Cost accountants specialize in analyzing production costs to improve budgeting and operational efficiency, providing detailed insights into cost control and inventory valuation. Financial accountants prepare comprehensive financial statements in compliance with regulatory standards, focusing on the accuracy of financial reporting for stakeholders. Both roles are essential for a company's financial health but serve distinct purposes in internal management and external reporting.
Table of Comparison
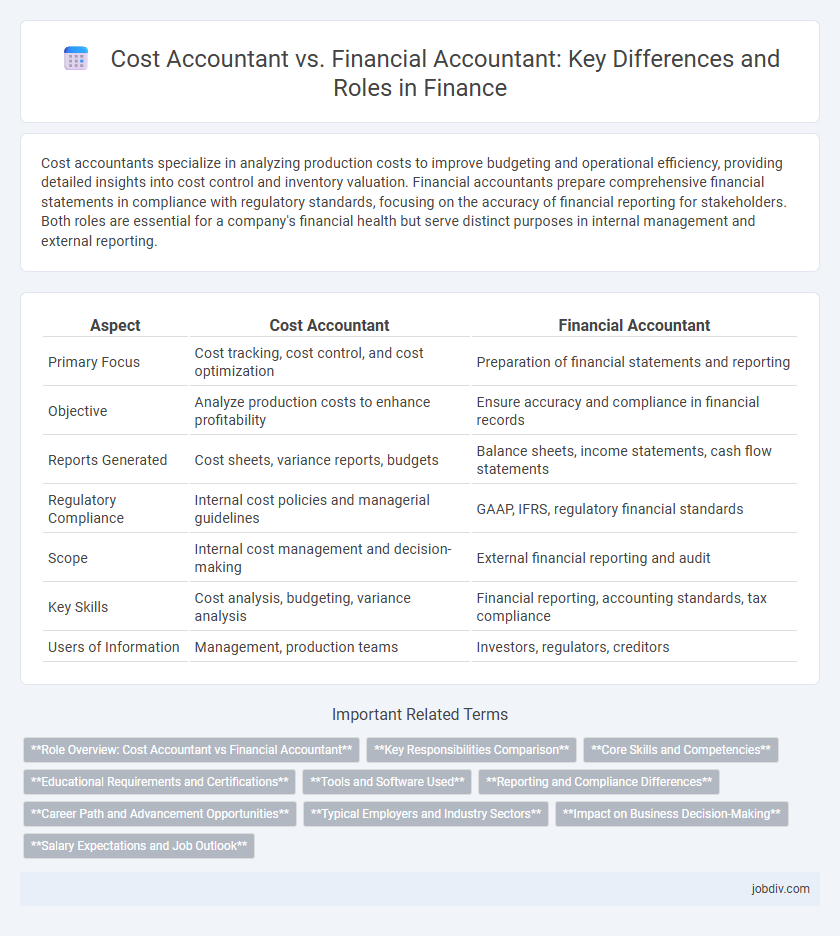
| Aspect | Cost Accountant | Financial Accountant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Cost tracking, cost control, and cost optimization | Preparation of financial statements and reporting |
| Objective | Analyze production costs to enhance profitability | Ensure accuracy and compliance in financial records |
| Reports Generated | Cost sheets, variance reports, budgets | Balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements |
| Regulatory Compliance | Internal cost policies and managerial guidelines | GAAP, IFRS, regulatory financial standards |
| Scope | Internal cost management and decision-making | External financial reporting and audit |
| Key Skills | Cost analysis, budgeting, variance analysis | Financial reporting, accounting standards, tax compliance |
| Users of Information | Management, production teams | Investors, regulators, creditors |
Role Overview: Cost Accountant vs Financial Accountant
Cost accountants specialize in analyzing production costs, budgeting, and cost control to improve operational efficiency and profitability. Financial accountants focus on preparing financial statements, ensuring compliance with accounting standards, and providing an accurate financial overview for stakeholders and regulatory bodies. Both roles require strong accounting expertise but differ in their primary focus areas and reporting objectives within the finance function.
Key Responsibilities Comparison
Cost accountants specialize in analyzing production and operational costs to optimize budgeting and improve profitability by tracking expenses and variances. Financial accountants focus on preparing accurate financial statements, ensuring compliance with accounting standards, and providing an overall view of the company's financial health for stakeholders. Both roles require detailed record-keeping, but cost accountants emphasize internal cost control while financial accountants prioritize external reporting and regulatory adherence.
Core Skills and Competencies
Cost Accountants specialize in cost analysis, budgeting, and inventory management, excelling in variance analysis and cost control techniques to optimize manufacturing and operational expenses. Financial Accountants focus on financial reporting, compliance with accounting standards (GAAP or IFRS), and preparation of financial statements, requiring strong skills in audit coordination and regulatory knowledge. Both roles demand proficiency in accounting software, analytical thinking, and attention to detail, but Cost Accountants prioritize internal cost efficiency while Financial Accountants emphasize external financial accuracy and transparency.
Educational Requirements and Certifications
Cost accountants typically require a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or a related field, with many pursuing certifications like the Certified Management Accountant (CMA) to enhance expertise in cost analysis and budgeting. Financial accountants generally hold a bachelor's degree in accounting or finance and often obtain the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) designation to demonstrate proficiency in financial reporting and compliance. Both roles benefit from continuing professional education, but their certifications reflect specialized knowledge aligned with their distinct functions within the finance industry.
Tools and Software Used
Cost accountants primarily use specialized cost accounting software such as SAP Cost Management, Oracle Cost Accounting, and Activity-Based Costing tools to track production expenses and analyze cost behavior. Financial accountants rely heavily on general accounting software like QuickBooks, Microsoft Dynamics GP, and SAP Financial Accounting for managing ledgers, preparing financial statements, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Both roles increasingly incorporate advanced Excel functions and data analytics platforms like Power BI and Tableau to enhance accuracy and reporting efficiency.
Reporting and Compliance Differences
Cost accountants specialize in internal cost analysis and reporting, focusing on budgeting, cost control, and efficiency metrics to support managerial decision-making. Financial accountants prepare external financial statements in compliance with GAAP or IFRS, ensuring accurate representation for stakeholders and regulatory bodies. Reporting from cost accounting is detailed and operational, whereas financial accounting emphasizes statutory compliance and consolidated financial disclosures.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Cost accountants often advance by specializing in budgeting, cost control, and operational efficiency, eventually moving into managerial roles such as cost controller or financial analyst within manufacturing and production industries. Financial accountants typically progress toward senior positions like financial controller, finance manager, or chief financial officer, with opportunities extending into corporate finance, auditing, and regulatory compliance. Both career paths offer certifications such as CMA (Certified Management Accountant) for cost accountants and CPA (Certified Public Accountant) for financial accountants, which significantly enhance advancement prospects.
Typical Employers and Industry Sectors
Cost accountants are typically employed by manufacturing firms, construction companies, and retail businesses where detailed cost tracking and inventory management are essential for operational efficiency. Financial accountants commonly work in public accounting firms, corporate finance departments, and banking institutions, focusing on financial reporting, compliance, and audit processes. Both roles are critical in industries such as healthcare, telecommunications, and government agencies, but cost accountants emphasize internal cost analysis while financial accountants prioritize external financial statements.
Impact on Business Decision-Making
Cost accountants provide detailed insights into production costs and operational efficiency, enabling management to make informed budgeting and pricing decisions that enhance profitability. Financial accountants compile comprehensive financial statements and ensure regulatory compliance, which supports external stakeholder confidence and strategic investment choices. Both roles contribute critical data, but cost accountants influence internal decision-making processes, while financial accountants impact broader financial reporting and external communication.
Salary Expectations and Job Outlook
Cost accountants typically earn an average salary ranging from $55,000 to $80,000 annually, reflecting their specialization in internal costing and budgeting processes crucial for manufacturing and production industries. Financial accountants, with broader responsibilities in financial reporting and compliance, command salaries generally between $60,000 and $90,000, driven by demand in sectors such as banking, consulting, and corporate finance. Job outlook for both roles is positive, with cost accountants experiencing steady growth due to increasing emphasis on cost management, while financial accountants benefit from expanding regulatory requirements and globalization of business operations.
Cost Accountant vs Financial Accountant Infographic
 jobdiv.com
jobdiv.com