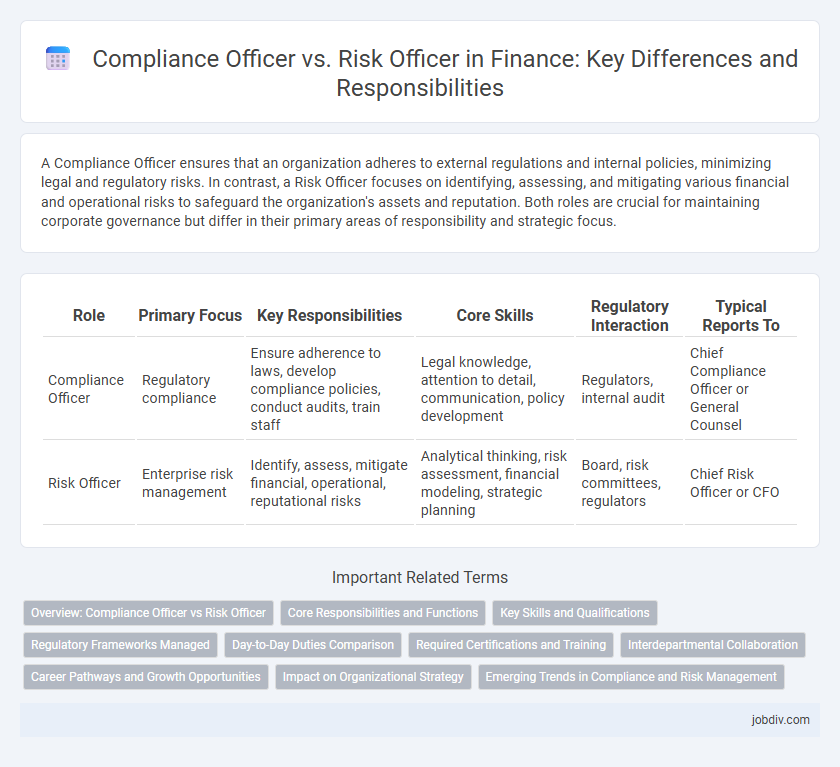
A Compliance Officer ensures that an organization adheres to external regulations and internal policies, minimizing legal and regulatory risks. In contrast, a Risk Officer focuses on identifying, assessing, and mitigating various financial and operational risks to safeguard the organization's assets and reputation. Both roles are crucial for maintaining corporate governance but differ in their primary areas of responsibility and strategic focus.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Primary Focus | Key Responsibilities | Core Skills | Regulatory Interaction | Typical Reports To |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compliance Officer | Regulatory compliance | Ensure adherence to laws, develop compliance policies, conduct audits, train staff | Legal knowledge, attention to detail, communication, policy development | Regulators, internal audit | Chief Compliance Officer or General Counsel |
| Risk Officer | Enterprise risk management | Identify, assess, mitigate financial, operational, reputational risks | Analytical thinking, risk assessment, financial modeling, strategic planning | Board, risk committees, regulators | Chief Risk Officer or CFO |
Overview: Compliance Officer vs Risk Officer
Compliance Officers ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies by developing and implementing compliance programs that prevent legal violations and safeguard organizational integrity. Risk Officers identify, assess, and mitigate financial and operational risks through comprehensive risk management strategies aimed at minimizing potential losses and enhancing decision-making. Both roles collaborate closely to uphold corporate governance but differ in scope, with Compliance focused on regulatory adherence and Risk emphasizing proactive risk assessment and control.
Core Responsibilities and Functions
Compliance Officers ensure adherence to regulatory requirements by developing and implementing policies that prevent legal violations within financial institutions. Risk Officers identify, assess, and mitigate financial, operational, and strategic risks through robust risk management frameworks and continuous monitoring. Both roles collaborate to protect the organization's integrity but focus respectively on regulatory compliance and risk assessment frameworks.
Key Skills and Qualifications
Compliance Officers require deep knowledge of regulatory frameworks, strong analytical skills, and expertise in implementing internal controls to ensure adherence to laws and standards. Risk Officers must excel in risk assessment techniques, quantitative analysis, and strategic planning to identify, evaluate, and mitigate financial risks effectively. Both roles demand excellent communication abilities and proficiency with compliance management systems and risk modeling software.
Regulatory Frameworks Managed
Compliance Officers primarily manage regulatory frameworks by ensuring adherence to laws such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, Dodd-Frank Act, and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, focusing on internal policies and regulatory reporting. Risk Officers oversee frameworks related to risk assessment standards like Basel III and COSO, emphasizing the measurement and mitigation of financial, operational, and strategic risks. Both roles are integral to maintaining organizational integrity, but Compliance Officers align operations with legal mandates, while Risk Officers prioritize risk identification and control within those regulatory boundaries.
Day-to-Day Duties Comparison
Compliance Officers conduct daily monitoring of regulatory adherence, implement internal policies, and ensure that financial activities meet legal standards. Risk Officers focus on identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential financial risks through regular analysis of market trends, credit exposures, and operational vulnerabilities. Both roles require continuous reporting and collaboration with internal teams to safeguard the organization's financial integrity.
Required Certifications and Training
Compliance Officers typically require certifications such as Certified Compliance & Ethics Professional (CCEP) or Certified Regulatory Compliance Manager (CRCM), emphasizing regulatory adherence and ethical standards. Risk Officers often pursue certifications like Financial Risk Manager (FRM) or Professional Risk Manager (PRM), focusing on identifying, assessing, and mitigating financial risks. Both roles benefit from ongoing training in financial regulations, industry standards, and risk management frameworks to maintain effectiveness in dynamic regulatory environments.
Interdepartmental Collaboration
Compliance Officers and Risk Officers maintain interdepartmental collaboration by aligning regulatory requirements with risk management strategies to ensure organizational integrity. Compliance Officers focus on adherence to laws and regulations, while Risk Officers identify, assess, and mitigate potential threats, requiring continuous communication between legal, finance, and operational departments. This collaboration enhances proactive risk detection and compliance enforcement, minimizing financial and reputational exposure.
Career Pathways and Growth Opportunities
Compliance Officers typically advance by gaining expertise in regulatory frameworks, moving into senior compliance roles or chief compliance officer positions overseeing corporate governance. Risk Officers often build on their analytical skills, progressing to risk management leadership roles such as chief risk officer, focusing on enterprise risk strategies and mitigation. Both paths offer growth in financial institutions, with opportunities to influence strategic decision-making and corporate policy implementation.
Impact on Organizational Strategy
Compliance Officers ensure organizational adherence to legal regulations, embedding regulatory requirements into business strategies to mitigate legal risks and avoid penalties. Risk Officers focus on identifying, assessing, and managing financial, operational, and strategic risks to safeguard assets and promote sustainable growth. Both roles influence organizational strategy by balancing risk tolerance with regulatory compliance to optimize decision-making and protect stakeholder value.
Emerging Trends in Compliance and Risk Management
Compliance Officers increasingly leverage artificial intelligence and blockchain technology to enhance regulatory adherence and automate reporting processes, ensuring real-time monitoring of evolving legal frameworks. Risk Officers prioritize advanced data analytics and machine learning to predict and mitigate financial risks, integrating sustainability risk factors and cybersecurity threats into enterprise-wide risk management strategies. Collaborative use of RegTech tools enables both roles to address complex regulatory environments and dynamic market conditions effectively.
Compliance Officer vs Risk Officer Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com