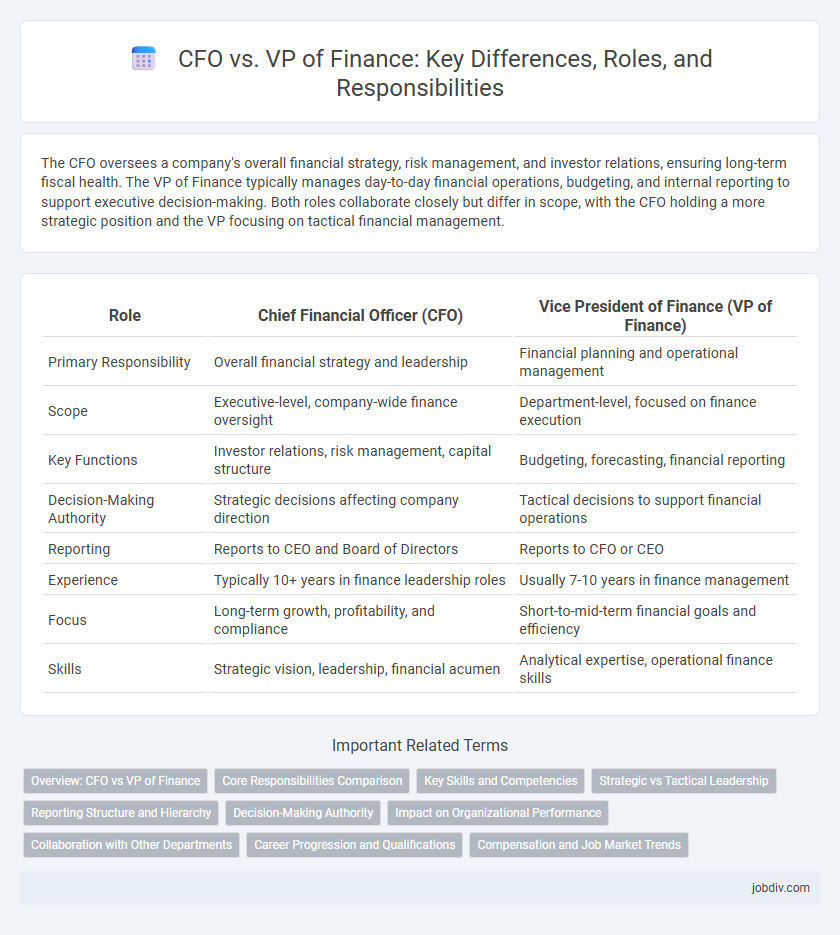
The CFO oversees a company's overall financial strategy, risk management, and investor relations, ensuring long-term fiscal health. The VP of Finance typically manages day-to-day financial operations, budgeting, and internal reporting to support executive decision-making. Both roles collaborate closely but differ in scope, with the CFO holding a more strategic position and the VP focusing on tactical financial management.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Chief Financial Officer (CFO) | Vice President of Finance (VP of Finance) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Overall financial strategy and leadership | Financial planning and operational management |
| Scope | Executive-level, company-wide finance oversight | Department-level, focused on finance execution |
| Key Functions | Investor relations, risk management, capital structure | Budgeting, forecasting, financial reporting |
| Decision-Making Authority | Strategic decisions affecting company direction | Tactical decisions to support financial operations |
| Reporting | Reports to CEO and Board of Directors | Reports to CFO or CEO |
| Experience | Typically 10+ years in finance leadership roles | Usually 7-10 years in finance management |
| Focus | Long-term growth, profitability, and compliance | Short-to-mid-term financial goals and efficiency |
| Skills | Strategic vision, leadership, financial acumen | Analytical expertise, operational finance skills |
Overview: CFO vs VP of Finance
The Chief Financial Officer (CFO) oversees the entire financial strategy, driving long-term growth, risk management, and investor relations, while the Vice President (VP) of Finance typically manages daily financial operations, budgeting, and internal reporting. CFOs focus on high-level decision-making and aligning finance with corporate goals, whereas VPs of Finance execute tactical plans and supervise finance teams. Both roles are critical for organizational financial health, but the CFO holds a broader, strategic leadership position compared to the operational scope of the VP of Finance.
Core Responsibilities Comparison
The CFO oversees overall financial strategy, risk management, and investor relations, ensuring alignment with corporate goals and regulatory compliance. The VP of Finance manages daily financial operations, including budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting to support executive decision-making. Both roles collaborate to optimize capital allocation and drive financial performance but differ in scope and strategic influence.
Key Skills and Competencies
The CFO excels in strategic leadership, financial planning, and risk management, demonstrating expertise in corporate finance, stakeholder communication, and regulatory compliance. The VP of Finance focuses on operational finance, budgeting, financial analysis, and team management, ensuring effective internal controls and accurate financial reporting. Both roles require strong analytical skills and proficiency in financial software, with the CFO emphasizing broader business acumen and the VP prioritizing detailed financial execution.
Strategic vs Tactical Leadership
The CFO drives strategic leadership by shaping long-term financial goals, risk management, and capital allocation to enhance shareholder value. The VP of Finance focuses on tactical leadership, managing day-to-day financial operations, budgeting, and performance monitoring to ensure operational efficiency. This distinction aligns the CFO with visionary decision-making, while the VP of Finance ensures execution and financial discipline.
Reporting Structure and Hierarchy
The CFO typically holds the highest financial leadership position, overseeing the entire finance function and reporting directly to the CEO or board of directors. The VP of Finance reports to the CFO and manages day-to-day financial operations, including budgeting, forecasting, and financial analysis. In hierarchical terms, the CFO drives strategic financial decision-making, while the VP of Finance ensures operational execution and detailed financial reporting.
Decision-Making Authority
The CFO holds the highest decision-making authority in financial strategy, overseeing budgeting, forecasting, and capital allocation across the entire organization. The VP of Finance typically manages day-to-day financial operations and report preparation, supporting the CFO's strategic directives. While the CFO drives high-level financial decisions impacting company-wide growth, the VP of Finance ensures accurate execution and compliance within financial processes.
Impact on Organizational Performance
A CFO drives strategic financial planning and risk management, directly influencing organizational growth and investor confidence. The VP of Finance oversees budgeting, forecasting, and operational financial processes that ensure efficient resource allocation and cost control. Both roles collaboratively enhance financial stability and support data-driven decision-making to optimize overall organizational performance.
Collaboration with Other Departments
The CFO and VP of Finance work closely with departments like Marketing, Sales, and Operations to align financial strategies with business goals. The CFO focuses on high-level financial planning and stakeholder communication, while the VP of Finance manages day-to-day budget execution and financial reporting. Effective collaboration ensures accurate forecasting, resource allocation, and risk management across the organization.
Career Progression and Qualifications
The CFO typically holds extensive experience in strategic financial management and leadership, often requiring advanced degrees such as an MBA or CPA certification, while the VP of Finance generally focuses on operational financial oversight with a strong background in accounting and budgeting. Career progression usually involves moving from VP of Finance to CFO as professionals gain expertise in corporate finance, risk management, and investor relations. Mastery in financial reporting standards, regulatory compliance, and cross-functional team leadership are essential qualifications that distinguish CFO roles in large enterprises.
Compensation and Job Market Trends
Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) typically command higher compensation packages than Vice Presidents of Finance, reflecting their broader strategic responsibilities and impact on overall corporate direction. Market trends indicate increasing demand for CFOs with expertise in digital transformation and risk management, driving salaries upward in competitive industries. Vice Presidents of Finance see steady wage growth, particularly in sectors emphasizing financial planning and operational efficiency.
CFO vs VP of Finance Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com