oracle Hyperion, and SAP BPC to create, monitor, and manage organizational budgets, emphasizing data accuracy and compliance. FP&A Analysts rely heavily on advanced financial modeling software such as Anaplan, Adaptive Insights, and Tableau for scenario analysis, forecasting, and performance reporting to support strategic decision-making. Both roles require proficiency in ERP systems and data visualization tools, but FP&A Analysts often leverage predictive analytics and business intelligence platforms for deeper insights.
Salary Expectations
Budget Analysts typically earn an average salary ranging from $60,000 to $80,000 annually, reflecting their role in monitoring and controlling organizational spending. FP&A Analysts command higher salaries, often between $75,000 and $105,000, due to their strategic focus on financial forecasting, budgeting, and performance analysis. Salary variations depend on factors such as industry, company size, and geographic location, with FP&A roles generally offering greater earning potential in corporate finance settings.
Job Outlook and Market Demand
The job outlook for Budget Analysts is projected to grow by 5% from 2022 to 2032, driven by federal government demand and healthcare industry expansion. FP&A Analysts show a stronger market demand with a 7% growth rate in the same period, fueled by increased corporate focus on strategic financial planning and data analytics. Both roles require strong analytical skills, but FP&A Analysts benefit from rising adoption of advanced financial technologies and predictive modeling.
Core Differences in Job Functions
Budget Analysts primarily focus on developing, managing, and monitoring organizational budgets, ensuring financial resources are allocated efficiently and adhering to financial regulations. FP&A Analysts specialize in financial forecasting, variance analysis, and strategic planning to support decision-making and long-term financial goals. While Budget Analysts emphasize cost control and budget compliance, FP&A Analysts concentrate on financial modeling and performance analysis to drive business growth.
Choosing Between Budget Analyst and FP&A Analyst
Choosing between a Budget Analyst and an FP&A Analyst depends on career goals and job responsibilities within finance. Budget Analysts primarily focus on preparing, managing, and analyzing organizational budgets, ensuring compliance with fiscal policies. FP&A Analysts specialize in forecasting, financial modeling, and strategic planning to support decision-making and long-term business growth.
Budget Analyst vs FP&A Analyst Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com